(Press-News.org) The results of scientific tests using replicas of two ancient Egyptian artificial toes, including one that was found on the foot of a mummy, suggest that they're likely to be the world's first prosthetic body parts.
The University of Manchester researcher Dr Jacky Finch wanted to find out if a three part wood and leather toe dating from between 950 to 710 BC found on a female mummy buried near Luxor in Egypt, and the Greville Chester artificial toe from before 600 BC and made of cartonnage (a sort of papier maché mixture made using linen, glue and plaster), could be used as practical tools to help their owners to walk. Both display significant signs of wear and their design features also suggest they may have been more than cosmetic additions.
Dr Finch says: "Several experts have examined these objects and had suggested that they were the earliest prosthetic devices in existence. There are many instances of the ancient Egyptians creating false body parts for burial but the wear plus their design both suggest they were used by people to help them to walk. To try to prove this has been a complex and challenging process involving experts in not only Egyptian burial practices but also in prosthetic design and in computerized gait assessment."
Dr Finch, who is based in the Faculty of Life Sciences' KNH Centre for Biomedical Egyptology, recruited two volunteers who were both missing their right big toe. Design replicas of the ancient toes were made to fit each volunteer along with replica leather ancient Egyptian style sandals.
The tests were carried out at the Gait Laboratory at Salford University's Centre for Rehabilitation and Human Performance Research. Each volunteer was asked to walk on a 10 metre walkway bare foot, in their own shoes and wearing the replicas with and without the sandals. Their movement was tracked using 10 special cameras and the pressure of their footsteps was measured using a special mat. The 10 best walking trials were recorded for each foot, using their normal left foot as the control.
It was surprising how well both volunteers were able to walk using these devices although one volunteer performed much better than the other. The camera footage revealed that when wearing the sandals with the cartonnage replica, one of the volunteers achieved 87% of the flexion achieved by their normal left toe. The three part wood and leather design producing nearly 78%. Interestingly the ability to push off using the prosthetic toe was not as good when this volunteer wasn't wearing the sandals. The second volunteer was still able to produce between 60-63% flexion wearing the replicas with or without the sandals.
When wearing the replicas the pressure measurements showed that for both volunteers there were no overly high pressure points. This indicated that the false toes were not causing any undue discomfort or possible tissue damage. However, when the volunteers wore just the replica sandals without the false toes the pressure being applied under the foot rose sharply.
Dr Finch says: "The pressure data tells us that it would have been very difficult for an ancient Egyptian missing a big toe to walk normally wearing traditional sandals. They could of course remained bare foot or perhaps have worn some sort of sock or boot over the false toe, but our research suggests that wearing these false toes made walking in a sandal more comfortable."
Alongside the test data Dr Finch also asked her volunteers to fill in a questionnaire about how they felt when doing the trials in the gait laboratory. Despite it having performed well the comfort scores for the cartonnage replica were disappointing although it was felt to be an excellent cosmetic replacement. Describing the performance of the three part wooden and leather toe both volunteers found this one to be extremely comfortable, scoring it highly, one volunteer commenting that with time he could get used to walking in it.
Assessing the volunteers' experience Dr Finch said: "It was very encouraging that both volunteers were able to walk wearing the replicas. Now that we have the gait analysis data and volunteer feedback alongside the obvious signs of wear we can provide a more convincing argument that the original artefacts had some intended prosthetic function.
The findings from this study, which have been published in full in the Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics, means the earliest known prosthetic is now more likely to come from ancient Egypt. The three part example pre-dates by some 400 years what is currently thought to be the oldest, although untested, prosthetic device. This is a bronze and wooden leg that was found in a Roman burial in Capua, Southern Italy. That has been dated to 300 BC although only a replica now remains as the original was destroyed in a bombing raid over London during the war.
### END
Egyptian toe tests show they're likely to be the world's oldest prosthetics
2012-10-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The water flow of the Amazon River in a natural climate archive
2012-10-02
Oxygen isotopes in tree rings are an excellent archive of precipitation dynamics in the tropical Amazon region. The precise determination of the ratios of stable oxygen isotopes (18O/16O) proves to be a new parameter for detecting the dynamics of the water cycle in tropical rain forest areas. It can therefore replace the classic climate observables such as tree ring width or wood density, which are unsuitable for high-quality reconstructions of climate conditions in tropical areas. These are the findings of a group of researchers from the GFZ German Research Centre for ...
The Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice focuses on periodontal and implant treatments
2012-10-02
St. Louis, MO, October 2, 2012 – What's the latest, research-supported best practice in periodontal care and implant dentistry? Dental specialists and generalists alike can read about it in the first of a new series from The Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice (JEBDP), the foremost publication of information about evidence-based dental practice, published by Elsevier.
