Using data collected by NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft, a team from UCLA crafted the first accurate thermal model of the solar system's innermost planet, successfully pinpointing the extremely cold regions where ice has been found on or below the surface.
The researchers say the newly discovered black deposits are a thin crust of residual organic material brought to the planet over the past several million years through impacts by water-rich asteroids and comets.
Understanding how water ice has been preserved on Mercury and where it came from may help scientists determine the conditions necessary for sustaining life on other planets.
This research, one of three MESSENGER papers published online today in the journal Science (and scheduled for upcoming print publication), sheds light on the long-standing issue of ice on Mercury. Several independent lines of evidence now reveal that the sun-scorched planet has extensive water ice deposits at its poles.
In the early 1990s, scientists were surprised to find that areas near Mercury's poles were unusually bright when observed with radar from Earth, a potential indication that ice might be present.
UCLA's David Paige, the lead author of one of the new Science papers and a self-described "professional ice finder," has studied the poles of planetary bodies in the solar system, from Mercury to Pluto.
"Mercury is the innermost planet in the solar system, and, arguably, it's among the least explored," said Paige, a professor of Earth and space sciences. "The surface of Mercury exhibits the most extreme range of temperatures of any body we know of in the solar system."
Within a single polar crater on Mercury, there are spots that reach the oven-like temperature of 500 degrees Fahrenheit within sight of areas cold enough to freeze and preserve water ice for billions of years. These "natural freezers" exist within the shadowed areas of polar-crater rims, which never experience direct sunlight due to the low angle of the sun at such high latitudes, Paige said.
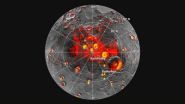
Paige's team was able to use the first detailed topographic map of Mercury's north polar region produced by MESSENGER to generate an accurate thermal model of the pole. Their calculations of the planet's sub-surface temperatures are a near-perfect match to Earth-based radar observations and surface-brightness measurements made by the Mercury Laser Altimeter (MLA) instrument onboard the orbiting spacecraft.
Where their temperature model predicts water ice should be stable on the surface, the MLA nearly always measures unusually bright patches, indicative of surface ice deposits. In places where it is too warm for surface ice but cold enough for ice to exist beneath the surface, the MLA sees unusually dark material.
"This stuff we find covering the ice is darker than the rest of Mercury, which is already a really dark planet. That's amazing," Paige said. "At the very least, it means there is something out of the ordinary going on inside these permanently shadowed areas where the ice has accumulated."
The mysterious dark substance likely arrived on Mercury as part of the comets and asteroids that periodically crash into the planet, bringing water ice and a diverse cocktail of organic material, Paige said. In the searing daytime heat of Mercury, the only place water and organics can survive is within permanently shadowed craters.
But only in the very coldest areas of the permanently shadowed regions can water ice exist on the surface. In the warmer shadowed areas, the top layers of ice begin to evaporate away into space, leaving behind a layer of hardy organic molecules that are stable at higher temperatures and which turn black over time when exposed at the surface. Once the dark layer is thick enough, it protects the ice underneath, allowing a sub-surface ice deposit to survive.
"There are areas on the surface where it is too hot for ice to exist, but radar data from Earth show something bright reflecting from these areas, so we're pretty sure that there's water ice buried underneath," said co-author Matthew Siegler, a researcher at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and a UCLA alumnus. "You need some kind of insulating layer to keep that heat from getting down to the ice."
The presence of bright ice and dark organics on Mercury's surface presents a mystery for MESSENGER researchers. Large comets and asteroids periodically impact Mercury, covering a huge swath of the planet in a layer of dirt and dust and adding further craters to the airless planet's already scarred landscape. For the water ice and black organic layers to remain exposed on Mercury's ancient surface, the deposits must have formed recently in the planet's geological history, or they must be maintained by new water brought to Mercury by smaller, more frequent impacts.
"Billions of years ago, the Earth acquired a layer of water and other volatile material that formed atmospheres, oceans and even the first organic molecules that started life," Paige said. "Understanding the origin of that material is a very important problem and is essential to finding out about the potential habitability of planetary systems around other stars."
Ellen Harju, a graduate student in the UCLA Department of Earth and Space Sciences, is a co-author of the paper.
Paige's study was published alongside two other MESSENGER papers, with colleagues David Lawrence and Greg Neumann as the lead authors. All three research discoveries were showcased today in a press conference on NASA TV.
Launched in 2004, MESSENGER became the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury in March of 2011. Previously, the closest glimpse of the planet was provided by three fly-bys by the Mariner 10 spacecraft in 1974-75. The name MESSENGER, short for MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry and Ranging, was chosen to evoke the Greco-Roman messenger deity Mercury, a god of trade, merchants and travel.
INFORMATION:
To learn more about this discovery, visit the website of the UCLA Institute for Planets and Exoplanets.
UCLA is California's largest university, with an enrollment of more than 40,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The UCLA College of Letters and Science and the university's 11 professional schools feature renowned faculty and offer 337 degree programs and majors. UCLA is a national and international leader in the breadth and quality of its academic, research, health care, cultural, continuing education and athletic programs. Six alumni and six faculty have been awarded the Nobel Prize.
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
END