(Press-News.org) Although many people look forward to getting away on vacation or just putting their feet up at home, there are others who can get as anxious about taking time to relax as they would if they were delivering a national address. Christina Luberto, a doctoral student in the University of Cincinnati's Department of Psychology, has now developed a questionnaire, the Relaxation Sensitivity Index (RSI), to examine the phenomenon.
Preliminary findings on the RSI will be presented on Nov.17, at the 46th annual convention of the Association of Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies (ABCT) in National Harbor, Md.
"Relaxation-induced anxiety, or the paradoxical increase in anxiety as a result of relaxation, is a relatively common occurrence," explains Luberto.
"We wanted to develop a test to examine why certain individuals fear relaxation events or sensations associated with taking a time-out just to relax."
The RSI is a 21-item questionnaire that explores fears related to relaxation anxiety in three key categories:
Physical Issues – "It scares me when my breathing becomes deeper; I hate getting massages because of the feeling it creates when my muscles relax…"
Cognitive Issues – "I don't like to relax because I don't like it when my thoughts slow down; I don't like to relax because it makes me feel out of control…"
Social Issues – "I worry that when I let my body relax, I'll look unattractive; I worry that if I relax, other people will think I'm lazy…"
Participants rate how much each statement applies to them on a scale of 0 to 5. Three-hundred undergraduate college students participated in the study. They were, on average, 21 years old, female and Caucasian.
Luberto says that exploring the idea of relaxation sensitivity was based on a related concept of anxiety sensitivity, which is the fear of arousal. Early results from the RSI study found that people who are high in relaxation sensitivity are also high in anxiety sensitivity. "This suggests that for some people, any deviation from normal functioning, whether it is arousal or relaxation, is stressful," says Luberto. Results also suggested that the RSI is a valid and reliable measure of relaxation-related fears and is able to identify which individuals have experienced increased anxiety when relaxing in the past.
Luberto states that additional research needs to be conducted to examine the effectiveness of the RSI in more diverse populations (including beyond college age), as well as among individuals with psychiatric disorders.
Ultimately, the RSI could be used to identify patients who would not respond to being treated through relaxation therapies, which is a common component of treatment for anxiety disorders.
###
The study was supported by the UC Department of Psychology's Frakes Foundation Endowment Fund and William Seeman Psychology Fund.
The ABCT is a multidisciplinary organization committed to the advancement of scientific approaches to the understanding and improvement of human functioning through the investigation and application of behavioral, cognitive and other evidence-based principles to the assessment, prevention, treatment of human problems and enhancement of health and well-being.
The UC Department of Psychology is recognized nationally for the quality of its undergraduate major and the excellence of its graduate training programs in clinical and experimental psychology.
University of Cincinnati research examines why some people are afraid to relax
2012-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Driving drones can be a drag
2012-11-14
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- On its surface, operating a military drone looks a lot like playing a video game: Operators sit at workstations, manipulating joysticks to remotely adjust a drone's pitch and elevation, while grainy images from the vehicle's camera project onto a computer screen. An operator can issue a command to fire if an image reveals a hostile target, but such adrenaline-charged moments are few and far between.
Instead, a drone operator — often a seasoned fighter pilot — spends most of his shift watching and waiting, as automated systems keep the vehicle running. ...
Queen's research gives fresh hope to couples with 'unexplained infertility'
2012-11-14
New research from Queen's University Belfast has uncovered the cause of infertility for 80 per cent of couples previously diagnosed with 'unexplained infertility'.
At present some 50,000 couples require fertility treatment across the UK each year, with the figure reaching one million worldwide. Up to one third of these couples are diagnosed with unexplained or idiopathic infertility. This means that, using current tests, neither partner has been diagnosed with any detectable problem.
Published in Reproductive Biomedicine Online, and carried out by Professor Sheena Lewis ...
Cancer therapy -- Nanokey opens tumors to attack
2012-11-14
There are plenty of effective anticancer agents around. The problem is that, very often, they cannot gain access to all the cells in solid tumors. A new gene delivery vehicle may provide a way of making tracks to the heart of the target.
