(Press-News.org) This press release is available in Spanish.
One of the critical moments in the final quality of the potato occurs during its storage, as there exists the risk of sprouting or rotting due to pathogenic agents such as bacteria and fungi. In order to avoid this, agricultural engineer David Gómez Castillo carried out research for his PhD on the possibility of substituting the current use of chemical products by treating the tuber with essential oils of mint, caraway, coriander, eucalyptus and clove, "which have proved to be great potential inhibitors in the main problems detected".
The chemical product Clorprofam (CIPC) is the most commonly used as a sprout suppressant on stored potatoes. Nevertheless, possible reductions in permitted dosages, market and consumer pressures seeking healthier and, moreover, more environmentally-friendly products, have made it necessary to find alternatives to these synthetic products, with the market, culinary and technological quality of the potato remaining unaltered.
This is the context of the research by David Gómez Castillo, who has evaluated alternative treatment using essential oils of mint, caraway, coriander, eucalyptus and clove. In concrete, he studied the effect of applying these oils with table-stock varieties of the potato (Agata and Monalisa) and industrial ones (Agria and Kennebec), and compared the results thereof with those that had been treated chemically.
A good alternative
The research analysed two parameters: the commercial quality (germination, texture and colour of the tuber) and the culinary and technological quality (colour and texture of slices of the potato, dry material, total soluble solids, reductor sugars and sensorial analysis). Evaluations at 10, 25, 40, 55 and 70 days in storage were also undertaken, the antimicrobial effect of essential oils being assessed for the principal phytopathogens (fungi and bacteria).
According to Mr Gómez, "we found a high antigerminant capacity with treatment using the essential oil of coriander for industrial crops, and with the essential oil of mint for both industrial and table-stock crops. These showed great inhibitory potential on the principal phytopathogenic problems studied and all this makes a good alternative to CPIC use for storage of potatoes".
It was also shown that the essential oil of eucalyptus, for its high antigerminant capacity with table-stock potatoes, "could be another alternative for reducing post-harvest losses due to phytopathogenic problems, obtaining even better results if the treatment is accompanied by the essential oil of clove".
In the opinion of this researcher, the use of treatment with essential oils in the storage of potatoes "can provide added value in the application of antigerminant treatment, due to its efficacy in controlling the progress of important phytopathogens".
### END
Essential oils as antigerminants for the storage of potatoes
The use of essential oils as antigerminants for the storage of potatoes could be a good solution as an alternative to chemical treatment
2012-10-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A white mouse
2012-10-05
These proteins are required for melanocyte stem cell self-maintenance and, as such, correct pigmentation throughout the mice's life span. Without these two proteins, the mice's fur turns white.
Their research is published in the review 'Cell Report' and paves the way for serious possibilities in terms of stopping the formation of melanomas, tumours that originate from melanocyte cells.
Melanocytes are cells in the organism used for skin, fur and hair pigment. This pigmentation function provides protection from the sun and lends organisms their colour. Malfunctions in ...
Mosquito genetics may offer clues to malaria control, Virginia Tech researchers say
2012-10-05
An African mosquito species with a deadly capacity to transmit malaria has a perplexing evolutionary history, according to discovery by researchers at the Fralin Life Science Institute at Virginia Tech.
Closely related African mosquito species originated the ability to transmit human malaria multiple times during their recent evolution, according to a study published this week in PLoS Pathogens by Igor Sharakhov, an associate professor of entomology in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and Maryam Kamali of Tehran, Iran, a Ph.D. student in the department of ...
Building 3-D structures from a 2-D template
2012-10-05
This press release is available in German.
Deep below the silicon surface, the SPRIE method produces regular structures in the micrometer range that refract light. (Photo: KIT/CFN)
In modern telecommunications, light carries digital information over kilometers within seconds. Adapted optical materials control the light signals. In the AFM journal, researchers from Berlin, Louvain, and from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology present a method to produce photonic crystals. Their optical properties are adjusted by structures of micrometer size. The method is rapid, cheap, ...
