Controversial treatment for autism may do more harm than good, Baylor University researchers find
2012-11-30
(Press-News.org) ABOUT BAYLOR SCHOOL OF EDUCATION
The Baylor School of Education is accredited by the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education and consists of four departments: Curriculum and Instruction (preparation for classroom teachers and specialists); Educational Administration (post-graduate preparation for school leadership); Educational Psychology (undergraduate and graduate programs for those who are interested in learning, development, measurement, and exceptionalities); and Health, Human Performance and Recreation (preparing for sport- and health-related careers, athletic training and careers in recreational professions, including churches).The School of Education enrolls more than 1,000 undergraduate students and 300 graduate students, employs 70 faculty, and is one of the few school s in the State of Texas that offers a yearlong teaching internship.
Note: Video of Dr. Tonya N. Davis is available at http://www.baylor.edu/mediacommunications/news.php?action=story&story=125490
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-11-30
(Phoenix, AZ Nov. 27, 2012) – Lung cancer researchers at St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center in Phoenix, Ariz., in collaboration with researchers at the Translational Genomics Research Institute and other institutions, have identified a gene that plays a role in the growth and spread of non-small cell lung cancer tumors, opening the door for potential new treatment options.
The study, titled "Elevated Expression of Fn14 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Correlates with Activated EGFR and Promotes Tumor Cell Migration and Invasion," was published in the May 2012 issue ...
2012-11-30
VIDEO:
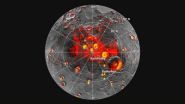
MESSENGER's Mercury Laser Altimeter sends out laser pulses that hit the ground and return to the instrument. The amount of light that returns for each pulse gives the reflectance at...
Click here for more information.
A Goddard-built instrument on NASA's MESSENGER mission provided one of three new lines of evidence that water ice exists near the north pole of Mercury. Most of the ice is covered by a thin layer of material that blankets and protects the ice, but in ...
2012-11-30
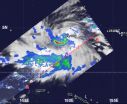
VIDEO:
On Nov. 27, 2012, NASA's TRMM satellite revealed that rain in Tropical Storm Bopha was falling at a rate of over 70mm/hour (about 1.75 inches) in the red areas. TRMM...
Click here for more information.
NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites captured images of Tropical Storm Bopha as it continues to move through Micronesia in the western North Pacific Ocean and trigger warnings and watches throughout.
From its orbit in space, NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission ...
2012-11-30
PHILADELPHIA—Treating Parkinson's disease patients with the experimental drug GM1 ganglioside improved symptoms and slowed their progression during a two and a half-year trial, Thomas Jefferson University researchers report in a new study published online November 28 in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Although the precise mechanisms of action of this drug are still unclear, the drug may protect patients' dopamine-producing neurons from dying and at least partially restore their function, thereby increasing levels of dopamine, the key neurochemical missing in ...
2012-11-30
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—November 27, 2012—Scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have defined for the first time a key underlying process implicated in multiple sclerosis (MS)—a disease that causes progressive and irreversible damage to nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. This discovery offers new hope for the millions who suffer from this debilitating disease for which there is no cure.
Researchers in the laboratory of Gladstone Investigator Katerina Akassoglou, PhD, have identified in animal models precisely how a protein that seeps from the blood into the brain sets ...
2012-11-30
VIDEO:
Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's...
Click here for more information.
Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a super massive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble Space Telescope's ...
2012-11-30
(PHILADELPHIA) – Cancer and stress go hand-in-hand, and high stress levels can lead to poorer health outcomes in cancer patients. The Jefferson-Myrna Brind Center of Integrative Medicine combined creative art therapy with a Mindfulness-based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program for women with breast cancer and showed changes in brain activity associated with lower stress and anxiety after the eight-week program. Their new study appears in the December issue of the journal Stress and Health.
Daniel Monti, MD, director of the Jefferson-Myrna Brind Center of Integrative Medicine ...
2012-11-30
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 30, 2012 – Turkey raises and releases thousands of non-native guineafowl to eat ticks that carry the deadly Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. Yet research suggests guineafowl eat few ticks, but carry the parasites on their feathers, possibly spreading the disease they were meant to stop, says a Turkish biologist working at the University of Utah.
"They are introducing a species that is not eating many ticks, based on studies of stomach content, and is carrying the ticks, which are the best conduit for spreading Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever," ...
2012-11-30
Cincinnati, OH, November 30, 2012 -- Rates of childhood obesity have tripled in the past 30 years, and food marketing has been implicated as one factor contributing to this trend. Every year, companies spend more than $10 billion in the US marketing their food and beverages to children; 98% of the food products advertised to children on television are high in fat, sugar, or sodium. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers used neuroimaging to study the effects of food logos on obese and healthy weight children.
Amanda S. Bruce, ...
2012-11-30
Charlottesville, VA (November 30, 2012). Researchers at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center in Lebanon, New Hampshire, have found an association in the United States between a higher density of neurologists and neurosurgeons and a decreased risk of death from stroke. The findings of their study are described in the article "Association of a higher density of specialist neuroscience providers with fewer deaths from stroke in the United States population. Clinical article," by Atman Desai, M.D., and colleagues, published today online, ahead of print, in the Journal of Neurosurgery. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Controversial treatment for autism may do more harm than good, Baylor University researchers find