(Press-News.org) Miss hitting the "sweet spot" on a baseball bat and the resulting vibrations can zing your hands. Bat companies have tried for decades to reduce these painful shocks with limited success. But Daniel Russell, a professor in the graduate program in acoustics at Pennsylvania State University in University Park, has figured out that bat vibrations between 600 and 700 hertz (Hz) cause the most pain and that specifically tuned vibration absorbers are the best at combatting the sting. He will present the results of his damping technique comparisons at the 164th meeting of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA), held from Oct. 22 – 26 in Kansas City, Missouri.
Human hands are sensitive to vibration frequencies between 200 Hz and 700 Hz, Russell says. When a ball impacts a baseball bat, two of the resulting bat vibration frequencies fall within that range. Previous damping techniques eliminated oscillations around 200 Hz, which causes pain in whichever hand is lowest on the bat. But after consulting baseball players, Russell learned that the most painful sensations occur in the top hand, where vibration frequencies between 600 and 700 Hz reside.
High-speed video analysis showed that these vibrations are so violent, "the hands lose contact with the bat during a swing," says Russell. "The fingers [and thumb] are being flung away from the bat because of the vibration." Foam fillings in an aluminum bat's handle can dampen these vibrations but do not eliminate them. So Russell worked with baseball bat manufacturer Marucci Sports to tune a vibration absorber that cancels out some of these painful oscillations.
The result is a mass-spring device nestled in the baseball bat's knob that quickly eliminates the bending pattern, or vibration, responsible for the bat's more painful sting. These absorbers must be specifically tuned, since the painful vibration frequencies vary depending on a bat's length.
The vibration absorbers Russell helped calibrate have been used in commercially available bats since 2010, and so far the response from players and consumers has been very encouraging, he notes.
INFORMATION:
MORE INFORMATION ABOUT THE 164th ASA MEETING
The Kansas City Marriott Downtown Hotel is located at 200 West 12th Street, Kansas City, Missouri, 64105. The hotel main numbers are: 816-421-6800; fax: 816-855-4418.
USEFUL LINKS
Main meeting website: http://acousticalsociety.org/meetings/kansas_city
Meeting Abstract Database: http://asa.aip.org/asasearch.html
Hotel site: https://resweb.passkey.com/Resweb.do?mode=welcome_ei_new&eventID=8120158
WORLD WIDE PRESS ROOM
ASA's World Wide Press Room contains additional tips about newsworthy stories and with lay-language papers, which are 300-1200 word summaries of presentations written by scientists for a general audience and accompanied by photos, audio, and video.
PRESS REGISTRATION
ASA will grant free registration to credentialed full-time journalists and professional freelance journalists working on assignment for major news outlets. If you are a reporter and would like to attend, contact Charles E. Blue (cblue@aip.org, 301-209-3091), who can also help with setting up interviews and obtaining images, sound clips, or background information.
This news release was prepared for the Acoustical Society of America (ASA) by the American Institute of Physics (AIP).
ABOUT THE ACOUSTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7,000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (the world's leading journal on acoustics), Acoustics Today magazine, ECHOES newsletter, books, and standards on acoustics. The Society also holds two major scientific meetings each year. For more information about ASA, visit our website at http://www.acousticalsociety.org.
END
Earthquakes sway buildings, buckle terrain, and rumble – both audibly and in infrasound, frequencies below the threshold of human hearing. New computer modeling by a team of researchers indicates that most of the low-frequency infrasound comes from an unexpected source: the actual "pumping" of the Earth's surface. The researchers confirmed their models by studying data from an actual earthquake.
"It's basically like a loudspeaker," said Stephen Arrowsmith, a researcher with the Geophysics Group at Los Alamos National Laboratory in Santa Fe, N.M., who presents his team's ...
VIDEO:
Einstein predicted gravity waves in his general theory of relativity, but to date these ripples in the fabric of space-time have never been observed. Now a scientific research technique called...
Click here for more information.
A pioneering technology capable of atomic-level precision is now being developed to detect what so far has remained imperceptible: gravitational waves or ripples in space-time caused by cataclysmic events including even the Big Bang itself.
