(Press-News.org) LIVERMORE, Calif. -- In an effort to identify the thousands of John/Jane Doe cold cases in the United States, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researcher and a team of international collaborators have found a multidisciplinary approach to identifying the remains of missing persons.
Using "bomb pulse" radiocarbon analysis developed at Lawrence Livermore, combined with recently developed anthropological analysis and forensic DNA techniques, the researchers were able to identify the remains of a missing child 41 years after the discovery of the body.
In 1968, a child's cranium was recovered from the banks of a northern Canadian river. Initial analysis conducted by investigators, using technology at the time, concluded that the cranium came from the body of a 7-9-year-old child and no identity could be determined. The case went cold and was reopened later.
The cranium underwent reanalysis at the Centre for Forensic Research, Simon Fraser University in Canada, where skull measurements, skeletal ossification, and dental formation indicated an age-at-death of approximately 4 ½ years old. At Lawrence Livermore, researchers conducted radiocarbon analysis of enamel from two teeth indicated a more precise birth date. Forensic DNA analysis, conducted at Simon Fraser University, indicated the child was a male, and the obtained mitochondrial profile matched a living maternal relative to the presumed missing child.
The multidisciplinary analyses resulted in a legal identification 41 years after the discovery of the remains, highlighting the enormous potential of combining radiocarbon analysis with anthropological and mitochondrial DNA analyses in producing confident personal identifications in forensic cold cases dating to within the last 60 years.
"There are thousands of John Doe and Jane Doe cold cases in the United States," said Livermore scientist Bruce Buchholz, who conducted the radiocarbon analysis in the case. "I believe we could provide birthdates and death dates for many of these cases."
Age determination of unknown human bodies is important in the setting of a crime investigation or a mass disaster, because the age at death, birth date, and year of death, as well as gender, can guide investigators to the correct identity among a large number of possible matches.
Using the Laboratory's Center for Accelerator Mass Spectrometry, Buchholz determined that the radioactive carbon-14 produced by above-ground nuclear testing in the 1950s and 1960s remains in the dental enamel, the hardest substance in the body. The radiocarbon analysis shows that dating teeth with the carbon-14 method estimates the birth date within one to two years.
Above-ground testing of nuclear weapons during the Cold War (1955) caused a surge in global levels of carbon-14 (14C), which has been carefully recorded over time. The radiocarbon technique determines the amount of 14C in tooth enamel. Scientists can relate the extensive atmospheric record for 14C to when the tooth was formed and calculate the age of the tooth and its owner.
In forensic cases where teeth are unavailable, the radiocarbon analysis of bone also can provide useful information whether the time of death occurred prior to 1955 or afterward.
In the missing child case, Buchholz determined radiocarbon values for two teeth, which once analyzed showed that that the average of the crown's enamel formation span occurred between 1959 and 1961.
"In a conservative estimate, the carbon-14 value for the crown's enamel would correspond with a birth year between 1958 and 1962," Buchholz said.
In summary, the 14C dates in combination with the age-at-death estimate using anthropological techniques suggest that the child was born between 1958 and 1962 and died between 1963 and 1968.
The research also has implications for the identity of victims in mass graves or mass fatality contexts, where a combined DNA and radiocarbon analysis approach provides the additional benefit of distinguishing between maternal relations.
###
Besides Livermore and Simon Fraser University, other institutions participating in the research include the Karolinska Institute in Sweden and the British Columbia Institute of Technology.
The research appears in the September issue of the Journal of Forensic Sciences.
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration. END
Cold cases heat up through Lawrence Livermore approach to identifying remains
2012-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sweeping X-ray imaging survey of dying stars is 'uncharted territory'
2012-10-11
The death throes of dying stars are the focus of a sweeping new survey using NASA's Chandra X-ray satellite observatory.
More than two dozen astronomers have aligned their research goals to use Chandra to image a set of dying stars in the neighborhood of the Sun. The resulting X-ray images of these dying stars—called planetary nebulae—are shedding light on the violent "end game" of a Sun-like star's life.
The research team, led by Joel Kastner from Rochester Institute of Technology, won seven days of observing time with Chandra in 2011 to survey and image nearly two ...
Mount Sinai researchers discover gene signature that predicts prostate cancer survival
2012-10-11
Researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine have identified a six-gene signature that can be used in a test to predict survival in men with aggressive prostate cancer, according to new research published in the October issue of The Lancet Oncology. This is the first study to demonstrate how prognostic markers may be useful in a clinical setting.
