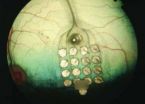
(Press-News.org) NORFOLK, VA -- Surgeons at Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters (CHKD) have fitted a patient with a device that might eliminate the need for surgery in some patients with one of the world's most common chest deformities, pectus excavatum, often called sunken chest syndrome.
Known as the vacuum bell, it works much like devices in body shops that use sustained vacuum to pop out a dent.
"Years from now, we may look at the surgeries and realize that many of these conditions could have been corrected with vacuum devices," said Dr. Robert J. Obermeyer, who is leading the project at CHKD, the nation's top research center for chest-wall deformities and a training site for surgeons from around the world.
Pectus excavatum is the most common congenital deformity of the chest wall. Caused by an overgrowth of cartilage in the ribs and sternum, its defining feature is a depression, or indentation, in the middle of the chest.
Until the 1980s, the only correction was a radical surgery that involved removing cartilage and ribs. In the late 1980s, Dr. Donald Nuss, a CHKD pediatric surgeon, developed a minimally invasive technique that involved placing a concave bar into the chest then flipping it over so that it pushes the depression of the chest upward. The Nuss Procedure has since become the surgical gold standard.
Today, CHKD performs more pectus excavatum surgeries than any facility in the United States and remains a major training site for surgeons and a center for research on chest wall deformities.
But even the minimally invasive surgery results in an average hospital stay of five days. Pectus specialists have been exploring less invasive techniques; research is being conducted in San Francisco on implanting magnets in the chest wall that are attracted to a chest brace.
The vacuum bell procedure marks the first use by pectus specialists of a non-surgical device. "CHKD has always made efforts to minimize surgical intervention and I believe this could eliminate the need for surgery in some pectus excavatum patients," said Dr. Obermeyer, who has been instrumental in bringing the technology to the U.S.
The vacuum bell device looks something like a large, silicone doughnut, with a bulb attached to remove air pressure. It must be fitted to each patient and fit snugly on the chest. The bulb is used to create a vacuum inside the device.
The vacuum bell must be used about an hour a day and slowly pulls up the depressed area of cartilage. After three to six months of use, the depression in the chest reaches close to the maximum correction. The patient must continue to use the vacuum bell for about two years to make the correction permanent, similar to wearing a retainer after one's teeth are straightened.
In Europe, the concept of a vacuum device to correct sunken chest syndrome has been discussed for decades, but technology lagged behind. German engineer Eckart Klobe, who suffered pectus excavatum, developed hundreds of prototypes before developing a device that worked reliably.
The vacuum bell has been used in Europe for several years, and research suggests that the correction might be permanent. Dr. Obermeyer visited pectus specialists in Switzerland who used the vacuum bell, met with Klobe, toured the production facility where the devices are manufactured and helped expedite its categorization by the Food and Drug Administration as a class 1 medical device, which allows for sale and use in the United States.
While the vacuum bell is non-surgical, it should be used under the supervision of a pectus excavatum specialist because underlying cardiac conditions can make the device dangerous, Dr. Obermeyer cautioned.
CHKD this week performed the first two procedures by pectus experts in the United States and will monitor their progress as well as the long-term effectiveness of the innovative non-surgical procedure.
INFORMATION: END
Immune globulin replacement began decades ago as a treatment for patients who could not make their own protective antibodies, but has proven to have much broader benefits than originally expected. With new uses regularly being discovered for this limited and expensive resource, including as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease, now is the time to discover exactly how intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) treatments work, and to engineer a protein that can provide similar benefits, writes Erwin Gelfand, MD, chair of pediatrics at National Jewish Health in the November ...
A hungry mantis shrimp may be the last thing that a passing fish sees before it is snatched from the water by the predator. Maya deVries from the University of California, Berkeley, says 'Spearer mantis shrimps stay in their sandy burrows and they wait for a fast-moving prey item to come by, but then they come out of nowhere and grab the prey with their long skinny appendages.' However, little was know about how these vicious predators unleash their lightning-fast attacks. According to deVries, the spearing shrimp are closely related to smasher mantis shrimps, which pulverise ...
VIDEO:
In this video, a patient reads words with the Argus II setup using the camera and not the direct braille stimulation.
Click here for more information.
For the very first time researchers have streamed braille patterns directly into a blind patient's retina, allowing him to read four-letter words accurately and quickly with an ocular neuroprosthetic device. The device, the Argus II, has been implanted in over 50 patients, many of who can now see color, movement and ...
Discount Buses Bring Increased Risk of Death and Injury to Passengers
The ramifications from a Megabus crash in Chicago, Illinois in August that killed one person and injured 47 people continue. Illinois State Police suspect the crash was the result of a tire blowout and not necessarily driver error. The parents of the single fatality from the accident, a graduate student killed in the crash, recently brought a wrongful death suit against Megabus, Coach Leasing and the driver of the bus for improper maintenance and a failure to inspect the bus and its tires. The suit ...
Crackdown on Synthetic Drugs in Missouri
Synthetic drugs present a problem to government regulation and can often have very adverse effects on the human body. Because of the dangers, law enforcement officers and lawmakers are working to get the products out of head shops. To regulate the problem, several areas, including Missouri, are working on crackdowns with hopes to get the products off of the market once and for all.
Synthetic Drugs
Synthetic drugs are basically substances that contain chemicals very similar to those in traditional illegal drugs. The synthetic ...
Planning for a divorce after the holidays
The stress of the holiday season, along with the chance for a fresh start at the beginning of the year, makes January a popular time to divorce. Often married couples will put family ahead of personal needs until after the holiday season is over. However, if divorce is in the future, preparing for divorce can begin before the actual filing takes place in January. Planning ahead can make the process easier on everyone and protect your financial assets for the new year. While the steps below are good practice for any time of the ...
The toll of bicycle accidents
The Texas Department of Transportation and a nonprofit organization stepped up efforts to educate motorists and bicyclists in the wake of a tragic accident near Amarillo. Two bicyclists riding on a popular bicycling road were killed when a motorist struck them from behind. The driver claimed he was blinded by sunlight.
Share the Road! is a nonprofit that was created in 2010 for raising safety awareness for pedestrians. A spokesman for the organization stated that any driver on the frontage road where the accident occurred ought to be ...
Measure 11 and Oregon's Violent Crime Rate
We've all heard the saying, "If you can't do the time, don't commit the crime." It captures the sentiment that the tougher the sentence the stronger the disincentive to commit crime. While it may be easy to believe that a relationship exists between crime rates and incarceration, many criminal defense attorneys and others in the criminal justice world question the connection.
In the 1980s and mid-1990s the number of violent crimes committed in Oregon dramatically increased. Believing that a lack of deterrents created ...
New York acts to take repeat DWI offenders off the road
New York is getting tougher on drunk drivers. Under a new administrative policy announced in September 2012, the New York Department of Motor Vehicles will not issue or renew a driver's license for a person who has incurred five or more DWI convictions throughout a lifetime.
Stricter rules will apply to license reinstatement
The policy also denies a driver's license to anyone with three or more DWI convictions over a 25-year period plus another serious motor vehicle offense. When a driver with three or more ...
Reducing car accidents: Legal restrictions for safer teen driving
In August 2008 months of work by Connecticut's Teen Driving Task Force culminated when a new teen driving law took effect.
Over four years later, Connecticut has come out near the top in two national studies on teen driving safety. The AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety and the Governors Highway Safety Association found an alarming 11 percent increase nationwide in traffic deaths involving 16- and 17-year-old drivers. However, teen driver deaths in Connecticut have gone down by 91 percent over the past ...