(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
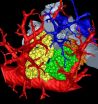
The video shows the imaging of a section of a mouse lung. As the image rotates, more respiratory branches (bronchioles) are shown, along with three acini (yellow, green and orange...
Click here for more information.
Amidst the extraordinarily dense network of pathways in a mammal lung is a common destination. There, any road leads to a cul-de-sac of sorts called the pulmonary acinus. This place looks like a bunch of grapes attached to a stem (acinus means "berry" in Latin).
Scientists have struggled to understand more specifically what happens in this microscopic, labyrinthine intersection of alleys and dead ends. To find out, a research team led by the University of Iowa created the most detailed, three-dimensional rendering of the pulmonary acinus. The computerized model, derived from mice, faithfully mimics each twist and turn in this region, including the length, direction and angles of the respiratory branches that lead to the all-important air sacs called alveoli.
"The imaging and image analysis methods described here provide for branch morphometry at the acinar level that has not been available previously," the researchers write in the paper, published this week in the online early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The model is important, because it can help scientists understand where and how lung diseases emerge as well as the role the pulmonary acinus plays in the delivery of drugs, such as those commonly administered with inhalers.
"These methods allow us to understand where in the lung periphery disease begins and how it progresses," says Eric Hoffman, professor in the departments of radiology, medicine, and biomedical engineering at the UI and corresponding author on the paper.
"How do gases and inhaled substances get there and do they accumulate in one or another acinus? How do they swirl around and clear out? We just don't have a complete understanding how that happens."
As an example, Hoffman said the model could be used to determine how smoking-induced emphysema originates. "It has been hypothesized recently that it begins with the loss of peripheral airways rather than the lung air sacs," he says, citing ongoing research by James Hogg at the University of British Columbia, who was not involved in this study. It also could shed light and lead to more effective treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which causes irreversible damage to the lung, says Dragos Vasilescu, first author on the paper who based his thesis on the research while a graduate student at the UI.
For years, the best that lung anatomy pioneers such as study co-corresponding author Ewald Weibel, professor emeritus of anatomy at the University of Bern, could do to study specific areas of a lung was to make measurements in two dimensions or create 3D casts of a lung's air spaces. The techniques, while giving the earliest insights into a lungs's makeup and functioning, had their limitations. For one, they did not directly replicate a lung's structure in real life, and they could not convey how various parts act together as a whole. Yet advances in imaging and computation have enabled researchers to more fully explore how gases and other inhaled substances act in the lung's furthest recesses.
In this study, the team worked with 22 pulmonary acini culled from young and old mice. They then set to "reconstruct" the acini based on micro computed tomography imaging of scanned lungs in mice and extracted from them. The extracted lungs were preserved in a way that kept the anatomy intact—including the tiny air spaces required for successful imaging. From that, the researchers were able to measure an acinus, estimate the number of acini for each mouse lung and even count the alveoli and measure their surface area.
The mouse lung, in its structure and function, is remarkably similar to the human lung. That means researchers can alter the genetics of a mouse and see how those changes affect the peripheral structure of the lung and its performance.
Already, the researchers found in the current study that mouse alveoli increase in number long past the two weeks that at least one previous study had indicated. Hoffman adds that a separate study is needed to determine whether humans, too, increase the number of air sacs past a certain, predetermined age.
The researchers next aim to use the model to more fully understand how gases interact with the bloodstream within the acini and the alveoli.
"Our imaging and image-analysis methodologies enable new ways to investigate the lung's structure and can now be used to further investigate the normal healthy-lung anatomy in humans and be used to visualize and assess the pathological changes in animal models of specific structural diseases," says Vasilescu, who is a postdoctoral researchfellow at the University of British Columbia.
INFORMATION:
Contributing authors include Zhiyun Gao, post-doctoral researcher in the department of electrical engineering at the UI; Punam Saha, associate professor in the department of electrical engineering at the UI; Leilei Yin, at the University of Illinois; Ge Wang, former radiology professor at the UI and now at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University; Beatrice Haefeli-Bleuer, of the University of Bern; and Matthias Ochs, of Hannover Medical School in Germany.
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation and the Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research.
A mammal lung, in 3-D
Researchers create model of mysterious region
2012-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Alberta has $12.3-billion impact on Alberta economy
2012-10-03
(Edmonton) The University of Alberta's impact on the Alberta economy is estimated to be $12.3 billion, which is five per cent of the province's gross domestic product—or the equivalent of having 135 Edmonton Oilers NHL teams in Alberta, according to a new study.
"When a university educates a population, it's the whole region that benefits," said study co-author Anthony Briggs, an assistant professor in the Alberta School of Business at the U of A. "We're not looking at the cost of the education and research, which is just one slice, but estimating the value of the investment. ...