Using blood from 202 men with treatment-resistant prostate cancer, researchers found six genes characteristic of treatment-resistant prostate cancer. Men with the six-gene signature were high-risk, with a survival time of ...
Scientists pinpoint gene variations linked to higher risk of bipolar disorder
2012-10-11
JUPITER, FL, October 10, 2012 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have identified small variations in a number of genes that are closely linked to an increased risk of bipolar disorder, a mental illness that affects nearly six million Americans, according to the National Institute of Mental Health.
"Using samples from some 3,400 individuals, we identified several new variants in genes closely associated with bipolar disorder," said Scripps Florida Professor Ron Davis, who led the new study, which was published recently by the ...
Study challenges assumptions on wartime sexual violence
2012-10-11
A new study by the Simon Fraser University-based Human Security Report Project (HSRP), released today at the United Nations headquarters in New York, finds that there is no compelling evidence to support a host of widely held beliefs regarding wartime sexual violence.
The study, presented by HSRP director Andrew Mack, disputes the common assumption that conflict-related sexual violence is on the rise, and argues that the experience of a small number of countries afflicted by extreme levels of sexual violence is not the norm for all war-affected countries.
Key findings ...
Palm oil massive source of carbon dioxide
2012-10-11
New Haven, Conn. -- Expanding production of palm oil, a common ingredient in processed foods, soaps and personal care products, is driving rainforest destruction and massive carbon dioxide emissions, according to a new study by Yale and Stanford researchers.
The study, published in the journal Nature Climate Change, shows that deforestation for the development of oil palm plantations in Indonesian Borneo is becoming a globally significant source of carbon dioxide emissions.
Plantation expansion is projected to pump more than 558 million metric tons of carbon dioxide ...
Checklists can effectively assess work-related risk of musculoskeletal injuries
2012-10-11
Amsterdam, NL, October 10, 2012 – A new paper by Thomas J. Albin, PE, CPE, of High Plains Engineering Services in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, confirms that observational assessment tools, often called checklists, used to assess risk factors such as wrist extension and motion repetition, can be valid tools in identifying work-related risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries. Published in Work: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment, and Rehabilitation, Albin presents a comprehensive, multi-step yet simple approach for improving the use and effectiveness of checklists.
Previous ...
NASA eyes Typhoon Prapiroon's U-turn
2012-10-11
Typhoon Prapiroon is making a U-turn in the Philippine Sea, changing direction from northwest to northeast. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of the typhoon as it began turning. Visible satellite imagery revealed its most powerful thunderstorms south and east of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Prapiroon on Oct. 10 at 0435 UTC (12:35 a.m. EDT) and captured a visible image of the storm. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument was able to get a visible image of the typhoon, because it was 1:35 p.m. local Asia/Tokyo ...
Suomi NPP satellite sees auroras over North America
2012-10-11
Overnight on October 4-5, 2012, a mass of energetic particles from the atmosphere of the Sun were flung out into space, a phenomenon known as a coronal mass ejection. Three days later, the storm from the Sun stirred up the magnetic field around Earth and produced gorgeous displays of northern lights. NASA satellites track such storms from their origin to their crossing of interplanetary space to their arrival in the atmosphere of Earth.
Using the "day-night band" (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership ...
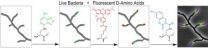
Filming bacterial life in multicolor as a new diagnostic and antibiotic discovery tool
2012-10-11
An international team of scientists led by Indiana University chemist Michael S. VanNieuwenhze and biologist Yves Brun has discovered a revolutionary new method for coloring the cell wall of bacterial cells to determine how they grow, in turn providing a new, much-needed tool for the development of new antibiotics.
Discovery of the new method is expected to broadly impact both basic and applied research tied to understanding, controlling or preventing bacterial cell growth in specific environments, said the two scientists in IU Bloomington's College of Arts and Sciences. ...
Choreography of submerged whale lunges revealed
2012-10-11
Returning briefly to the surface for great lungfuls of air, the underwater lifestyles of whales had been a complete mystery until a small group of pioneers from various global institutions – including Malene Simon, Mark Johnson and Peter Madsen – began attaching data-logging tags to these enigmatic creatures. Knowing that Jeremy Goldbogen and colleagues had successful tagged blue, fin and humpback whales to reveal how they lunge through giant shoals of krill, Simon and her colleagues headed off to Greenland where they tagged five humpback whales to discover how the animals ...