(Press-News.org) A new study by the Simon Fraser University-based Human Security Report Project (HSRP), released today at the United Nations headquarters in New York, finds that there is no compelling evidence to support a host of widely held beliefs regarding wartime sexual violence.
The study, presented by HSRP director Andrew Mack, disputes the common assumption that conflict-related sexual violence is on the rise, and argues that the experience of a small number of countries afflicted by extreme levels of sexual violence is not the norm for all war-affected countries.
Key findings include:
In more than half of the years in which countries around the world experienced conflict between 2000-2009, levels of reported conflict-related sexual violence were low to negligible.
There is no evidence to support frequent claims that rape as a "weapon of war" is widespread, nor that its incidence has been growing.
Domestic sexual violence victimizes far more women in war-affected countries than does the conflict-related sexual violence that is perpetrated by combatants.
Recent studies show that male victims and female perpetrators may be more numerous than generally believed.
The study also finds that the mainstream view of the impact of war on children's education as highly damaging is incorrect, and that educational outcomes in war-affected countries improve over time despite fighting, even in regions most affected by war.
###
The complete study is available online at www.hsrgroup.org and will soon be available in print.
The HSRP has received funding from the Department for International Development (United Kingdom); the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation; the Norwegian Royal Ministry of Foreign Affairs; the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency; the Swiss Federal Department of Foreign Affairs; and the UBS Optimus Foundation.
Simon Fraser University is Canada's top-ranked comprehensive university and one of the top 50 universities in the world under 50 years old. With campuses in Vancouver, Burnaby and Surrey, B.C., SFU engages actively with the community in its research and teaching, delivers almost 150 programs to more than 30,000 students, and has more than 120,000 alumni in 130 countries.
Simon Fraser University: Engaging Students. Engaging Research. Engaging Communities.
Contact:
Andrew Mack, Human Security Report Project, 604.803.3548 (cell), amack@sfu.ca
Sebastian Merz, Human Security Report Project, 778.846.6846 (cell), smerz@sfu.ca
Marianne Meadahl, PAMR, 778.782.3210; Marianne_Meadahl@sfu.ca
UN webcast at: http://webtv.un.org/ END
Study challenges assumptions on wartime sexual violence
2012-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Palm oil massive source of carbon dioxide
2012-10-11
New Haven, Conn. -- Expanding production of palm oil, a common ingredient in processed foods, soaps and personal care products, is driving rainforest destruction and massive carbon dioxide emissions, according to a new study by Yale and Stanford researchers.
The study, published in the journal Nature Climate Change, shows that deforestation for the development of oil palm plantations in Indonesian Borneo is becoming a globally significant source of carbon dioxide emissions.
Plantation expansion is projected to pump more than 558 million metric tons of carbon dioxide ...
Checklists can effectively assess work-related risk of musculoskeletal injuries
2012-10-11
Amsterdam, NL, October 10, 2012 – A new paper by Thomas J. Albin, PE, CPE, of High Plains Engineering Services in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, confirms that observational assessment tools, often called checklists, used to assess risk factors such as wrist extension and motion repetition, can be valid tools in identifying work-related risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries. Published in Work: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment, and Rehabilitation, Albin presents a comprehensive, multi-step yet simple approach for improving the use and effectiveness of checklists.
Previous ...
NASA eyes Typhoon Prapiroon's U-turn
2012-10-11
Typhoon Prapiroon is making a U-turn in the Philippine Sea, changing direction from northwest to northeast. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of the typhoon as it began turning. Visible satellite imagery revealed its most powerful thunderstorms south and east of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Prapiroon on Oct. 10 at 0435 UTC (12:35 a.m. EDT) and captured a visible image of the storm. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument was able to get a visible image of the typhoon, because it was 1:35 p.m. local Asia/Tokyo ...
Suomi NPP satellite sees auroras over North America
2012-10-11
Overnight on October 4-5, 2012, a mass of energetic particles from the atmosphere of the Sun were flung out into space, a phenomenon known as a coronal mass ejection. Three days later, the storm from the Sun stirred up the magnetic field around Earth and produced gorgeous displays of northern lights. NASA satellites track such storms from their origin to their crossing of interplanetary space to their arrival in the atmosphere of Earth.
Using the "day-night band" (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership ...
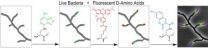
Filming bacterial life in multicolor as a new diagnostic and antibiotic discovery tool
2012-10-11
An international team of scientists led by Indiana University chemist Michael S. VanNieuwenhze and biologist Yves Brun has discovered a revolutionary new method for coloring the cell wall of bacterial cells to determine how they grow, in turn providing a new, much-needed tool for the development of new antibiotics.
Discovery of the new method is expected to broadly impact both basic and applied research tied to understanding, controlling or preventing bacterial cell growth in specific environments, said the two scientists in IU Bloomington's College of Arts and Sciences. ...
Choreography of submerged whale lunges revealed
2012-10-11
Returning briefly to the surface for great lungfuls of air, the underwater lifestyles of whales had been a complete mystery until a small group of pioneers from various global institutions – including Malene Simon, Mark Johnson and Peter Madsen – began attaching data-logging tags to these enigmatic creatures. Knowing that Jeremy Goldbogen and colleagues had successful tagged blue, fin and humpback whales to reveal how they lunge through giant shoals of krill, Simon and her colleagues headed off to Greenland where they tagged five humpback whales to discover how the animals ...
Soft-shelled turtles urinate through mouth
2012-10-11
Chinese soft-shelled turtles are exquisitely adapted to their aquatic lifestyle, sitting contentedly on the bottom of brackish muddy swamps or snorkelling at the surface to breath. According to Y. K. Ip from the National University of Singapore, they even immerse their heads in puddles when their swampy homes dry up: which intrigued Ip and his colleagues. Why do these air-breathing turtles submerge their heads when they mainly depend on their lungs to breathe and are unlikely to breathe in water? Given that some fish excrete waste nitrogen as urea – in addition to ammonia ...
Techniques used to infer pathways of protein evolution found unreliable
2012-10-11
A key assumption that biologists have relied on widely over the past quarter-century in studying the evolution of protein molecules is "highly questionable," according to an article published in the November issue of BioScience.
The article, by Shozo Yokoyama, a vision researcher at Emory University, summarizes experimental work that involved creating and measuring the properties of dozens of reconstructed ancestral versions of visual pigments found in the eyes of vertebrates, including humans, as well as deliberately altered variants. Yokoyama concludes that the studies ...
How food marketers can help consumers eat better while improving their bottom line!
2012-10-11
Food marketers are masters at getting people to crave and consume the foods that they promote. In this study authors Dr. Brian Wansink, co-director of the Cornell University Center for Behavioral Economics in Child Nutrition and Professor of Marketing and Dr. Pierre Chandon, professor of Marketing at the leading French graduate school of business, INSEAD challenge popular assumptions that link food marketing and obesity. Their findings presented last weekend at the Association for Consumer Research Conference in Vancouver, Canada point to ways in which smart food marketers ...
Prospective Alzheimer's drug builds new brain cell connections
2012-10-11
PULLMAN, Wash.—Washington State University researchers have developed a new drug candidate that dramatically improves the cognitive function of rats with Alzheimer's-like mental impairment.
Their compound, which is intended to repair brain damage that has already occurred, is a significant departure from current Alzheimer's treatments, which either slow the process of cell death or inhibit cholinesterase, an enzyme believed to break down a key neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory development.
Such drugs, says Joe Harding, a professor in WSU's College of Veterinary ...