(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Leeds have identified a crucial stage in the lifecycle of simple viruses like polio and the common cold that could open a new front in the war on viral disease.
The team are the first to observe at a single-molecule level how the genetic material (genome) that forms the core of a single-strand RNA virus particle packs itself into its outer shell of proteins. Lead researcher Professor Peter Stockley said their results overturn accepted thinking about the process and could open a chink in the armour of a wide range of viruses.
"If we can target this process, it could lead to a completely new class of anti-virals that would be less likely to create resistant viruses than existing drugs, which tend to target individual proteins," Professor Stockley said.
A number of important viruses like the common cold and polio have RNA (ribonucleic acid) instead of DNA as their genetic material. The observations reveal that the viruses' RNA initially has a much greater volume than the virus particles created after they are packed inside their protein shell.
"We realised that the RNA genome must have to be intricately folded to fit into the final container, just like when you pack to go on holiday and need to fold your clothes to fit into the space in your suitcase," said co-author Dr Roman Tuma from the University of Leeds' Faculty of Biological Sciences.
When the team added proteins to the viral RNA they saw an immediate collapse in its volume.
"It seems that viral RNAs have evolved a self-folding mechanism that makes closing the 'viral suitcase' very efficient. It's as though 'the suitcase and the clothes' work together to close the lid and protect the content," Dr Tuma said.
"The viral RNAs, and only the viral RNAs, can do this trick of folding up to fit as soon as they see the 'suitcase' coming. That's the important thing. If we can interfere in that process we've got a completely novel drug target in the lifecycle of viruses," Professor Stockley said.
"At the moment there are relatively few antiviral drugs and they tend to target enzymes that the virus encodes in its genome. The problem is that the drugs target one enzyme initially and, within the year, scientists are identifying strains that have become resistant. Individual proteins are extremely susceptible to this mutation. A fundamental process like the one we're looking at opens the possibility of targeting the collective behaviour of essential molecules, which could be much less susceptible to developing resistance," explained Professor Stockley.
The same phenomenon is seen in both bacterial and plant viruses. "While we have not proved it yet, I would put money on animal viruses showing the same mechanism too," Professor Stockley added.
The team used sophisticated instrumentation custom built at the University that allowed them to make the first ever single-molecule measurements of viral assembly. This allowed researchers to observe individual viral particles one at a time. "The specific collapse, which can only be seen in such assays, was totally unexpected and overturns the current thinking about assembly," Professor Stockley said.
The team also includes PhD student Alexander Borodavka, whose Wellcome Trust studentship funded the new research. They have recently secured a grant from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) to extend their research.
"We're now perfectly positioned to pursue questions about how this mechanism works in other viruses and we're already thinking about ways to start designing new antiviral drugs that would target this newly recognised feature of viral lifecycles," Professor Stockley said.
###
The research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Viruses act like 'self-packing suitcases'
2012-10-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists harness immune system to prevent lymphoma relapse
2012-10-18
UK scientists hope that lymphoma patients could benefit from a new drug that triggers the cancer-fighting properties of the body's own immune system, after highly promising early laboratory results.
The University of Manchester researchers, who were funded by the charity Leukaemia & Lymphoma Research, have shown that, when used in conjunction with radiotherapy, the new drug is potentially four times more likely to lead to long-term survival than radiotherapy alone.
Relapse is a common fate for many lymphoma patients and new treatments are desperately needed. The new ...
Genes and immune system shaped by childhood poverty, stress
2012-10-18
A University of British Columbia and Centre for Molecular Medicine and Therapeutics (CMMT) study has revealed that childhood poverty, stress as an adult, and demographics such as age, sex and ethnicity, all leave an imprint on a person's genes. And, that this imprint could play a role in our immune response.
The study was published last week in a special volume of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that looks at how experiences beginning before birth and in the years after can affect the course of a person's life.
Known as epigenetics, or the study ...