Visionary transparent memory a step closer to reality
2012-10-03
HOUSTON – (Oct. 2, 2012) – Researchers at Rice University are designing transparent, two-terminal, three-dimensional computer memories on flexible sheets that show promise for electronics and sophisticated heads-up displays.
The technique based on the switching properties of silicon oxide, a breakthrough discovery by Rice in 2008, was reported today in the online journal Nature Communications.
The Rice team led by chemist James Tour and physicist Douglas Natelson is making highly transparent, nonvolatile resistive memory devices based on the revelation that silicon ...
Starting antiretroviral therapy improves HIV-infected Africans' nutrition
2012-10-03
Starting HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy reduces food insecurity and improves physical health, thereby contributing to the disruption of a lethal syndemic, UCSF and Massachusetts General Hospital researchers have found in a study focused on sub-Saharan Africa.
The study was published this week in the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes.
With more than 20 million people infected with HIV/AIDS and almost 240 million people lacking access to enough food, sub-Saharan Africa is experiencing co-epidemics of food insecurity and HIV/AIDS that intensify ...
For elephants, deciding to leave watering hole demands conversation, Stanford study shows
2012-10-03
STANFORD, Calif. — In the wilds of Africa, when it's time for a family of elephants gathered at a watering hole to leave, the matriarch of the group gives the "let's-go rumble" — as it's referred to in scientific literature — kicking off a coordinated and well-timed conversation, of sorts, between the leaders of the clan.
First, the head honcho moves away from the group, turns her back and gives a long, slightly modulated and — to human ears — soft rumble while steadily flapping her ears. This spurs a series of back and forth vocalizations, or rumbles, within the group ...
University of Minnesota engineers invent new device that could increase Internet download speeds
2012-10-03
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/02/2012) —A team of scientists and engineers at the University of Minnesota has invented a unique microscale optical device that could greatly increase the speed of downloading information online and reduce the cost of Internet transmission.
The device uses the force generated by light to flop a mechanical switch of light on and off at a very high speed. This development could lead to advances in computation and signal processing using light instead of electrical current with higher performance and lower power consumption.
The research results ...
1 glue, 2 functions
2012-10-03
Akron, Ohio, Oct. 2, 2012 — While the common house spider may be creepy, it also has been inspiring researchers to find new and better ways to develop adhesives for human applications such as wound healing and industrial-strength tape. Think about an adhesive suture strong enough to heal a fractured shoulder and that same adhesive designed with a light tackiness ideal for "ouch-free" bandages.
University of Akron polymer scientists and biologists have discovered that this house spider — in order to more efficiently capture different types of prey — performs an uncommon ...
Too little nitrogen may restrain plants' carbon storage capability, U of M paper shows
2012-10-03
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/02/2012) —Plants' ability to absorb increased levels of carbon dioxide in the air may have been overestimated, a new University of Minnesota study shows.
The study, published this week in the journal Nature Climate Change, shows that even though plants absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide and actually can benefit from higher levels of it, they may not get enough of the nutrients they need from typical soils to absorb as much CO2 as scientists had previously estimated. Carbon dioxide absorption is an important factor in mitigating fossil-fuel ...
Acoustic cell-sorting chip may lead to cell phone-sized medical labs
2012-10-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A technique that uses acoustic waves to sort cells on a chip may create miniature medical analytic devices that could make Star Trek's tricorder seem a bit bulky in comparison, according to a team of researchers.
The device uses two beams of acoustic -- or sound -- waves to act as acoustic tweezers and sort a continuous flow of cells on a dime-sized chip, said Tony Jun Huang, associate professor of engineering science and mechanics, Penn State. By changing the frequency of the acoustic waves, researchers can easily alter the paths of the cells.
Huang ...
Payoff lacking for casino comps
2012-10-03
A study of widely used complimentary offers at Atlantic City casinos finds that common giveaways such as free rooms and dining credits are less profitable – and lead to unhealthy competition among casinos – than alternative comps such as free travel and parking.
The research, co-authored by Seul Ki Lee, an assistant professor at Temple University's School of Tourism and Hospitality Management, analyzed monthly promotional allowance and expenditure data from 11 casinos in the Atlantic City market from 2008 to 2010. Atlantic City is the second largest gaming market in ...
Study reveals differences in overall health of Latino-American subgroups
2012-10-03
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. - Despite a shared Latino heritage, there are significant differences in the overall health and the use of health-care services among Cuban-Americans, Mexican-Americans and Puerto Rican-Americans — even between men and women in the same subgroup — according to two recently published studies by Florida State University researchers.
The authors, led by College of Social Work Professor and Associate Dean Amy L. Ai, evaluated the physical and behavioral health, as well as the health care service usage, of all three major Latino subgroups in the United States. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] A mammal lung, in 3-DResearchers create model of mysterious region