(Press-News.org) UNIQUE research conducted by a University of Huddersfield professor confirms just how successfully the 2012 Olympics and Paralympics were designed, organised and delivered. His findings will reveal to planners of the 2016 Games in Brazil just what they must do to meet or exceed the standards set by London.
Professor David Bamford, an expert in the theory of operations management and how it can be applied to the sports arena, was granted full access to the Paralympics village in London and with his team of researchers he quizzed hundreds of athletes, seeking their views on the organisation, facilities and other aspects of the Games.
This was the largest survey that had been carried for a Paralympic Games and the responses were highly positive.
"From a service quality perspective, they were exceptionally high," said Prof Bamford. "This speaks well for the attention to detail and the design of the facilities provided at London 2012. Now the opportunity and the challenge for Brazil is how they are going to replicate this. The bar is very high indeed."
A special questionnaire was devised and a total of 250 Paralympians took part, either in face-to-face interviews or by responding online. The blend of nationalities, athletic disciplines and disabilities ensured that the findings were statistically valid.
The questions covered topics such as transport, catering, competition venues, staff, ceremonies and anti-doping procedures. Respondents attached most importance to the facilities at the Paralympics village.
Questions used the Likert scale - ranging from "dissatisfied" to "very satisfied" – and 70 per cent of the responses were in the "very satisfied" range, said Professor Bamford.
"That went right across the board from the Paralympics village throughto the delivery of anti-doping services. It was an extremely positive set of feedback. And the volunteers and staff were by far the best rated of all the services. In terms of their performance, they were absolutely outstanding," he added.
International Paralympics Committee
The research project was initiated by the International Paralympics Committee (IPC) in tandem with the Manchester-based World Academy of Sport, which undertakes the education delivery of knowledge management for the IPC which included the IPC Observers Programme for future Paralympic Games organisers.
An IPC Academy Campus was instituted throughout the Games and Professor Bamford was appointed its Research Fellow. He then recruited five interns in conjunction with the IPC and WAoS to assist with the research. The team was granted complete access to the Paralympic village and competition venues while the games were in progress.
The aim of the project was to establish a benchmark for the provision of services at the Paralympics particularly in relation to infrastructure requirements and operational delivery, said Professor Bamford. His preliminary report will form part of the discussions at the official IPC Debrief on London 2012 in Rio during late November. His full report will then be available for Games organisers when they meet again in the spring of 2013, this time to look ahead to 2016 and adopt key recommendations into their planning for the next edition of the Paralympic Games.
INFORMATION:
Further outputs from the Athletes Client Experience Survey - as it was named – will include academic papers, and case studies will be used for teaching purposes at the University of Huddersfield's Business School, where David Bamford is Professor of Operations Management.
Huddersfield professor's ground-breaking research shows just how well the 2012 Games were run
2012-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robotic fish research swims into new ethorobotics waters
2012-11-20
NEW YORK, November 20, 2012 – Researchers at the Polytechnic Institute of New York University (NYU-Poly) have published findings that further illuminate the emerging field of ethorobotics — the study of bioinspired robots interacting with live animal counterparts.
Maurizio Porfiri, associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NYU-Poly, doctoral candidates Vladislav Kopman and Jeffrey Laut and research scholar Giovanni Polverino studied the role of real-time feedback in attracting or repelling live zebrafish in the presence of a robotic fish.
Their ...
Proposals to record the age of youngsters when buying mobile phones
2012-11-20
Mobile telephone operators should verify the age of children and youngsters when they access multimedia services by having a record of users' dates of birth. This is one of the recommendations in a report by researchers from the Polytechnic University of Valencia (Spain), that also suggest content classifications for mobiles by age, like in the case of video games.
"Verification of age upon access to mobile phone services is not effective because the child can also falsify their age by checking a different box," as explained to SINC by María de Miguel Molina, lecturer ...