Female Pulitzer Prize winners require higher qualifications, MU study finds
2012-10-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. —The Pulitzer Prize in Journalism is one of the world's most prestigious awards. Despite progress in the last few decades, gender disparities in the field of journalism have existed as long as the profession has. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has found that female Pulitzer Prize winners are more likely to have greater qualifications than their male counterparts in order to win the coveted award.
In a study to be published in Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly, Yong Volz, an assistant professor of journalism studies in the MU School of ...
College students and credit card debt -- parents at fault?
2012-10-18
Parents need to be good role models to help their children make sensible financial decisions, according to Adam Hancock and his team, from East Carolina University in the US. Their work highlights that parents who argue about finances contribute to increasing credit card debt among their children during their student years. Their work is published online in Springer's Journal of Family and Economic Issues.
Credit card debt among college students has been a growing concern for researchers and policymakers over the last decade. In addition, there is growing concern among ...
A cancer diagnosis does not make young people religious
2012-10-18
A sociologist of religion from the University of Copenhagen has interviewed 21 young patients diagnosed with a life-threatening cancer about their religious beliefs. She concludes that a cancer diagnosis will not make young people, who are not religious already, turn to religion. But it can confirm already existing beliefs.
"My research shows that young cancer patients' views on existential issues show consistency before and after the diagnosis: Their faith and their religious practices remain the same. However, the beliefs they already had can be confirmed and strengthened ...
How flick knife thumbs help Japan's rare fighting frogs
2012-10-18
Combat-ready spikes which shoot from fingers sounds like the weaponry of a comic book hero, but a Japanese scientist has found exactly this in a rare breed of frog. The discovery, which is published in the Journal of Zoology, reveals how the Otton frog uses spikes which protrude from a false thumb for both combat and mating.
The study, conducted by Dr Noriko Iwai from the University of Tokyo, focused on the Otton frog (Babina subaspera), whose habitat is the Amami islands of Southern Japan. Unlike most other frogs the Otton has an extra digit-like structure, a trait it ...
Ozone affects forest watersheds
2012-10-18
U.S. Forest Service and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) scientists have found that rising levels of ozone, a greenhouse gas, may amplify the impacts of higher temperatures and reduce streamflow from forests to rivers, streams, and other water bodies. Such effects could potentially reduce water supplies available to support forest ecosystems and people in the southeastern United States.
Impacts of ozone, a global scale pollutant, on forests are not well understood at a large scale. This modeling study indicates that current and projected increases in ozone in the ...
Ongoing disparities in breastfeeding highlighted at Fourth Annual Summit on Breastfeeding
2012-10-18
New Rochelle, NY, October 18, 2012—Despite efforts to reduce disparities in breastfeeding, only 44% of African-American women report that they breastfeed compared with 66 and 68% of Hispanic and white women, respectively. According to UNICEF, there is a 14-fold difference in survival rates in the first 6 months, in developing countries, between children who have been breastfed exclusively and non-breastfed children. These disparities in breastfeeding and other key challenges and opportunities in the ongoing mission to encourage and support breastfeeding are discussed in ...
New tools for assessing the patient's experience with health care--progress report
2012-10-18
Philadelphia, Pa. (October 18, 2012) - An ongoing program is developing new tools for assessing health care quality from the most important viewpoint—that of the patient receiving care, according to a special supplement to Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The special issue presents a progress report on the Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS®) surveys —an Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) initiative to capture patients' perspectives on healthcare. The ...
A*Star scientists identify mutation that causes skin hyperproliferation
2012-10-18
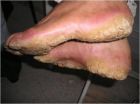
1. Scientists have identified a mutation in a gene that causes patches of very thick skin to appear on the palms and soles of affected people. This skin disorder is related, albeit in a much milder form, to that of the Indonesian 'Tree Man', Dede Koswara . These thick rough skin patches on hands and feet steadily increase in number as a person ages and often coalesce to form larger lesions. In severe cases, these lesions can be painful and debilitating.
2. The team of scientists from A*STAR's Institute of Medical Biology (IMB), in collaboration with hospitals and research ...