Whether we like someone affects how our brain processes movement
2012-10-06
(Press-News.org) Hate the Lakers? Do the Celtics make you want to hurl? Whether you like someone can affect how your brain processes their actions, according to new research from the Brain and Creativity Institute at USC.
Most of the time, watching someone else move causes a 'mirroring' effect – that is, the parts of our brains responsible for motor skills are activated by watching someone else in action.
But a study by USC researchers appearing Oct. 5 in PLOS ONE shows that whether or not you like the person you're watching can actually have an effect on brain activity related to motor actions and lead to "differential processing" – for example, thinking the person you dislike is moving more slowly than they actually are.
"We address the basic question of whether social factors influence our perception of simple actions," says Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, an assistant professor with the Brain and Creativity Institute at USC and the Division of Occupational Science. "These results indicate that an abstract sense of group membership, and not only differences in physical appearance, can affect basic sensory-motor processing."
Past research has shown that race or physical similarity can influence brain processes, and we tend to have more empathy for people who look more like us.
In this study, the researchers controlled for race, age and gender, but introduced a back story that primed participants to dislike some of the people they were observing: half were presented as neo-Nazis, and half were presented as likeable and open-minded. All study participants recruited for the study were Jewish males.
The researchers found that when people viewed someone they disliked, a part of their brain that was otherwise activated in "mirroring" – the right ventral premotor cortex – had a different pattern of activity for the disliked individuals as compared to the liked individuals.
Importantly, the effect was specific to watching the other person move. There was no difference in brain activity in the motor region when participants simply watched still videos of the people they liked or disliked.
"Even something as basic as how we process visual stimuli of a movement is modulated by social factors, such as our interpersonal relationships and social group membership," says Mona Sobhani, lead author of the paper and a graduate student in neuroscience at USC. "These findings lend important support for the notion that social factors influence our perceptual processing."
Glenn R. Fox and Jonas Kaplan of the Brain and Creativity Insitute at USC were co-authors of the paper.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-10-06
Pop quiz! Tests are good for: (a) Assessing what you've learned; (b) Learning new information; (c) a & b; (d) None of the above.
The correct answer?
According to research from psychological science, it's both (a) and (b) – while testing can be useful as an assessment tool, the actual process of taking a test can also help us to learn and retain new information over the long term and apply it across different contexts.
New research published in journals of the Association for Psychological Science explores the nuanced interactions between testing, memory, and learning ...
2012-10-06
Chronic morphine exposure has the opposite effect on the brain compared to cocaine in mice, providing new insight into the basis of opiate addiction, according to Mount Sinai School of Medicine researchers. They found that a protein called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is increased in cocaine addiction, is inhibited in opioid addiction. The research is published in the October 5 issue of Science.
"Our study shows that BDNF responds completely differently with opioid administration compared to cocaine," said Ja Wook Koo, PhD, Postdoctoral Fellow in ...
2012-10-06
This press release is available in French.
Methadone reduces the risk of HIV transmission in people who inject drugs (PWID), as reported by an international team of researchers in a paper published today in the online edition of the British Medical Journal. This team included Dr. Julie Bruneau from the CHUM Research Centre (CRCHUM) and the Department of Family Medicine at the Université de Montréal.
"There is good evidence to suggest that opiate substitution therapies (OST) reduce drug-related mortality, morbidity and some of the injection risk behaviors among PWID. ...
2012-10-06
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Swift satellite recently detected a rising tide of high-energy X-rays from a source toward the center of our Milky Way galaxy. The outburst, produced by a rare X-ray nova, announced the presence of a previously unknown stellar-mass black hole.
"Bright X-ray novae are so rare that they're essentially once-a-mission events and this is the first one Swift has seen," said Neil Gehrels, the mission's principal investigator, at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "This is really something we've been waiting for."
An X-ray nova is a short-lived ...
2012-10-06
At 11:24 p.m. EDT on Oct. 4, 2012, the sun unleashed a coronal mass ejection (CME). Not to be confused with a solar flare, which is a burst of light and radiation, CMEs are a phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and can reach Earth one to three days later. Experimental NASA research models show the CME to be traveling at about 400 miles per second.
When Earth-directed, CMEs can affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth. CMEs of this speed, however, have not generally caused major effects in the past. Further updates will be provided if needed.INFORMATION:
NOAA's ...
2012-10-06
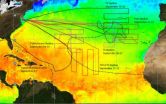
NASA's Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel or HS3 scientists had a fascinating tropical cyclone to study in long-lived Hurricane Nadine. NASA's Global Hawk aircraft has investigated Nadine five times during the storm's lifetime.
NASA's Global Hawk also circled around the eastern side of Hurricane Leslie when it initially flew from NASA's Dryden Research Flight Center, Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. to the HS3 base at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va. on Sept. 6-7, 2012.
Nadine has been a great tropical cyclone to study because it has lived so long ...
2012-10-06
From Sept. 6 to Sept. 29, 2012, NASA's Solar Dynamic Observatory (SDO) moved into its semi-annual eclipse season, a time when Earth blocks the telescope's view of the sun for a period of time each day. Scientists choose orbits for solar telescopes to minimize eclipses as much as possible, but they are a fact of life -– one that comes with a period of fuzzy imagery directly after the eclipse.
The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) on SDO observes the sun through a glass window. The window can change shape in response to temperature changes, and does so dramatically ...
2012-10-06
It is easy to see the effect of the strong northeasterly wind shear battering Tropical Storm Gaemi in satellite imagery from NASA. Visible imagery on Oct. 5 shows a large oval-shaped area of showers and thunderstorms associated with the storm, southwest of the exposed center of circulation.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gaemi as it was approaching Vietnam on Oct. 5, 2012 at 0550 UTC (1:50 a.m. EDT). A true-color image of the storm was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument and shows bulk of showers and thunderstorms ...
2012-10-06
(Boston) – Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) investigators have led the first genome-wide evaluation of genetic variants associated with Parkinson's disease (PD). The study, which is published online in PLOS ONE, points to the involvement of specific genes and alterations in their expression as influencing the risk for developing PD.
Jeanne Latourelle, DSc, assistant professor of neurology at BUSM, served as the study's lead author and Richard H. Myers, PhD, professor of neurology at BUSM, served as the study's principal investigator and senior author.
A ...
2012-10-06
With the rapid development of industrialization and urbanization in China, the demand for electricity continues to grow, according to a report by State Grid Corporation of China. Exploring and utilizing renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency are significant to the energy supply, energy structure adjustment and energy-saving in China. Being the No. 1 Electric Power Expo in China, The 14th International Exhibition on Electric Power Equipment and Technology, The 7th International Exhibition on Electrical Equipment and 2012 International Exhibition on Electric Power ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Whether we like someone affects how our brain processes movement