(Press-News.org) A fossil which has lain in a museum drawer for over a century has been recognized by a University of Leicester geologist as a unique clue to the long-lost skills of some of the most sophisticated animal architects that have ever lived on this planet.
It has provided evidence that early organisms developed specialised roles and that these specialists displayed co-operation in order to construct their homes – much like today's builders employ a team of bricklayers, plasters and decorators.
The fossil is a graptolite, a planktonic colony from nearly half a billion years ago, found by nineteenth century geologists in the Southern Uplands of Scotland. Graptolites are common in rocks of this age, but only as the beautifully intricate multistorey floating 'homes' that these animals constructed – the animals that made them were delicate creatures with long tentacle-bearing arms, but these have long rotted away.
Dr. Jan Zalasiewicz of the Department of Geology of the University of Leicester was routinely examining the rock slab when noticed something previously overlooked. This particular, unique fossil does not show the animals themselves – but it shows what look like the connections between them, rather like finding the ropes that once held a team of mountaineers together.
These connections indicate that the animals of the colony could not have been all basically the same, as had been assumed. Rather, they must have been very different in shape and organization in different parts of the colony.
Dr Zalasiewicz said, "The light caught one of the fossils in just the right way, and it showed complex structures I had never seen in a graptolite before. It was a sheer stroke of luck…one of those Eureka moments.
"In some parts of the colony, these fossilized connections look like slender criss-crossing branches; others look like little hourglasses.
"Hence, a key element in the ancient success of these animals must have been an elaborate division of labour, in which different members of the colony took on different tasks, for feeding, building and so on. This amazing fossil shows sophisticated prehistoric co-operation, preserved in stone."
It has been a mystery how such tiny 'lowly' prehistoric creatures could have co-operated to build such impressively sophisticated living quarters – it is a skill long been lost among the animals of the world's oceans. Now, this single fossil, which has been carefully preserved in the collections of the British Geological Survey since 1882, sheds light on these ancient master builders.
Remarkably, over that past century, the fossil slab had been examined by some of the world's best experts on these fossils because it includes key specimens of a rare and unusual species.
Dr. Mike Howe, manager of the British Geological Survey's fossil collections and a co-author of the study, commented "This shows that museum collections are a treasure trove, where fossils collected long ago can drive new science."
INFORMATION:
Notes to editors:
For further information contact:
Dr. Jan Zalasiewicz, University of Leicester: jaz1@le.ac.uk and 0116 2523928; or Dr. Mark Williams on mri@le.ac.uk and 0116 2523642
Or
Dr. Mike Howe, British Geological Survey, mhowe@bgs.ac.uk and 0115 9363105
The scientific study, just published online, is:
Zalasiewicz, J.A., Page, A.A., Rickards, R.B., Williams, M., Wilby, P.R., Howe, M.P.A. & Snelling, A. 2012. Polymorphic organization in a planktonic graptoloid (Hemichordata: Pterobranchia) colony of late Ordovician age. Geological Magazine.
The British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS), a component body of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), is the nation's principal supplier of objective, impartial and up-to-date geological expertise and information for decision making for governmental, commercial and individual users. The BGS maintains and develops the nation's understanding of its geology to improve policy making, enhance national wealth and reduce risk. It also collaborates with the national and international scientific community in carrying out research in strategic areas, including energy and natural resources, our vulnerability to environmental change and hazards, and our general knowledge of the Earth system. More about the BGS can be found at www.bgs.ac.uk.
Prehistoric builders reveal trade secrets
Long-overlooked museum fossil is a clue to vanished skills of prehistoric animal architects
2012-10-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Egyptian toe tests show they're likely to be the world's oldest prosthetics
2012-10-02
The results of scientific tests using replicas of two ancient Egyptian artificial toes, including one that was found on the foot of a mummy, suggest that they're likely to be the world's first prosthetic body parts.
The University of Manchester researcher Dr Jacky Finch wanted to find out if a three part wood and leather toe dating from between 950 to 710 BC found on a female mummy buried near Luxor in Egypt, and the Greville Chester artificial toe from before 600 BC and made of cartonnage (a sort of papier maché mixture made using linen, glue and plaster), could be ...
The water flow of the Amazon River in a natural climate archive
2012-10-02
Oxygen isotopes in tree rings are an excellent archive of precipitation dynamics in the tropical Amazon region. The precise determination of the ratios of stable oxygen isotopes (18O/16O) proves to be a new parameter for detecting the dynamics of the water cycle in tropical rain forest areas. It can therefore replace the classic climate observables such as tree ring width or wood density, which are unsuitable for high-quality reconstructions of climate conditions in tropical areas. These are the findings of a group of researchers from the GFZ German Research Centre for ...
The Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice focuses on periodontal and implant treatments
2012-10-02
St. Louis, MO, October 2, 2012 – What's the latest, research-supported best practice in periodontal care and implant dentistry? Dental specialists and generalists alike can read about it in the first of a new series from The Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice (JEBDP), the foremost publication of information about evidence-based dental practice, published by Elsevier.
The inaugural edition of the Annual Report on Periodontal and Implant Treatment is now available, containing concise, authoritative reviews based on the evidence about practice-critical topics. Mark ...
Study suggests immune system can boost regeneration of peripheral nerves
2012-10-02
Modulating immune response to injury could accelerate the regeneration of severed peripheral nerves, a new study in an animal model has found. By altering activity of the macrophage cells that respond to injuries, researchers dramatically increased the rate at which nerve processes regrew.
Influencing the macrophages immediately after injury may affect the whole cascade of biochemical events that occurs after nerve damage, potentially eliminating the need to directly stimulate the growth of axons using nerve growth factors. If the results of this first-ever study can ...
Happiness at work depends on a good salary, but also on how much colleagues earn
2012-10-02
This press release is available in Spanish.
The study, published by Professor Eduardo Pérez Asenjo of UC3M's Economics Department, shows that relative earnings affect our happiness and our job performance. Summing up: if the people with whom I compare myself earn more than I do, I will be unhappier and I will work more. "This confirms the hypothesis of what I perceived, but not the way I would like things to be," the author of the study comments. "I would find it healthier not to compare what we earn to what others earn and I think it would be 'better' if these things ...
Length matters in gene expression
2012-10-02
Gene ends communicate
Human genomes harbour thousands of genes, each of which gives rise to proteins when it is active. But which inherent features of a gene determine its activity? Postdoctoral Scholar Pia Kjølhede Andersen and Senior Researcher Søren Lykke-Andersen from the Danish National Research Foundation's Centre for mRNP Biogenesis and Metabolism have now found that the distance between the gene start, termed the 'promoter', and the gene end, the 'terminator', is crucial for the activity of a protein-coding gene. If the distance is too short, the gene is transcriptionally ...
Intelligence is in the genes, but where?
2012-10-02
You can thank your parents for your smarts—or at least some of them. Psychologists have long known that intelligence, like most other traits, is partly genetic. But a new study led by psychological scientist Christopher Chabris reveals the surprising fact that most of the specific genes long thought to be linked to intelligence probably have no bearing on one's IQ. And it may be some time before researchers can identify intelligence's specific genetic roots.
Chabris and David Laibson, a Harvard economist, led an international team of researchers that analyzed a dozen ...
Superman-strength bacteria produce gold
2012-10-02
EAST LANSING, Mich. — At a time when the value of gold has reached an all-time high, Michigan State University researchers have discovered a bacterium's ability to withstand incredible amounts of toxicity is key to creating 24-karat gold.
"Microbial alchemy is what we're doing – transforming gold from something that has no value into a solid, precious metal that's valuable," said Kazem Kashefi, assistant professor of microbiology and molecular genetics.
He and Adam Brown, associate professor of electronic art and intermedia, found the metal-tolerant bacteria Cupriavidus ...
Solar cell consisting of a single molecule
2012-10-02
This press release is available in German.
A team of scientists, led by Joachim Reichert, Johannes Barth, and Alexander Holleitner (Technische Universitaet Muenchen, Clusters of Excellence MAP and NIM), and Itai Carmeli (Tel Aviv University) developed a method to measure photocurrents of a single functionalized photosynthetic protein system. The scientists could demonstrate that such a system can be integrated and selectively addressed in artificial photovoltaic device architectures while retaining their biomolecular functional properties. The proteins represent light-driven, ...
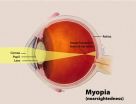
Specialty contact lenses may one day help halt the progression of nearsightedness in children
2012-10-02
WASHINGTON, Oct. 2—Nearsightedness, or myopia, affects more than 40 percent of people in the U.S. and up to 90 percent of children in some parts of Asia. The problem begins in childhood and often progresses with age. Standard prescription lenses can correct the defocus but do not cure nearsightedness, and do not slow progression rates as children grow. But recent experimental work by biomedical scientist David Troilo and colleagues at the State University of New York (SUNY) College of Optometry in New York City supports the development of a potential cure for myopia by ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Prehistoric builders reveal trade secretsLong-overlooked museum fossil is a clue to vanished skills of prehistoric animal architects