(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. — With the U.S. economy vulnerable to weather events costing billions of dollars, an expert panel today asked Congress to create the first U.S. Weather Commission. The commission would provide guidance to policymakers on leveraging weather expertise across government and the private sector to better protect lives and businesses.
"The nation must focus its weather resources on the areas of greatest need in order to keep our economy competitive and provide maximum protection of lives and property," says Thomas Bogdan, president of the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. "Emerging technologies are providing an opportunity to create forecasts that are more accurate and detailed than ever, and to communicate them instantly to key communities and businesses. We need a U.S. Weather Commission to ensure that our entire weather research and technology enterprise provides maximum benefit to the nation."
At a time of fast-changing technological innovation, the commission would advise federal policymakers on setting priorities for improving forecasts and creating a more weather-proof nation. The goal is to help ensure cost-effective spending on the nation's weather systems while minimizing the impacts of both major storms, which last year alone cost about $52 billion, and normal fluctuations in weather, which have an estimated annual economic impact of $485 billion.
Earlier this year, the National Academy of Sciences released a hallmark report, Weather Services for the Nation: Becoming Second to None. The report concluded that, even with recent concerted and much-needed efforts to modernize the National Weather Service, the country faces challenges in harnessing the best science and private sector resources available for protecting the nation from weather impacts.
These challenges are rooted in evolving scientific and technological advances, rapidly changing needs of the nation's weather information consumers, and an increasingly capable and growing third-party community of weather services providers.
Congress has twice created an ocean commission for setting direction on commerce, research, and defense related to the world's oceans. But there has never been a U.S. Weather Commission, even though weather has far-reaching effects on all Americans.
Commissioners would provide guidance on issues such as making appropriate investments in satellite and radar systems, protecting vulnerable communities, setting research priorities, and meeting the needs of key sectors, ranging from agriculture to utilities to the U.S. armed forces.
"Weather is immeasurably important to public safety and our economic competitiveness," says Pam Emch, a senior staff engineer/scientist with Northrop Grumman Corporation and one of the panelists. "Effective organization of the diverse entities that span our weather enterprise is necessary for economic stability, innovation, and the good of the nation."
"Improved weather information can be an engine for economic growth," says panelist William Gail, co-founder and chief technology officer of the Global Weather Corporation. "As we develop increasingly detailed understanding of our atmosphere, there is enormous potential for helping the public and businesses."
"We must keep pace with accelerating scientific and technological advances and meet expanding user needs in our increasingly information-centric society," says panelist John Armstrong, chair of the Committee on the Assessment of the National Weather Service's Modernization Program.
Bogdan says that a commission approach, guided by key actors across the entire weather enterprise, will provide needed direction and consensus.
"The U.S. Weather Commission offers the promise of better research, state-of-the-art prediction, and protection for the health and prosperity of the U.S.," he says. "It will also foster growth for the innovative private weather sector we have all come to rely upon. This is an issue that affects all members of Congress and all their constituents, no matter where they live."
Today's panel briefing was the first step in a process that will continue into the next Congress. The panel's next steps are to brief staff and members on the importance of the commission and the role it will play, seeking their guidance and support for establishing the commission in 2013.
INFORMATION:
The University Corporation for Atmospheric Research manages the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado, under sponsorship by the National Science Foundation. Any opinions, findings and conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
On the Web:
For news releases, images, and more
www.ucar.edu/atmosnews
Experts call on Congress to create first US Weather Commission
2012-09-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
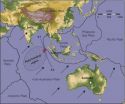
Big quake was part of crustal plate breakup
2012-09-27
SALT LAKE CITY Sept. 26, 2012 – Seismologists have known for years that the Indo-Australian plate of Earth's crust is slowly breaking apart, but they saw it in action last April when at least four faults broke in a magnitude-8.7 earthquake that may be the largest of its type ever recorded.
The great Indian Ocean quake of April 11, 2012 previously was reported as 8.6 magnitude, and the new estimate means the quake was 40 percent larger than had been believed, scientists from the University of Utah and University of California, Santa Cruz, report in the Sept. 27 issue of ...
Study reveals complex rupture process in surprising 2012 Sumatra quake
2012-09-27
SANTA CRUZ, CA--The massive earthquake that struck under the Indian Ocean southwest of Sumatra on April 11, 2012, came as a surprise to seismologists and left them scrambling to figure out exactly what had happened. Analysis of the seismic waves generated during the event has now revealed a complicated faulting process unlike anything seen before.