Low incidence of needlestick injuries among staff at national pharmacy chain
2012-10-05
CHICAGO (October 5, 2012) – Vaccinations for flu, tetanus and other common vaccines are increasingly taking place in non-medical settings such as supermarkets and drug stores. This added responsibility for pharmacists increases the risk of needlestick injuries (NSIs), puncture wounds often suffered while preparing or after use of a needle. NSIs can transmit bloodborne pathogens, including hepatitis C and HIV, from an infected patient to the person administering the vaccine.
A new report published in the November issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the ...
Genotyping helps identify source of clinic infection outbreak
2012-10-05
CHICAGO (October 5, 2012) – Researchers from East Carolina University used a new technique of genotyping to identify the source of a hematology clinic outbreak of Mycobacterium mucogenicum, a gram-positive, acid-fast bacteria found in tap water. This is the first outbreak of M. mucogenicum in an ambulatory care setting; five other outbreaks have been reported in hospital settings since 1995. The study was published in the November issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Using repetitive ...
MIT Research: What number is halfway between 1 and 9? Is it 5 -- or 3?
2012-10-05
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — Ask adults from the industrialized world what number is halfway between 1 and 9, and most will say 5. But pose the same question to small children, or people living in some traditional societies, and they're likely to answer 3.
Cognitive scientists theorize that that's because it's actually more natural for humans to think logarithmically than linearly: 30 is 1, and 32 is 9, so logarithmically, the number halfway between them is 31, or 3. Neural circuits seem to bear out that theory. For instance, psychological experiments suggest that multiplying the ...
How will smart cars affect the future of driving?
2012-10-05
California, Nevada, and Florida have already made driverless cars street-legal, and continuing advances in the technology have led many to predict that the commercialization of automated vehicles is a real possibility in the not-so-distant future. As driverless vehicles become more commonplace, it is important to understand how humans interact with this new technology. The Human Factors special issue on automation, featuring the latest articles on designing automated vehicles with the driver in mind, is now available online. The October 2012 issue may be found at http://hfs.sagepub.com/content/current. ...
'Disgusted' rats teaching scientists about nausea, work may lead to new cancer treatments
2012-10-05
Nausea is a common and distressing side effect of many drugs and treatments. Unlike vomiting, nausea is not well understood, but new research by University of Guelph scientists may soon change that.
Guelph PhD student Katharine Tuerke, neuroscience researcher Cheryl Limebeer and Prof. Linda Parker in the Department of Psychology believe they've found the mechanism in the brain that is responsible for the sensation of nausea – with the help of some "disgusted" rats.
Their study was published this week in Journal of Neuroscience.
"Although everyone has experienced ...
Tree nut research may unexpectedly lead to medical advances
2012-10-05
This press release is available in Spanish.
Prescription drugs that today help patients fight severe fungal infections might tomorrow be even more effective, thanks to unexpected findings from agriculture-based, food-safety-focused studies by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and their colleagues.
Petri-dish experiments conducted by now-retired USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) research leader Bruce C. Campbell, ARS molecular biologist Jong H. Kim, and their co-investigators suggest that pairing conventional antifungal medicines with natural, edible ...
NASA notes Nadine now no more
2012-10-05
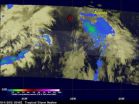
Twenty-three days after Nadine was born, the tropical cyclone's life came to an end in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. NASA's TRMM satellite caught a look at the fading Nadine one final time on Oct. 3 before it dissipated.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed above long-lasting Nadine for the last time before the tropical storm's dissipation on October 4, 2012 at 0249 UTC (10:49 p.m. EDT October 3, 2012).
TRMM measures rainfall from space and there was very little remaining in Nadine when it passed overhead. Rainfall data from TRMM's Microwave ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How Japanese medical trainees view artificial intelligence in medicine
MambaAlign fusion framework for detecting defects missed by inspection systems
Children born with upper limb difference show the incredible adaptability of the young brain
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
Fast-paced lives demand faster vision: ecology shapes how “quickly” animals see time
Global warming and heat stress risk close in on the Tour de France
New technology reveals hidden DNA scaffolding built before life ‘switches on’
New study reveals early healthy eating shapes lifelong brain health
Trashing cancer’s ‘undruggable’ proteins
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
[Press-News.org] Essential oils as antigerminants for the storage of potatoesThe use of essential oils as antigerminants for the storage of potatoes could be a good solution as an alternative to chemical treatment