(Press-News.org) Most people equate "gray matter" with the brain and its higher functions, such as sensation and perception, but this is only one part of the anatomical puzzle inside our heads. Another cerebral component is the white matter, which makes up about half the brain by volume and serves as the communications network.
The gray matter, with its densely packed nerve cell bodies, does the thinking, the computing, the decision-making. But projecting from these cell bodies are the axons—the network cables. They constitute the white matter. Its color derives from myelin--a fat that wraps around the axons, acting like insulation.
Alex Schelgel, first author on a paper in the August 2012 Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, has been using the white matter as a landscape on which to study brain function. An important result of the research is showing that you can indeed "teach old dogs new tricks." The brain you have as an adult is not necessarily the brain you are always going to have. It can still change, even for the better.
"This work is contributing to a new understanding that the brain stays this plastic organ throughout your life, capable of change," Schlegel says. "Knowing what actually happens in the organization of the brain when you are learning has implications for the development of new models of learning as well as potential interventions in cases of stroke and brain damage."
Schlegel is a graduate student working under Peter Tse, an associate professor of psychological and brain sciences and a coauthor on the paper. "This study was Peter's idea," Schlegel says. "He wanted to know if we could see white matter change as a result of a long-term learning process. Chinese seemed to him like the most intensive learning experience he could think of."
Twenty-seven Dartmouth students were enrolled in a nine-month Chinese language course between 2007 and 2009, enabling Schlegel to study their white matter in action. While many neuroscientists use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain studies, Schlegel turned to a new MRI technology, called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). He used DTI to measure the diffusion of water in axons, tracking the communication pathways in the brain. Restrictions in this diffusion can indicate that more myelin has wrapped around an axon.
"An increase in myelination tells us that axons are being used more, transmitting messages between processing areas," Schlegel says. "It means there is an active process under way."
Their data suggest that white matter myelination is precisely what was seen among the language students. There is a structural change that goes along with this learning process. While some studies have shown that changes in white matter occurred with learning, these observations were made in simple skill learning and strictly on a "before and after" basis.
"This was the first study looking at a really complex, long-term learning process over time, actually looking at changes in individuals as they learn a task," says Schlegel. "You have a much stronger causal argument when you can do that."
The work demonstrates that significant changes are occurring in adults who are learning. The structure of their brains undergoes change.
"This flies in the face of all these traditional views that all structural development happens in infancy, early in childhood," Schlegel says. "Now that we actually do have tools to watch a brain change, we are discovering that in many cases the brain can be just as malleable as an adult as it is when you are a child or an adolescent."
INFORMATION:
White matter, old dogs, and new tricks at Dartmouth
2012-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bone marrow holds secrets for treating colitis and Crohn's
2012-09-25
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Michigan State University researchers have unlocked secrets in bone marrow that could lead to improved treatments for colitis and Crohn's disease.
The results, featured in the current issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences, show that the havoc inflammatory bowel diseases wreaks on the digestive tract is mirrored in bone marrow. Early indications also show that the disorders of the gut could potentially be treated through the bone marrow, said Pam Fraker, MSU University Distinguished Professor of biochemistry and molecular biology.
"It's ...
MRI helps identify patients with prostate cancer who may benefit from active surveillance
2012-09-25
Philadelphia, PA, September 24, 2012 – PSA screening has resulted in improved prostate cancer survival, but the high rate of diagnosis and treatment side effects raise concerns about overtreatment. In the quest to prevent overtreatment, "active surveillance" has emerged as a plausible option, encouraged for men whose tumors may not need immediate treatment and may never progress to more serious illness. Appropriate criteria for selecting patients for active surveillance are continuously debated. A group of investigators from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in ...
Feeling guilty versus feeling angry -- who can tell the difference?
2012-09-25
When you rear-end the car in front of you at a stoplight, you may feel a mix of different emotions such as anger, anxiety, and guilt. The person whose car you rear-ended may feel angered and frustrated by your carelessness, but it's unlikely that he'll feel much guilt.
