(Press-News.org) An international team of biologists led by Indiana University's David M. Kehoe has identified both the enzyme and molecular mechanism critical for controlling a chameleon-like process that allows one of the world's most abundant ocean phytoplankton, once known as blue-green algae, to maximize light harvesting for photosynthesis.
Responsible for contributing about 20 percent of the total oxygen production on the planet, the cyanobacteria Synechococcus uses its own unique form of a sophisticated response called chromatic acclimation to fine tune the absorption properties of its photosynthetic antenna complexes to the predominant ambient light color. The researchers identified and characterized an enzyme, MpeZ, that plays a pivotal role in the mechanism that allows two different water-soluble proteins in Synechococcus -- phycoerythrin I and II -- to alter their pigmentation in order to maximize photon capture for photosynthesis.
Scientists want to understand how cyanobacteria optimize their photosynthetic activities in different light conditions to gain a better appreciation of how human activities affect the phytoplankton's ability to produce oxygen and uptake the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide, which they consume in order to grow. Science and industry also use the pigment-protein complex phycoerythrin for fluorescent imaging and as fluorescent markers in biotechnology and health care applications.
"We now have the ability to attach a novel chromophore, part of a molecule responsible for its color, to phycoerythrin, which provides a new chromophore-protein combination that absorbs and fluoresces at a wavelength that is not currently commercially available," said Kehoe, a professor in the IU Bloomington College of Arts and Sciences' Department of Biology. "Our results suggest that this new chromoprotein is brighter and more stable than most on the market today."
Kehoe also noted IU has begun the process of filing a patent on the invention.
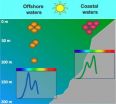
The team found that the gene encoding the MpeZ enzyme is activated in blue light. Once produced, MpeZ then binds to antenna proteins containing pigments that normally catch green light and attaches an alternative chromophore that allows the antennae to capture blue light. The specific mechanism, called type IV chromatic acclimation, involves replacing three molecules of the green light-absorbing chromophore with an equal number of blue light-absorbing chromophore.
This color-shifting is reversible and is controlled by the ratio of blue to green light in the environment.
"These 'chromatic adapters' are true chameleons that can efficiently live in green coastal waters as well as in blue offshore waters by modifying their pigmentation," Kehoe said. "Synechococcus cells maintained in blue light harvest preferentially blue light, while cells grown in green light harvest more green."
"A phycoerythrin-specific bilin lyase-isomerase controls blue-green chromatic acclimation in marine Synechococcus" was published online in the Early Edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Co-authors with Kehoe, also affiliated with IU Bloomington's Indiana Molecular Biology Institute, were IU Ph.D. student Animesh Shukla; Avijit Biswas and Wendy M. Schluchter of the University of New Orleans; Nicolas Blot of Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris 06, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and Clermont Université in France; Frederic Partensky and Laurence Garczarek of Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris 06 and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique; IU Bloomington Department of Chemistry METACyt Biochemical Analysis Center mass spectrometry facility manager and assistant scientist Jonathan A. Karty and assistant scientist Loubna A. Hammad; and former IU biology graduate student Andrian Gutu, now of Harvard University.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this work came from the Agence Nationale Recherches in France, the European program MicroB3, IU's Office of International Programs, the National Science Foundation and the Lilly Foundation.
IU-led team uncovers process for chameleon-like changes in world's most abundant phytoplankton
IU seeks patent for discovery with implications for health care, climate change research
2012-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly insured patients may have trouble finding primary care physicians
2012-11-27
Implementation of the Affordable Care Act – now assured by the re-election of President Obama – is expected to result in up to 50 million currently uninsured Americans acquiring some type of health insurance coverage. But a study by researchers at the Mongan Institute for Health Policy at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) finds that a significant percentage of the primary care physicians most likely to care for newly insured patients may be not be accepting new patients. The investigators note that strategies designed to increase and support these "safety-net" physicians ...
UIC scientists find ancient microbes in salty, ice-sealed Antarctic lake
2012-11-27
Shedding light on the limits of life in extreme environments, scientists have discovered abundant and diverse metabolically active bacteria in the brine of an Antarctic lake sealed under more than 65 feet of ice.
