(Press-News.org) Herpes zoster, or shingles, does not increase the risk of cancer in the general population, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Although herpes zoster is more common in patients with cancer than in those without, it is unknown whether the risk of cancer is increased for people with herpes zoster. Several studies have indicated an association although most were conducted in western countries.
A large study of 35 871 patients in Taiwan with newly diagnosed herpes zoster found no increased risk of cancer in patients with herpes zoster.
"We found no overall increased risk of cancer among patients with herpes zoster compared with the general population, regardless of sex, age or years of follow-up," writes Dr. Yi-Tsung Lin, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, with coauthors.
The study included data on other illnesses in patients with herpes zoster, such as diabetes, chronic obstructive lung disease, autoimmune disease and heart disease. Most previous studies did not adjust for comorbidity.
"These findings suggest that the extensive investigations for occult cancer at the time of diagnosis of herpes zoster or enhanced surveillance for cancer after such a diagnosis is unnecessary," conclude the authors.
### END
No increased risk of cancer for people with shingles
2012-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adequate sleep helps weight loss
2012-09-17
Adequate sleep is an important part of a weight loss plan and should be added to the recommended mix of diet and exercise, states a commentary in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Although calorie restriction and increased physical activity are recommended for weight loss, there is significant evidence that inadequate sleep is contributing to obesity. Lack of sleep increases the stimulus to consume more food and increases appetite-regulating hormones.
"The solution [to weight loss] is not as simple as 'eat less, move more, sleep more,'" write Drs. Jean-Phillippe ...
Canada needs approach to combat elder abuse
2012-09-17
Canada needs a comprehensive approach to reduce elder abuse that includes financial supports and programs for seniors and their caregivers, argues an editorial in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
In Canada, an estimated 4% of seniors — 200 000 to 500 000 people — experience some form of abuse or neglect.
"The broader solution lies in a more comprehensive approach that requires the support of government and the Canadian health care system," writes Barbara Sibbald, deputy editor, CMAJ with Jayna Holroyd-Leduc, associate professor, Geriatric Medicine Section, ...
JCI early table of contents for Sept. 17, 2012
2012-09-17
A non-invasive method to track Huntington's disease progression
Huntington's disease is a fatal, inherited neurodegenerative disorder caused by a mutation in the gene encoding huntingtin. Expresion of mutant huntingtin (mHTT) protein is correlated with the onset and progression of the disease and new therapies are being developed to reduce the expression of mHTT. In order to evaluate these new therapies, researchers need to be able to quantify the amount of mHTT in a particular patient; however, non-invasive quantification of mHTT isn't currently possible. In this issue ...
A non-invasive method to track Huntington's disease progression
2012-09-17
Huntington's disease is a fatal, inherited neurodegenerative disorder caused by a mutation in the gene encoding huntingtin. Expresion of mutant huntingtin (mHTT) protein is correlated with the onset and progression of the disease and new therapies are being developed to reduce the expression of mHTT. In order to evaluate these new therapies, researchers need to be able to quantify the amount of mHTT in a particular patient; however, non-invasive quantification of mHTT isn't currently possible. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Sarah ...
Report: Cancer now leading cause of death in US hispanics
2012-09-17
ATLANTA –September 17, 2012– A new report from American Cancer Society researchers finds that despite declining death rates, cancer has surpassed heart disease as the leading cause of death among Hispanics in the U.S. In 2009, the most recent year for which actual data are available, 29,935 people of Hispanic origin in the U.S. died of cancer, compared to 29,611 deaths from heart disease. Among non-Hispanic whites and African Americans, heart disease remains the number one cause of death.
The figures come from Cancer Statistics for Hispanics/Latinos 2012-2014, appearing ...
Scientists reveal how natural antibiotic kills tuberculosis bacterium
2012-09-17
HEIDELBERG, 17 September 2012 – A natural product secreted by a soil bacterium shows promise as a new drug to treat tuberculosis report scientists in a new study published in EMBO Molecular Medicine. A team of scientists working in Switzerland has shown how pyridomycin, a natural antibiotic produced by the bacterium Dactylosporangium fulvum, works. This promising drug candidate is active against many of the drug-resistant types of the tuberculosis bacterium that no longer respond to treatment with the front-line drug isoniazid.
"Nature and evolution have equipped some ...
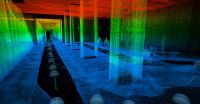
Improved positioning indoors
2012-09-17
The NAVVIS positioning system is primarily based on visual information. The TUM researchers had to develop a special location recognition system for this project. They started by taking photos of a building, simultaneously mapping prominent features like stairs and signs. A smartphone app then lets users view the map images to find their current location. All they have to do is take a photo of their surroundings. The program then compares the photo with the images stored in its database and works out the user's exact position (down to the nearest meter) and the direction ...
Noteworthy studies at the ESMO 2012 Congress
2012-09-17
Lugano, Switzerland, 14 September 2012 -- Ahead of the top 48 abstracts (LBA and PR suffix) that will be released during the ESMO 2012 Congress, over 1,600 abstracts will be published online on Monday, 17 September 2012 at 9:00 (CEST) to anticipate the flavor of an ESMO Congress that once again "will be presenting emerging strategies set to combat cancer, signposting future directions in patient treatment and care, boldly addressing the many new challenges that lie ahead." (Josep Tabernero, ESMO 2012 Scientific Chair)
http://www.esmo.org/events/vienna-2012-congress/program.html
--> ...
New 'ATM' takes old phones and gives back green
2012-09-17
When new cell phones or tablets enter the marketplace, yesterday's hot technology can quickly become obsolete - for some consumers. For others, the device still has value as an affordable alternative, or even as spare parts.
With support from the National Science Foundation (NSF), ecoATM of San Diego, Calif., has developed a unique, automated system that lets consumers trade in those devices for reimbursement or recycling.
Using sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) developed through two NSF Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grants, ecoATM kiosks can ...
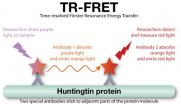
Toxic protein build-up in blood shines light on fatal brain disease
2012-09-17
A new light-based technique for measuring levels of the toxic protein that causes Huntington's disease (HD) has been used to demonstrate that the protein builds up gradually in blood cells. Published today (17th) in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, the findings shed light on how the protein causes damage in the brain, and could be useful for monitoring the progression of HD, or testing new drugs aimed at suppressing production of the harmful protein.
HD is a fatal, incurable, genetic neurological disease that usually develops in adulthood and causes abnormal involuntary ...