(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. ¬— The weight gain commonly known as the "Freshman 15" is a negative aspect of the college experience for many college freshmen who are independent for the first time, most making lifestyle decisions about eating and exercise. Researchers say it's no surprise freshmen experience one of the largest weight gains in their lifetimes when they attend college. A new study from the University of Missouri has found that a brief intervention, sometimes as little as 30 minutes, can help put students back on the right track to a healthy lifestyle – a change that can impact the rest of their lives.
"What we found in our study was that getting personalized feedback about health issues is important," said Matt Martens, associate professor of counseling psychology in the College of Education. "It may not matter matter how long or short that intervention is; what seems to be important is getting the feedback. These simple interventions can be used at a doctor's office prior to an appointment, possibly while the individual is sitting in the waiting room. The idea behind these methods is to open the conversations, identifying the unhealthy lifestyle decisions and setting goals for the future."
Brief interventions can be delivered in many forms. In the current study, participants were asked to complete a 10-minute questionnaire. They were then given a feedback sheet based on their responses, which they discussed with a clinician for approximately 25 to 30 minutes. After one month, those who received the intervention reported engaging in significantly more exercise compared to those who did not receive the intervention.
While it could be difficult to do this during every doctor visit, Martens said that healthcare providers could alter these suggestions to fit their patients. If providers can begin to include these intervention strategies, they could see their patients making better decisions about their lifestyles, Martens said.
Current federal activity guidelines recommend that individuals participate in 75 minutes of vigorous, physical activity per week or 150 minutes of moderate activity per week. Marten said that, prior to the intervention, the study participants fell far short of those recommendations.
Another benefit of this intervention is the low cost that is associated with this type of strategy. Potentially not much time, if any, is needed between the patient and the healthcare provider, but it could save a lot of money in prevention costs.
"The whole point of all these studies on exercise, interventions and lifestyle decisions is to keep people from getting sick," Martens said. "In the end, it comes down to individuals making good lifestyle decisions, but sometimes it's important for healthcare providers to bring certain decisions that do not contribute to a healthy lifestyle to the attention of the patient."
The study was published in the Journal of Physical Activity & Health.
INFORMATION:
Brief interventions can help college students return to a healthy lifestyle
2012-11-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
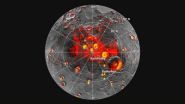
UCLA researchers find evidence for water ice deposits and organic material on Mercury
2012-11-30
Planetary scientists have identified water ice and unusually dark deposits within permanently shadowed areas at Mercury's north pole.
Using data collected by NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft, a team from UCLA crafted the first accurate thermal model of the solar system's innermost planet, successfully pinpointing the extremely cold regions where ice has been found on or below the surface.
The researchers say the newly discovered black deposits are a thin crust of residual organic material brought to the planet over the past several million years through impacts by water-rich ...
Activating ALC1: With a little help from friends
2012-11-30
KANSAS CITY, MO –Chromatin remodeling—the packaging and unpackaging of genomic DNA and its associated proteins—regulates a host of fundamental cellular processes including gene transcription, DNA repair, programmed cell death as well as cell fate. In their latest study, scientists at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research are continuing to unravel the finicky details of how these architectural alterations are controlled.
Through a series of biochemical experiments, Stowers Investigators Ron Conaway, Ph.D., and Joan Conaway, Ph.D., and their team discovered that chromatin ...
Garbage bug may help lower the cost of biofuel
2012-11-30
One reason that biofuels are expensive to make is that the organisms used to ferment the biomass cannot make effective use of hemicellulose, the next most abundant cell wall component after cellulose. They convert only the glucose in the cellulose, thus using less than half of the available plant material.
"Here at the EBI and other places in the biofuel world, people are trying to engineer microbes that can use both," said University of Illinois microbiologist Isaac Cann. "Most of the time what they do is they take genes from different locations and try and stitch all ...
Controversial treatment for autism may do more harm than good, Baylor University researchers find
2012-11-30
ABOUT BAYLOR SCHOOL OF EDUCATION
The Baylor School of Education is accredited by the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education and consists of four departments: Curriculum and Instruction (preparation for classroom teachers and specialists); Educational Administration (post-graduate preparation for school leadership); Educational Psychology (undergraduate and graduate programs for those who are interested in learning, development, measurement, and exceptionalities); and Health, Human Performance and Recreation (preparing for sport- and health-related careers, ...
St. Joseph's researchers identify gene involved in lung tumor growth
2012-11-30
(Phoenix, AZ Nov. 27, 2012) – Lung cancer researchers at St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center in Phoenix, Ariz., in collaboration with researchers at the Translational Genomics Research Institute and other institutions, have identified a gene that plays a role in the growth and spread of non-small cell lung cancer tumors, opening the door for potential new treatment options.
The study, titled "Elevated Expression of Fn14 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Correlates with Activated EGFR and Promotes Tumor Cell Migration and Invasion," was published in the May 2012 issue ...
Altimeter built at Goddard helped identify ice on Mercury
2012-11-30
VIDEO:
MESSENGER's Mercury Laser Altimeter sends out laser pulses that hit the ground and return to the instrument. The amount of light that returns for each pulse gives the reflectance at...
Click here for more information.
A Goddard-built instrument on NASA's MESSENGER mission provided one of three new lines of evidence that water ice exists near the north pole of Mercury. Most of the ice is covered by a thin layer of material that blankets and protects the ice, but in ...
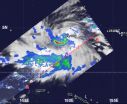
NASA sees Tropical Storm Bopha moving through Southern Yap state
2012-11-30
VIDEO:
On Nov. 27, 2012, NASA's TRMM satellite revealed that rain in Tropical Storm Bopha was falling at a rate of over 70mm/hour (about 1.75 inches) in the red areas. TRMM...
Click here for more information.
NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites captured images of Tropical Storm Bopha as it continues to move through Micronesia in the western North Pacific Ocean and trigger warnings and watches throughout.
From its orbit in space, NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission ...
Promising drug slows down advance of Parkinson's disease and improves symptoms
2012-11-30
PHILADELPHIA—Treating Parkinson's disease patients with the experimental drug GM1 ganglioside improved symptoms and slowed their progression during a two and a half-year trial, Thomas Jefferson University researchers report in a new study published online November 28 in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Although the precise mechanisms of action of this drug are still unclear, the drug may protect patients' dopamine-producing neurons from dying and at least partially restore their function, thereby increasing levels of dopamine, the key neurochemical missing in ...
Gladstone scientists identify key biological mechanism in multiple sclerosis
2012-11-30
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—November 27, 2012—Scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have defined for the first time a key underlying process implicated in multiple sclerosis (MS)—a disease that causes progressive and irreversible damage to nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. This discovery offers new hope for the millions who suffer from this debilitating disease for which there is no cure.
Researchers in the laboratory of Gladstone Investigator Katerina Akassoglou, PhD, have identified in animal models precisely how a protein that seeps from the blood into the brain sets ...
A multi-wavelength view of radio galaxy Hercules A
2012-11-30
VIDEO:
Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's...
Click here for more information.
Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a super massive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble Space Telescope's ...