"Nobody was anticipating an earthquake of this size and type, and the complexity of the faulting surprised everybody I've spoken to about this," said Thorne Lay, professor of Earth and planetary sciences at the University of ...
Men on the mind: Study finds male DNA in women's brains
2012-09-27
SEATTLE – Male DNA is commonly found in the brains of women, most likely derived from prior pregnancy with a male fetus, according to first-of-its-kind research conducted at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. While the medical implications of male DNA and male cells in the brain are unknown, studies of other kinds of microchimerism – the harboring of genetic material and cells that were exchanged between fetus and mother during pregnancy – have linked the phenomenon to autoimmune diseases and cancer, sometimes for better and other times for worse.
The study findings ...
Pregnancy generates maternal immune-suppressive cells that protect the fetus
2012-09-27
A new study published online in the journal Nature suggests it might be possible to develop vaccines to prevent premature birth and other pregnancy complications. If so, such vaccines would be the first intended to stimulate the subset of regulatory CD4 T cells that suppress the immune response.
Current vaccines are specifically designed to stimulate T cell subsets that activate the immune response.
The study, led by a researcher at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, shows the immune system of a pregnant mother stimulates cells that selectively prevent ...
Researchers define 2 categories of multiple sclerosis patients
2012-09-27
BOSTON, MA—There are approximately 400,000 people in the United States with multiple sclerosis. Worldwide, the number jumps to more than 2.1 million people. Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach to treating the millions with multiple sclerosis, what if doctors could categorize patients to create more personalized treatments? A new study by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) may one day make this idea a reality in the fight against the debilitating autoimmune disease.
A research team led by Philip De Jager, MD, PhD, BWH Department of Neurology, senior ...
Touch-sensitive tentacles catapult prey into carnivorous plant traps
2012-09-27
Swift predators are common in the animal world but are rare in the plant kingdom. New research shows that Drosera glanduligera, a small sundew from southern Australia, deploys one of the fastest and most spectacular trapping mechanisms known among carnivorous plants.
The study, published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE, is a collaboration between the Plant Biomechanics Group at the University of Freiburg and private sundew cultivators from Weil am Rhein, and provides the first experimental demonstration of fast-moving snap tentacles in sundew plants propelling ...
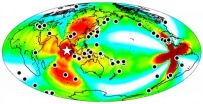
Large 2012 earthquake triggered temblors worldwide for nearly a week
2012-09-27
This year's largest earthquake, a magnitude 8.6 temblor on April 11 centered in the East Indian Ocean off Sumatra, did little damage, but it triggered quakes around the world for at least a week, according to a new analysis by seismologists from the University of California, Berkeley, and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).
The April 11 quake was unusually large – the tenth largest in the last 100 years and, similar to a few other recent large quakes, triggered small quakes during the three hours it took for seismic waves to travel through Earth's crust.
The new study ...
Cannabis withdrawal symptoms might have clinical importance
2012-09-27
Cannabis users have a greater chance of relapse to cannabis use when they experience certain withdrawal symptoms, according to research published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE led by David Allsop of the National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre (NCPIC) at the University of New South Wales.
The authors tested a group of dependent cannabis users over a two week period of abstinence for impairment related to their withdrawal symptoms. Findings were correlated with the probability of relapse to cannabis use during the abstinence period, and the level ...
First evidence of fetal DNA persisting in human brain tissue
2012-09-27
Small portions of male DNA, most likely left over in a mother's body by a male fetus can be detected in the maternal brain relatively frequently, according to a report published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by William Chan of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and his colleagues.
The process, called fetal 'microchimerism (Mc)', is common in other tissues such as blood, but this is the first evidence of male Mc in the human female brain. Microchimerism can be both beneficial and harmful to maternal health, since it is associated with processes such ...
Viewing gender-specific objects influences perception of gender identity
2012-09-27
Spending too much time looking at high heels may influence how a viewer perceives the gender of an androgynous face, according to new research published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Amir Homayoun Javadi of Technische Universität, Dresden and his colleagues. The study sheds new light on how the objects surrounding us may influence our perceptions of gender.
The authors found that when people view objects highly associated with one gender, like high heels for women or electric shavers for men, for a short period of time and are then asked to identify the ...