(Press-News.org) Infectious bacteria received a taste of their own medicine from University of Missouri researchers who used viruses to infect and kill colonies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, common disease-causing bacteria. The viruses, known as bacteriophages, could be used to efficiently sanitize water treatment facilities and may aid in the fight against deadly antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
"Our experiment was the first to use bacteriophages in conjunction with chlorine to destroy biofilms, which are layers of bacteria growing on a solid surface," said Zhiqiang Hu, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering in MU's College of Engineering. "The advantage to using viruses is that they can selectively kill harmful bacteria. Beneficial bacteria, such as those used to break down wastes in water treatment plants, are largely unaffected. Hence, viruses could be used to get rid of pathogenic bacteria in water filters that would otherwise have to be replaced. They could save taxpayers' money by reducing the cost of cleaning water."
Bacteria can be difficult to kill when they form a biofilm. The outer crust of bacteria in these biofilms can be killed by chlorine, but the inner bacteria are sheltered. Viruses solve this problem because they spread through an entire colony of bacteria. Hu noted that the bacteriophages are easier to create than the enzymes used to attack biofilms. The viruses also are better at targeting specific bacterial species.
Hu, along with MU's recent graduate, Yanyan Zhang, found the greatest success in killing biofilms by using a combination of bacteriophages and chlorine. An initial treatment with viruses followed by chlorine knocked out 97 percent of biofilms within five days of exposure. When used alone, viruses removed 89 percent of biofilms, while chlorine removed only 40 percent.
"The methods we used to kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa could be used against other dangerous bacteria, even those that have developed resistance to antibiotics," said Hu. "Our work opened the door to a new strategy for combating the dangers and costs of bacterial biofilms. The next step is to expand our experiment into a pilot study."
The study "Combined Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms with Bacteriophages and Chlorine" has been published in the journal Biotechnology and Bioengineering.
### END
Viruses help MU scientists battle pathogenic bacteria and improve water supply
Newly developed technique can kill antibiotic-resistant germs
2012-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First-ever treatment for rare childhood aging disease shows improvement in all trial participants
2012-09-25
BOSTON, MA (September 24, 2012) – Results of the first-ever clinical drug trial for children with Progeria, a rare, fatal "rapid-aging" disease, demonstrate the efficacy of a farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI), a drug originally developed to treat cancer. The clinical trial results, completed only six years after scientists identified the cause of Progeria, included significant improvements in weight gain, bone structure and, most importantly, the cardiovascular system, according to The Progeria Research Foundation (PRF) and Boston Children's Hospital. The study results ...
Florida State University chemist may hold key to building a better toxin mousetrap
2012-09-25
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — A Florida State University chemist's work could lead to big improvements in our ability to detect and eliminate specific toxins in our environment.
Featured on the cover of the prestigious Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), Sourav Saha's specialized work to strip electrons from the toxic chemical known as fluoride is producing a variety of unique results.
"I started out with the very basic premise of trying to find new ways to detect toxic fluoride in solutions," said Saha, an assistant professor of chemistry at Florida State. "As ...
Treating ovarian cancer: New pathways through genetics
2012-09-25
This press release is available in French.Montreal, September 24, 2012 – A new discovery that sheds light on the genetic make up of ovarian cancer cells could explain why some women survive longer than others with this deadly disease. A multi-disciplinary team led by the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI MUHC), in collaboration with the Lady Davis Institute of the Jewish General Hospital and the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre, has identified genetic patterns in ovarian cancer tumours that help to differentiate patients based ...
Exposing cancer's lethal couriers
2012-09-25
Malignant cells that leave a primary tumor, travel the bloodstream and grow out of control in new locations cause the vast majority of cancer deaths. New nanotechnology developed at Case Western Reserve University detects these metastases in mouse models of breast cancer far earlier than current methods, a step toward earlier, life-saving diagnosis and treatment.
A team of scientists, engineers and students across five disciplines built nanochains that home in on metastases before they've grown into new tissues, and, through magnetic resonance imaging, detect their locations. ...
White matter, old dogs, and new tricks at Dartmouth
2012-09-25
Most people equate "gray matter" with the brain and its higher functions, such as sensation and perception, but this is only one part of the anatomical puzzle inside our heads. Another cerebral component is the white matter, which makes up about half the brain by volume and serves as the communications network.
The gray matter, with its densely packed nerve cell bodies, does the thinking, the computing, the decision-making. But projecting from these cell bodies are the axons—the network cables. They constitute the white matter. Its color derives from myelin--a fat that ...
Bone marrow holds secrets for treating colitis and Crohn's
2012-09-25
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Michigan State University researchers have unlocked secrets in bone marrow that could lead to improved treatments for colitis and Crohn's disease.
The results, featured in the current issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences, show that the havoc inflammatory bowel diseases wreaks on the digestive tract is mirrored in bone marrow. Early indications also show that the disorders of the gut could potentially be treated through the bone marrow, said Pam Fraker, MSU University Distinguished Professor of biochemistry and molecular biology.
"It's ...
MRI helps identify patients with prostate cancer who may benefit from active surveillance
2012-09-25
Philadelphia, PA, September 24, 2012 – PSA screening has resulted in improved prostate cancer survival, but the high rate of diagnosis and treatment side effects raise concerns about overtreatment. In the quest to prevent overtreatment, "active surveillance" has emerged as a plausible option, encouraged for men whose tumors may not need immediate treatment and may never progress to more serious illness. Appropriate criteria for selecting patients for active surveillance are continuously debated. A group of investigators from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in ...
Feeling guilty versus feeling angry -- who can tell the difference?
2012-09-25
When you rear-end the car in front of you at a stoplight, you may feel a mix of different emotions such as anger, anxiety, and guilt. The person whose car you rear-ended may feel angered and frustrated by your carelessness, but it's unlikely that he'll feel much guilt.
The ability to identify and distinguish between negative emotions helps us address the problem that led to those emotions in the first place. But while some people can tell the difference between feeling angry and guilty, others may not be able to separate the two. Distinguishing between anger and frustration ...
Yale researchers call for specialty metals recycling
2012-09-25
New Haven, Conn. -- An international policy is needed for recycling scarce specialty metals that are critical in the production of consumer goods, according to Yale researchers in Science.
"A recycling rate of zero for specialty metals is alarming when we consider that their use is growing quickly," said co-author Barbara Reck, a research scientist at the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies.
Specialty metals, which include rare earth elements such as indium, gallium and germanium, account for more than 30 of the 60 metals in the periodic table. Because ...
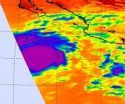
NASA's satellite saw 'power-trigger' around Hurricane Miriam's center
2012-09-25
ASA's Aqua satellite revealed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of Tropical Storm Miriam on Sept. 23 as it tracked through the Eastern Pacific Ocean. That power was the trigger that helped Miriam rapidly intensify into a major hurricane on Sept. 24.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern Pacific Ocean on Sept. 23 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Miriam's cloud top temperatures. Tropical Storm Miriam is born that day, about 640 miles (1,025 km) south-southeast of the southern ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Viruses help MU scientists battle pathogenic bacteria and improve water supplyNewly developed technique can kill antibiotic-resistant germs