(Press-News.org) A blistering sunburn during childhood or adolescence more than doubles the adult risk of skin cancer. The accumulation of long-term sun exposure may be equally dangerous. A study from the Colorado School of Public Health and the University of Colorado Cancer Center recently published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine shows one way to reduce this exposure: a double-blind randomized clinical trial of mailed sun protection packets led to higher frequency of sun protective behaviors including the use of long clothing, hats, shade, sunscreen, and midday sun avoidance.
"This is a low-cost, effective intervention that could be an important component in efforts to reduce sun exposure in children during the years that they acquire much of their risk for skin cancer," says the paper's first author, Lori Crane, PhD, MPH, CU Cancer Center investigator and chair of the Department of Community & Behavioral Health at the Colorado School of Public Health.
The study recruited 676 six-year-olds and their parents into the Colorado Kids Sun Care Program, half of whom completed phone interviews and other data collection, and half of whom also received intervention kits. Kits included newsletters and sun protection resources, such as swim shirts, hats, sunscreen and sun protection educational activities. They were mailed in April and May of the years 2005, 2006 and 2007, with the goal of guiding parents and children to ever-increasing stages of adopting sun-safe behaviors, from the early stage of "unaware" to fully engaged and actively practicing. Phone interviews determined not only the level of sun-protective behaviors, but also parents' knowledge about melanoma, their evaluation of their child's lifetime risk for the disease, and their opinion of skin cancer severity. Skin exams discovered children's level of tanning and number of nevi – the UV-influenced moles that can presage melanoma.
Across all measures of sun-protective behavior and awareness, the intervention group showed greater gains than the control group. Interestingly, the greatest increases were in the specific sun-protective behaviors emphasized in each yearly kit.
"After we emphasized long clothing in the spring of 2005, we saw a difference in clothing behavior in the summers of 2005 and 2006 not in 2007. Then after emphasizing hats in 2006, we saw a difference in hat use that year. And then after highlighting shade in 2007, we saw a corresponding increase in parents' awareness and use of shade as a sun-protective behavior," Crane says.
In Crane's opinion, this specific awareness and behavior change shows both the effectiveness of the intervention, but perhaps also the challenge of creating lasting behavior changes. Further study is needed to discover the durability of this intervention, and also how these increases in sun-protective behaviors influence skin cancer risk.
Crane and colleagues point out that although behavior changes in the trial were modest, the intervention was relatively inexpensive and, because it used postal mail, it could be readily delivered to a geographically broad population.
### END
3-year, 676-child trial shows effectiveness of low-cost intervention to improve sun protection
Mailed sun protection kits are easy, effective
2012-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
EARTH: Bakken boom and the new Wild West
2012-09-24
Alexandria, VA – Diesel-soaked clothing, 90-hour work weeks, and the constant groaning of a multimillion-dollar oil rig towering overhead: Welcome to life in Williston, N.D., home of the United States' latest oil boom. In this month's issue of EARTH Magazine, R. Tyler Powers, a young geologist thrust into the middle of the new boomtown, offers his perspective on what life is like today in the new Wild West.
Thousands of oil rigs sit atop the Bakken Formation, a Late Devonian to Early Mississippian rock formation that underlies parts of Montana, North Dakota, Saskatchewan ...
Tissues tell the tale: Non-invasive optical technique detects cancer by looking under the skin
2012-09-24
VIDEO:
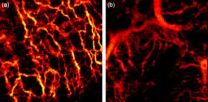
This is a 2x2x2mm extracted blood vessel structure of basal cell carcinoma in vivo exhibiting a chaotic vascular pattern (left). Virtually cut volume obtained with OCT displaying the embedded blood...
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, Sept. 24, 2012—The trained eye of a dermatologist can identify many types of skin lesions, but human sight only goes so far. Now an international team of researchers has developed an advanced optics system to noninvasively ...