The finding, described in this week's issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is surprising because previous studies indicate that the brine has been isolated from the surface environment -- and external sources of energy -- for at least 2,800 years, according to two of the report's authors, Peter Doran and Fabien Kenig, both professors ...
Cassini finds a video gamers' paradise at Saturn
2012-11-27
You could call this "Pac-Man, the Sequel." Scientists with NASA's Cassini mission have spotted a second feature shaped like the 1980s video game icon in the Saturn system, this time on the moon Tethys. (The first was found on Mimas in 2010). The pattern appears in thermal data obtained by Cassini's composite infrared spectrometer, with warmer areas making up the Pac-Man shape.
"Finding a second Pac-Man in the Saturn system tells us that the processes creating these Pac-Men are more widespread than previously thought," said Carly Howett, the lead author of a paper recently ...
NASA spots heavy rainfall in Tropical Depression 26W threatening Micronesia
2012-11-27
The twenty-sixth tropical cyclone of the western North Pacific Ocean season formed and has some areas of heavy rain, according to data from NASA's TRMM satellite. Tropical Depression 26W is threatening islands within Micronesia and warnings and watches are currently in effect.
Micronesia is a region in the western North Pacific Ocean made up of thousands of small islands. West of the region is the Philippines, while Indonesia is located to the southwest.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Tropical Depression 26W on Nov. 26 at 0526 ...
Scatter radiation from mammography presents no cancer risk
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – The radiation dose to areas of the body near the breast during mammography is negligible, or very low, and does not result in an increased risk of cancer, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The results suggest that the use of thyroid shields during mammography is unnecessary.
"Thyroid shields can impede good mammographic quality and, therefore, are not recommended during mammography," said Alison L. Chetlen, D.O., assistant professor of radiology at Penn State Hershey Medical Center.
During ...
Radiologic and physical findings identify elder abuse
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Radiologists in Toronto have begun to identify a pattern of injuries that may be indicative of elder abuse, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
According to lead researcher Kieran J. Murphy, M.D., F.R.C.P.C., F.S.I.R., interim radiologist-in-chief at University Health Network in Toronto, Canada, only 2 percent of physical elder abuse is reported by clinicians.
"Unlike cases of child abuse, there is very little information available on this subject," Dr. Murphy said. "It's a much ...
Breast cancer risk estimates increased with repeated prior ct and nuclear imaging
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Researchers reviewing the records of approximately 250,000 women enrolled in an integrated healthcare delivery system found that increased CT utilization between 2000 and 2010 could result in an increase in the risk of breast cancer for certain women, including younger patients and those who received repeat exams. According to the study, which was presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), nuclear medicine examinations may also contribute to increased breast cancer risk.
CT uses ionizing radiation in the form ...
Women with dense breasts welcome additional screening
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – A survey of women undergoing routine screening mammography found that many of them would be interested in pursuing additional screening tests if notified they had dense breast tissue, despite the possibility of false positives, invasive procedures, and out-of-pocket costs, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"Our study highlights the need for patient education regarding breast density," said Jafi Lipson, M.D., assistant professor of radiology at Stanford University School of Medicine ...
New studies show effects of mammography guideline changes
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Researchers assessing the impact of revised guidelines for screening mammography issued by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found evidence that the new recommendations may lead to missed cancers and a decline in screening, according to two studies presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Routine screening mammography has traditionally been recommended by both the USPSTF and the American Cancer Society for all women over the age of 40. In 2009, the USPSTF issued controversial new guidelines recommending ...
Researchers identify physiological evidence of 'chemo brain'
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Chemotherapy can induce changes in the brain that may affect concentration and memory, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Using positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography (PET/CT), researchers were able to detect physiological evidence of chemo brain, a common side effect in patients undergoing chemotherapy for cancer treatment.
"The chemo brain phenomenon is described as 'mental fog' and 'loss of coping skills' by patients who receive chemotherapy," said Rachel ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] IU-led team uncovers process for chameleon-like changes in world's most abundant phytoplanktonIU seeks patent for discovery with implications for health care, climate change research