(Press-News.org) ESA's Planck space telescope has made the first conclusive detection of a bridge of hot gas connecting a pair of galaxy clusters across 10 million light-years of intergalactic space.
Planck's primary task is to capture the most ancient light of the cosmos, the Cosmic Microwave Background, or CMB. As this faint light traverses the Universe, it encounters different types of structure including galaxies and galaxy clusters – assemblies of hundreds to thousands of galaxies bound together by gravity.
If the CMB light interacts with the hot gas permeating these huge cosmic structures, its energy distribution is modified in a characteristic way, a phenomenon known as the Sunyaev–Zel'dovich (SZ) effect, after the scientists who discovered it.
This effect has already been used by Planck to detect galaxy clusters themselves, but it also provides a way to detect faint filaments of gas that might connect one cluster to another.
In the early Universe, filaments of gaseous matter pervaded the cosmos in a giant web, with clusters eventually forming in the densest nodes.
Much of this tenuous, filamentary gas remains undetected, but astronomers expect that it could most likely be found between interacting galaxy clusters, where the filaments are compressed and heated up, making them easier to spot.
Planck's discovery of a bridge of hot gas connecting the clusters Abell 399 and Abell 401, each containing hundreds of galaxies, represents one such opportunity.
The presence of hot gas between the billion-light-year-distant clusters was first hinted at in X-ray data from ESA's XMM-Newton, and the new Planck data confirm the observation.
It also marks Planck's first detection of inter-cluster gas using the SZ effect technique.
By combining the Planck data with archival X-ray observations from the German satellite Rosat, the temperature of the gas in the bridge is found to be similar to the temperature of the gas in the two clusters – on the order of 80 million degrees Celsius.
Early analysis suggests the gas could be mixture of the elusive filaments of the cosmic web mixed with gas originating from the clusters.
A more detailed analysis and the possible detection of gas bridges connecting other clusters will help to provide a more conclusive answer.
The new finding highlights the ability of Planck to probe galaxy clusters to their outskirts and beyond, examining their connection with the gas that permeates the entire Universe and from which all groups of galaxies formed.
INFORMATION:
Planck spots hot gas bridging galaxy cluster pair
2012-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Music to the ears for a good night's sleep?
2012-11-20
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Nov. 20, 2012 – If you are among the 50 percent of Americans who suffer from insomnia, then you have probably tried everything – from warm milk to melatonin pills or prescription medications to induce sleep – with varying degrees of success and side effects. But what if sleep could be achieved not by a substance, but through 'balancing' brain activity?
Researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center have conducted a pilot clinical study to determine whether a non-invasive approach, that uses musical tones to balance brain activity, can 'reset' ...
Maple syrup, moose, and the local impacts of climate change
2012-11-20
Millbrook, N.Y. -- In the northern hardwood forest, climate change is poised to reduce the viability of the maple syrup industry, spread wildlife diseases and tree pests, and change timber resources. And, according to a new BioScience paper just released by twenty-one scientists, without long-term studies at the local scale—we will be ill-prepared to predict and manage these effects.
Following an exhaustive review of more than fifty years of long term data on environmental conditions at the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest, located in the White Mountains of New Hampshire, ...
Timely change for tweeters' tune
2012-11-20
Do birds change their tune in response to urban noise? It depends on the bird species, according to Dr. Alejandro Ariel Ríos-Chelén from the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México and colleagues. Their work shows that while some birds do adapt their songs in noisy conditions by means of frequency changes, others like the vermilion flycatchers adapt their song by means of changes in song lengths. The work is published online in Springer's journal, Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
Birds use their songs during social interactions to attract females and repel intruders. ...
Huddersfield professor's ground-breaking research shows just how well the 2012 Games were run
2012-11-20
UNIQUE research conducted by a University of Huddersfield professor confirms just how successfully the 2012 Olympics and Paralympics were designed, organised and delivered. His findings will reveal to planners of the 2016 Games in Brazil just what they must do to meet or exceed the standards set by London.
Professor David Bamford, an expert in the theory of operations management and how it can be applied to the sports arena, was granted full access to the Paralympics village in London and with his team of researchers he quizzed hundreds of athletes, seeking their views ...
Robotic fish research swims into new ethorobotics waters
2012-11-20
NEW YORK, November 20, 2012 – Researchers at the Polytechnic Institute of New York University (NYU-Poly) have published findings that further illuminate the emerging field of ethorobotics — the study of bioinspired robots interacting with live animal counterparts.
Maurizio Porfiri, associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NYU-Poly, doctoral candidates Vladislav Kopman and Jeffrey Laut and research scholar Giovanni Polverino studied the role of real-time feedback in attracting or repelling live zebrafish in the presence of a robotic fish.
Their ...
Proposals to record the age of youngsters when buying mobile phones
2012-11-20
Mobile telephone operators should verify the age of children and youngsters when they access multimedia services by having a record of users' dates of birth. This is one of the recommendations in a report by researchers from the Polytechnic University of Valencia (Spain), that also suggest content classifications for mobiles by age, like in the case of video games.
"Verification of age upon access to mobile phone services is not effective because the child can also falsify their age by checking a different box," as explained to SINC by María de Miguel Molina, lecturer ...
Wolters Kluwer Health and International Association of Forensic Nurses partner to publish the Journal of Forensic Nursing
2012-11-20
New York, NY -- (November 20, 2012) – Wolters Kluwer Health and the International Association of Forensic Nurses (IAFN) are pleased to announce an agreement to publish Journal of Forensic Nursing, the official journal of IAFN. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW), part of Wolters Kluwer Health, will become the publisher for Journal of Forensic Nursing, beginning with the first Quarter 2013 issue.
The only journal dedicated exclusively to this emerging nursing specialty, the Journal of Forensic Nursing will continue on its quarterly publication schedule. In addition to ...
Researchers improve technology to detect hazardous chemicals
2012-11-20
Scientists at Imperial College London have developed a system to quickly detect trace amounts of chemicals like pollutants, explosives or illegal drugs.
The new system can pick out a single target molecule from 10 000 trillion water molecules within milliseconds, by trapping it on a self-assembling single layer of gold nanoparticles.
The team of scientists, all from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, say this technology opens the way to develop devices that are compact, reusable and easy to assemble, and could have a range of uses including detecting illegal drugs, ...
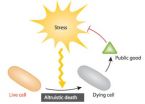
Engineered bacteria can make the ultimate sacrifice
2012-11-20
HEIDELBERG, 20 November 2012 – Scientists have engineered bacteria that are capable of sacrificing themselves for the good of the bacterial population. These altruistically inclined bacteria, which are described online in the journal Molecular Systems Biology, can be used to demonstrate the conditions where programmed cell death becomes a distinct advantage for the survival of the bacterial population.
"We have used a synthetic biology approach to explicitly measure and test the adaptive advantage of programmed bacterial cell death in Escherichia coli," said Lingchong ...
Impulsivity in first grade predicts problem gambling in late teen years for urban boys
2012-11-20
November 20, 2012 -- Results of a new study by researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health indicate that a developmental pattern of impulsiveness in young males is linked with gambling problems in late adolescence. Respondents considered to be in the high impulsivity track as early as first grade doubled the odds of meeting criteria for at-risk/problem gambling, and tripled the odds of meeting criteria for problem gambling. The study is the first to link a developmental pattern of impulsivity -- defined as a tendency to make rush decisions without ...