Heritability of avoidant and dependent personality disorder traits
2012-09-24
A new twin study from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health shows that the heritability of avoidant and dependent personality disorder traits might be higher than previously reported. People with avoidant personality disorder are often anxious in the company of others, while people with dependent personality disorder feel more secure.
Results from previous studies indicate that genetic factors explain about one third of the individual differences in these personality disorder traits, while the remaining variation is best explained by environmental influences. These ...
Newly discovered molecule could deliver drugs to treat diseases
2012-09-24
MANHATTAN, Kan. -- Kansas State University researchers have discovered a molecule that may be capable of delivering drugs inside the body to treat diseases.
For the first time, researchers have designed and created a membrane-bounded vesicle formed entirely of peptides -- molecules made up of amino acids, the building blocks of protein. The membrane could serve as a new drug delivery system to safely treat cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
A study led by John Tomich, professor of biochemistry at Kansas State University, has been published in the journal PLOS ONE ...
A windshield wiper for Mars dust is developed
2012-09-24
This press release is available in Spanish.
VIDEO:
A team of researchers at Universidad Carlos III in Madrid has developed a device that works as a windshield wiper to eliminate Mars dust from the sensors on the NASA...
Click here for more information.
Leading energy scientists from the UK and China are joining forces to develop green technology that will revolutionise the way electricity ...
Gas outlets off Spitsbergen are no new phenomenon
2012-09-24
Frequent storms and sub-zero temperatures – nature drove the marine researchers that were assessing gas outlets on the sea bed off the coast of Spitsbergen for four and a half weeks to their limits. Nevertheless the participants were very pleased when they returned: "We were able to gather many samples and data in the affected area. With the submersible JAGO we even managed to form an impression of the sea bed and the gas vents" summarised the chief scientist Professor Dr. Christian Berndt from GEOMAR | Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel.
The reason for the expedition ...
Therapeutic impact of cell transplantation aided by magnetic factor
2012-09-24
Putnam Valley, NY. (Sept. 24, 2012) – Two studies in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (21:6), now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/, demonstrate how the use of magnetic particles are a factor that can positively impact on the targeted delivery of transplanted stem cells and to also provide better cell retention.
A research team from the University of British Columbia used focused magnetic stem cell targeting to improve the delivery and transport of mensenchymal stem cells to the retinas of test rats while researchers from ...
In birds' development, researchers find diversity by the peck
2012-09-24
Cambridge, Mass. - September 24, 2012 - It has long been known that diversity of form and function in birds' specialized beaks is abundant. Charles Darwin famously studied the finches on the Galapagos Islands, tying the morphology (shape) of various species' beaks to the types of seeds they ate. In 2010, a team of Harvard biologists and applied mathematicians showed that Darwin's finches all actually shared the same developmental pathways, using the same gene products, controlling just size and curvature, to create 14 very different beaks.
Now, expanding that work to ...
Scientists shed light on riddle of sun's explosive events
2012-09-24
DURHAM, N.H. – Four decades of active research and debate by the solar physics community have failed to bring consensus on what drives the sun's powerful coronal mass ejections (CMEs) that can have profound "space weather" effects on Earth-based power grids and satellites in near-Earth geospace.
In a paper just published in Nature Physics, an international team of space scientists, including a researcher from the University of New Hampshire's Space Science Center (SSC), explains the mysterious physical mechanisms underlying the origin of CMEs. Their findings, based on ...
When they do not all look alike: Using identity to reduce own-race bias
2012-09-24
September 24, 2012 - People often remark that people of a different race "all look alike." However, when we have trouble recognizing people from another race, it may actually have little to do with the other person's race. Instead, new research finds that that we can improve our memory of members of another race by identifying ourselves as part of the same group. Such identification could improve everything from race relations to eyewitness identification.
"One of the most robust phenomena in social perception is the finding that people are better at remembering people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] 3-year, 676-child trial shows effectiveness of low-cost intervention to improve sun protectionMailed sun protection kits are easy, effective