Many types of tumor form a compact mass, like the phalanx formation of Greek antiquity. And although many drugs are known to be toxic to cancer cells, they are often unable to percolate into the inner recesses of the tumor. Upon intravenous administration, for instance, cytotoxic drugs may only be able to penetrate the outermost layers ...
Changing climate, not tourism, seems to be driving decline in chinstrap-penguin populations
2012-11-14
The breeding population of chinstrap penguins has declined significantly as temperatures have rapidly warmed on the Antarctic Peninsula, according to researchers funded in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF).
The study indicates that changing climatic conditions, rather than the impact of tourism, have had the greatest effect on the chinstrap population.
Ron Naveen, founder of a nonprofit science and conservation organization, Oceanites, Inc., of Chevy Chase, Md., documented the decline in a paper published in the journal Polar Biology. Naveen and coauthor ...
Preserving van Gogh's priceless masterpieces
2012-11-14
The chrome yellow pigment that renowned post-Impressionist artist Vincent van Gogh favored in priceless masterpieces like Sunflowers, the Yellow House and Wheatfield with Crows is especially sensitive to certain types of light and should be protected to prevent darkening. That's the conclusion of a series of studies in ACS' journal Analytical Chemistry, which could help preserve masterpieces by van Gogh and contemporaries like Gauguin, Cézanne and others.
Koen Janssens and colleagues explain that the chrome yellow pigment used by van Gogh and others in the 19th and 20th ...
Boosting the sensitivity of airport security screening
2012-11-14
Scientists are reporting a simple way to improve the sensitivity of the test often used to detect traces of explosives on the hands, carry-ons and other possessions of passengers at airport security screening stations. Their report appears in ACS' The Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
Yehuda Zeiri and colleagues explain that most tests for traces of explosives begin by rubbing a swab made from glass fiber, Teflon or cotton over the suspect material. Analysis of the swab in a detector — usually a device called an ion mobility spectrometer — alerts agents to any explosive ...
Ingredient in diarrhea medicine leads to sustainable new farm fertilizer
2012-11-14
The search for a sustainable slow-release fertilizer — a key to sustaining global food production at a time of burgeoning population growth — has led scientists to an ingredient used in some diarrhea medicines. They describe use of the substance, attapulgite, as a "carrier" for plant nutrients in a report in ACS' journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
Boli Ni and colleagues explain that about half of the 150 million tons of fertilizer used worldwide every year goes to waste. That's because most fertilizers release nutrients too fast for the crops to use. ...
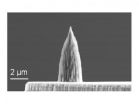
Nanometer-scale diamond tips improve nano-manufacturing
2012-11-14
One of the most promising innovations of nanotechnology has been the ability to perform rapid nanofabrication using nanometer-scale tips. The fabrication speed can be dramatically increased by using heat. High speed and high temperature have been known to degrade the tip… until now.
"Thermal processing is widely used in manufacturing," according to William King, the College of Engineering Bliss Professor at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "We have been working to shrink thermal processing to the nanometer scale, where we can use a nanometer-scale heat ...
Life and death in a star-forming cloud
2012-11-14
The aftershock of a stellar explosion rippling through space is captured in this new view of supernova remnant W44, which combines far-infrared and X-ray data from ESA's Herschel and XMM-Newton space observatories.
W44, located around 10 000 light-years away within a forest of dense star-forming clouds in the constellation of Aquila, the Eagle, is one of the best examples of a supernova remnant interacting with its parent molecular cloud.
The product of a massive star that has already reached the end of its life and expelled its outer layers in a dramatic explosion, ...
You can be a star -- on science's stage
2012-11-14
The rapid growth in "citizen science" projects during the past decade is enabling more and more science enthusiasts, hobbyists, students and other ordinary people to participate in the excitement of real-world scientific research and help solve serious scientific mysteries. That's the topic of the cover story in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society.
Deirdre Lockwood, C&EN contributing editor, traces the growth of citizen science from the Audubon Christmas Bird Count of 1900 ...