A ...
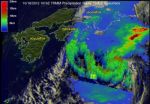
Tropical Storm Maria is moving away from Japan and strong wind shear is pushing its rainfall east of the storm's center, according to NASA satellite imagery.
On Oct. 18 at 0845 UTC (4:45 a.m. EDT), NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite saw that rain associated with Tropical Storm Maria was limited to the east of the storm's center. Rainfall was also light to moderate, falling at a rate between .78 to 1.57 inches/20 to 40 mm per hour. There were no areas of heavy rain remaining in the tropical cyclone. The low-level center of the storm is now exposed ...
When the lamp is shattered,
The light in the dust lies dead.
When the cloud is scattered,
The rainbow's glory is shed.
These words, which open Shelley's poem "When the Lamp is Shattered," employ visions of nature to symbolize life in decay and rebirth. It's as if he had somehow foreseen the creation of this new Gemini Legacy image, and penned a caption for it. What Gemini has captured is nothing short of poetry in motion: the colorful and dramatic tale of a life-and-death struggle between two galaxies interacting. All the action appears in a single frame, with the ...
Heavy rainfall returned to Typhoon Prapiroon for a brief time on Oct. 18 when NASA's TRMM satellite passed overhead. Prapiroon is battling strong wind shear and is expected to transition into an extra-tropical storm in the next day.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite captured rainfall data on Prapiroon twice on Oct. 18 when it passed overhead. The first orbit was at 0845UTC and the second at 1019 UTC. TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data show that rain associated with Prapiroon was falling at a rate of over 75mm/hour ...
Hurricane Rafael is no longer a tropical cyclone. The storm merged with a cold front on Oct. 18, but not before NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of the storm when it was in its last day as a hurricane.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Terra captured a visible image of Hurricane Rafael in the North Atlantic on Oct. 17 at 1440 UTC (10:40 a.m. EDT). Although Rafael was far from land, its northwestern fringe clouds were brushing Nova Scotia, Canada.
By 5 p.m. EDT on Oct. 17, Rafael had become extra-tropical, meaning that ...
In a new perspective piece being published Online First tonight in Annals of Internal Medicine, a physician recalls lessons learned from treating patients affected by the 2002 outbreak of Exophiala (Wangiella) dermatitidis meningitis or arthritis related to contaminated, injectable coticosteroids prepared from a compounding pharmacy.
According to the author, the lessons he learned in 2002 are applicable to the current outbreak. He warns that compounding of preservative-free corticosteroids requires meticulous sterility to ensure lack of fungal contamination. Without ...
NEW ORLEANS – Ashley Thomas was born with spina bifida and uses a wheelchair. She also holds a position on the U.S. national para-kayak team, and founded and runs a successful nonprofit organization called "Bridge II Sports." The North Carolina-based organization develops programs that provide opportunities for children and adults with physical disabilities to play team and individual sports. Ms. Thomas will be speaking about her experiences at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition (NCE) in New Orleans at 11:15 a.m., Friday, Oct. 19 in ...
NEW ORLEANS – An abstract presented Friday, Oct. 19, at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference and Exhibition in New Orleans highlights the risky behavior of child pedestrians who are struck by cars – including darting into the street, crossing in the middle of the block, and crossing while using an electronic device.
For the abstract, "Risky Behaviors of Pediatric Pedestrians Who are Struck by Motor Vehicles," researchers collected data on all pedestrians who were injured by a motor vehicle and presented to a Level I trauma center in New York City ...
NEW ORLEANS – Collective violence attributed to organized crime and poverty are adversely affecting the mental health of children living near the Texas-Mexico border, according to a poster presented Oct. 19 at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference and Exhibition in New Orleans.
In the study, "Children's Mental Health and Collective Violence: A Bi-National Study on the United States/Mexican Border," researchers compared psychosocial and behavior scores among children and adolescents living in El Paso, Texas and Ciudad Juarez, Chihuahua, Mexico in ...