The ability to identify and distinguish between negative emotions helps us address the problem that led to those emotions in the first place. But while some people can tell the difference between feeling angry and guilty, others may not be able to separate the two. Distinguishing between anger and frustration ...
Yale researchers call for specialty metals recycling
2012-09-25
New Haven, Conn. -- An international policy is needed for recycling scarce specialty metals that are critical in the production of consumer goods, according to Yale researchers in Science.
"A recycling rate of zero for specialty metals is alarming when we consider that their use is growing quickly," said co-author Barbara Reck, a research scientist at the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies.
Specialty metals, which include rare earth elements such as indium, gallium and germanium, account for more than 30 of the 60 metals in the periodic table. Because ...
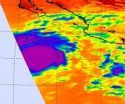
NASA's satellite saw 'power-trigger' around Hurricane Miriam's center
2012-09-25
ASA's Aqua satellite revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of Tropical Storm Miriam on Sept. 23 as it tracked through the Eastern Pacific Ocean. That power was the trigger that helped Miriam rapidly intensify into a major hurricane on Sept. 24.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern Pacific Ocean on Sept. 23 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Miriam's cloud top temperatures. Tropical Storm Miriam is born that day, about 640 miles (1,025 km) south-southeast of the southern ...
NASA's Global Hawk and satellites see tropical storm Nadine turning around
2012-09-25
Tropical Storm Nadine is turning around in two ways. When NASA's Global Hawk flew over the storm it learned that the storm was not transitioning into an extra-tropical storm. Now, NASA satellites see that Nadine is physically turning its direction, and heading back to the west-northwest and away from land.
The fifth science flight of NASA's Global Hawk concluded when the aircraft landed at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. on Sunday, Sept. 23 after flying over Tropical Storm Nadine in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean. The Hurricane and Severe Storms Sentinel ...
First 2 Webb Telescope flight mirrors delivered to NASA
2012-09-25
The first two of the 18 primary mirrors to fly aboard NASA's James Webb Space Telescope arrived at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
The mirrors are going through receiving and inspection and will then be stored in the Goddard cleanroom until engineers are ready to assemble them onto the telescope's backplane structure that will support them.
Ball Aerospace, Boulder, Colo., under contract to Northrop Grumman, is responsible for the Webb's optical technology and lightweight mirror system. On September 17, 2012, Ball Aerospace shipped the first two ...
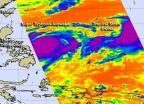
Frigid cloudtop temperatures indicate strength in Super Typhoon Jelawat and Tropical Storm Ewinar
2012-09-25
Tropical Storm Jelawat had been moving toward the Philippines since the week of Sept. 17 and on Sept. 24 it became a super typhoon east of the country. Meanwhile, the nineteenth tropical depression formed just east of Jelawat in the western North Pacific Ocean and quickly strengthened into a tropical storm. Both storms were captured on one infrared image from NASA's Aqua satellite.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of Typhoon Jelawat and a band of thunderstorms ...
Going viral to kill zits
2012-09-25
Watch out, acne. Doctors soon may have a new weapon against zits: a harmless virus living on our skin that naturally seeks out and kills the bacteria that cause pimples.
The Sept. 25 online edition of the American Society for Microbiology's mBio publishes the findings by scientists at UCLA and the University of Pittsburgh.
"Acne affects millions of people, yet we have few treatments that are both safe and effective," said principal investigator Dr. Robert Modlin, chief of dermatology and professor of microbiology, immunology and molecular genetics at the David Geffen ...
Could viruses be used to treat acne?
2012-09-25
Scientists have isolated and studied the genomes of 11 viruses, known as phage, that can infect and kill the acne-causing bacterium Propionibacterium acnes, potentially paving the way for topical therapies that use viruses or viral products to treat this vexing skin condition. Their results are reported in the September 25 issue of mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"There are two fairly obvious potential directions that could exploit this kind of research," says Graham Hatfull of the University of Pittsburgh, an author of ...