Wolters Kluwer Health and International Association of Forensic Nurses partner to publish the Journal of Forensic Nursing
2012-11-20
New York, NY -- (November 20, 2012) – Wolters Kluwer Health and the International Association of Forensic Nurses (IAFN) are pleased to announce an agreement to publish Journal of Forensic Nursing, the official journal of IAFN. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW), part of Wolters Kluwer Health, will become the publisher for Journal of Forensic Nursing, beginning with the first Quarter 2013 issue.
The only journal dedicated exclusively to this emerging nursing specialty, the Journal of Forensic Nursing will continue on its quarterly publication schedule. In addition to ...
Researchers improve technology to detect hazardous chemicals
2012-11-20
Scientists at Imperial College London have developed a system to quickly detect trace amounts of chemicals like pollutants, explosives or illegal drugs.
The new system can pick out a single target molecule from 10 000 trillion water molecules within milliseconds, by trapping it on a self-assembling single layer of gold nanoparticles.
The team of scientists, all from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, say this technology opens the way to develop devices that are compact, reusable and easy to assemble, and could have a range of uses including detecting illegal drugs, ...
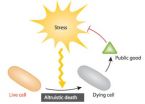
Engineered bacteria can make the ultimate sacrifice
2012-11-20
HEIDELBERG, 20 November 2012 – Scientists have engineered bacteria that are capable of sacrificing themselves for the good of the bacterial population. These altruistically inclined bacteria, which are described online in the journal Molecular Systems Biology, can be used to demonstrate the conditions where programmed cell death becomes a distinct advantage for the survival of the bacterial population.
"We have used a synthetic biology approach to explicitly measure and test the adaptive advantage of programmed bacterial cell death in Escherichia coli," said Lingchong ...
Impulsivity in first grade predicts problem gambling in late teen years for urban boys
2012-11-20
November 20, 2012 -- Results of a new study by researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health indicate that a developmental pattern of impulsiveness in young males is linked with gambling problems in late adolescence. Respondents considered to be in the high impulsivity track as early as first grade doubled the odds of meeting criteria for at-risk/problem gambling, and tripled the odds of meeting criteria for problem gambling. The study is the first to link a developmental pattern of impulsivity -- defined as a tendency to make rush decisions without ...
More than a machine
2012-11-20
Viruses can be elusive quarry. RNA viruses are particularly adept at defeating antiviral drugs because they are so inaccurate in making copies of themselves. With at least one error in every genome they copy, viral genomes are moving targets for antiviral drugs, creating resistant mutants as they multiply. In the best-known example of success against retroviruses, it takes multiple-drug cocktails to corner HIV and narrow its escape route.
Rather than target RNA viruses themselves, aiming at the host cells they invade could hold promise, but any such strategy would have ...
Call to establish 'Centers of Excellence' for pituitary diseases
2012-11-20
Philadelphia, Pa. (November 20, 2012) – The time has come to develop a pituitary "centers of excellence" (CoE) designation for hospitals with high-level surgical skills and other capabilities needed to provide state-of-the-art care for patients with pituitary tumors, according to an article in the November issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Recent advances in surgical and medical management—along with the high prevalence and impact ...
Why do meningiomas grow during pregnancy?
2012-11-20
Philadelphia, Pa. (November 16. 2012) – Meningiomas are a common type of benign brain tumor that sometimes grows dramatically in pregnant women. A new study suggests that this sudden tumor growth likely results from "hemodynamic changes" associated with pregnancy, reports the November issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The study also identifies some key characteristics associated with rapid growth of meningiomas in pregnant women. ...
Embattled childhoods may be the real trauma for soldiers with PTSD
2012-11-20
New research on posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in soldiers challenges popular assumptions about the origins and trajectory of PTSD, providing evidence that traumatic experiences in childhood - not combat - may predict which soldiers develop the disorder.
Psychological scientist Dorthe Berntsen of Aarhus University in Denmark and a team of Danish and American researchers wanted to understand why some soldiers develop PTSD but others don't. They also wanted to develop a clearer understanding of how the symptoms of the disorder progress.
"Most studies on PTSD in ...