The inaugural edition of the Annual Report on Periodontal and Implant Treatment is now available, containing concise, authoritative reviews based on the evidence about practice-critical topics. Mark ...
Study suggests immune system can boost regeneration of peripheral nerves
2012-10-02
Modulating immune response to injury could accelerate the regeneration of severed peripheral nerves, a new study in an animal model has found. By altering activity of the macrophage cells that respond to injuries, researchers dramatically increased the rate at which nerve processes regrew.
Influencing the macrophages immediately after injury may affect the whole cascade of biochemical events that occurs after nerve damage, potentially eliminating the need to directly stimulate the growth of axons using nerve growth factors. If the results of this first-ever study can ...
Happiness at work depends on a good salary, but also on how much colleagues earn
2012-10-02
This press release is available in Spanish.
The study, published by Professor Eduardo Pérez Asenjo of UC3M's Economics Department, shows that relative earnings affect our happiness and our job performance. Summing up: if the people with whom I compare myself earn more than I do, I will be unhappier and I will work more. "This confirms the hypothesis of what I perceived, but not the way I would like things to be," the author of the study comments. "I would find it healthier not to compare what we earn to what others earn and I think it would be 'better' if these things ...
Length matters in gene expression
2012-10-02
Gene ends communicate
Human genomes harbour thousands of genes, each of which gives rise to proteins when it is active. But which inherent features of a gene determine its activity? Postdoctoral Scholar Pia Kjølhede Andersen and Senior Researcher Søren Lykke-Andersen from the Danish National Research Foundation's Centre for mRNP Biogenesis and Metabolism have now found that the distance between the gene start, termed the 'promoter', and the gene end, the 'terminator', is crucial for the activity of a protein-coding gene. If the distance is too short, the gene is transcriptionally ...
Intelligence is in the genes, but where?
2012-10-02
You can thank your parents for your smarts—or at least some of them. Psychologists have long known that intelligence, like most other traits, is partly genetic. But a new study led by psychological scientist Christopher Chabris reveals the surprising fact that most of the specific genes long thought to be linked to intelligence probably have no bearing on one's IQ. And it may be some time before researchers can identify intelligence's specific genetic roots.
Chabris and David Laibson, a Harvard economist, led an international team of researchers that analyzed a dozen ...
Superman-strength bacteria produce gold
2012-10-02
EAST LANSING, Mich. — At a time when the value of gold has reached an all-time high, Michigan State University researchers have discovered a bacterium's ability to withstand incredible amounts of toxicity is key to creating 24-karat gold.
"Microbial alchemy is what we're doing – transforming gold from something that has no value into a solid, precious metal that's valuable," said Kazem Kashefi, assistant professor of microbiology and molecular genetics.
He and Adam Brown, associate professor of electronic art and intermedia, found the metal-tolerant bacteria Cupriavidus ...
Solar cell consisting of a single molecule
2012-10-02
This press release is available in German.
A team of scientists, led by Joachim Reichert, Johannes Barth, and Alexander Holleitner (Technische Universitaet Muenchen, Clusters of Excellence MAP and NIM), and Itai Carmeli (Tel Aviv University) developed a method to measure photocurrents of a single functionalized photosynthetic protein system. The scientists could demonstrate that such a system can be integrated and selectively addressed in artificial photovoltaic device architectures while retaining their biomolecular functional properties. The proteins represent light-driven, ...
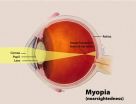
Specialty contact lenses may one day help halt the progression of nearsightedness in children
2012-10-02
WASHINGTON, Oct. 2—Nearsightedness, or myopia, affects more than 40 percent of people in the U.S. and up to 90 percent of children in some parts of Asia. The problem begins in childhood and often progresses with age. Standard prescription lenses can correct the defocus but do not cure nearsightedness, and do not slow progression rates as children grow. But recent experimental work by biomedical scientist David Troilo and colleagues at the State University of New York (SUNY) College of Optometry in New York City supports the development of a potential cure for myopia by ...
3-D medical scanner: New handheld imaging device to aid doctors on the 'diagnostic front lines'
2012-10-02
WASHINGTON, Oct. 2, 2012—In the operating room, surgeons can see inside the human body in real time using advanced imaging techniques, but primary care physicians, the people who are on the front lines of diagnosing illnesses, haven't commonly had access to the same technology – until now. Engineers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) have created a new imaging tool for primary care physicians: a handheld scanner that would enable them to image all the sites they commonly examine, and more, such as bacterial colonies in the middle ear in 3-D, or monitor ...