(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA – As public health researchers continue efforts to understand the effects of neighborhood conditions on health, residents themselves can provide valuable insights regarding public health issues and potential solutions. A new study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania uses in-depth interviews with local residents to examine perspectives on how vacant land affects community, physical, and mental health. The study highlights the importance of community engagement in promoting urban revitalization. Full results of the study, which mirror and expand upon previous studies linking vacant land to poor health, are published online in the Journal of Urban Health.
"This study prioritizes input from local residents to help us better understand community concerns. Residents in this study clearly see vacant land as a negative force that undermines health in their own neighborhoods," said lead author Eugenia C. Garvin, MD, a resident in the Department of Emergency Medicine. "As local communities work to recover from the recent housing crisis, which has caused a significant increase in vacancy rates, the perspectives of residents reinforce the idea that both the economy and health suffer when neighborhoods decline."
An analysis of 50 in-depth interviews reveals that residents are concerned about the effect of vacant land on community well being. Participants feel vacant land overshadows the positive aspects of their neighborhood. For example, illegal use of vacant land for dumping, prostitution, or drug sales contributes to a sense of helplessness and a lack of trust among neighbors. Prior research has shown that communities lacking collaboration and respect for one another are more likely to have increased rates of violence. Participants in the latest study echo the concern that vacancy promotes violent crime, making people feel less safe and often forcing them to stay inside. The presence of vacant lots – which are often strewn with garbage, vermin and other hazards such as broken glass – contributed to a sense of stress among Philadelphia residents, making them feel angry, or even depressed.
Though strategies for dealing with vacant land fall under the broad spectrum of urban planning and revitalization, the study suggests that the success of community programs aimed at reducing the negative effect neighborhood conditions have on health will depend heavily on incorporating the priorities and concerns of local residents into their design.
"Participants in the study had their own ideas for how to change vacant land from a negative to a positive influence in their communities," Garvin explained. "Some suggested transforming vacant lots to playgrounds and turning abandoned homes into subsidized housing. Some even felt they could take on small improvement projects themselves if given the proper resources by the city. Working with community groups and local residents is a huge opportunity for policy makers. The success of public health policies will depend heavily on the city's commitment to deploying the necessary resources and working with residents who experience the effects firsthand."
###
Charles Branas, PhD, associate professor of Epidemiology, Shimrit Kedem, manager of the Mixed Methods Research Lab, Jeffrey Sellman, research assistant, and Carolyn C. Cannuscio, ScD, assistant professor of Family Medicine and Community Health at Penn Medicine co-authored the study.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $479.3 million awarded in the 2011 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital — the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2011, Penn Medicine provided $854 million to benefit our community. END
Penn Study finds residents believe vacant land threatens community, physical and mental health
Resident perspectives provide essential insight on how vacant land affects neighborhood health
2012-11-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Latest volume of Crime and Justice series brings role of prosecutors into focus
2012-11-30
"The United States is, as in so many things involving the criminal justice system, the country most in need of change. It is also, because of the entrenched constitutional bases of its prosecution systems, probably the most resistant to change," Michael Tonry argues in Prosecutors and Politics: A Comparative Perspective.
The latest volume in the Crime and Justice series presents research that critically examines the role of prosecutors within the United States and cross-nationally, asking the question: Can policy makers look across national boundaries to find ways to ...
Making sustainability policies sustainable
2012-11-30
Sweeping environmental policies come with hidden challenges – not only striving to achieve sustainability and benefit the environment – but over time ensuring the program itself can endure.
Scientists at Michigan State University and their colleagues in China are examining China's massive Grain to Green Program (GTGP) – an effort to persuade farmers to return cropland to forest through financial incentives. Their results were reported in this week's journal Ecological Indicators.
The goal – developing a unique targeted approach that applies the combination of environmental ...
Molecular knock-out alleviates Alzheimer's symptoms in mice
2012-11-30
This press release is available in German.
Scientists from the DZNE sites in Göttingen and Bonn, the UMG as well as from the US participated in this basic research project on Alzheimer's disease. The study is published in "EMBO Molecular Medicine".
The researchers led by Prof. André Fischer, Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy at the University Medical Center Gottingen and Site Speaker of the DZNE in Göttingen, investigated mice with a modified genetic background. The animals showed behavioural disorders and brain deposits that are typically associated with Alzheimer's ...
Carbon dioxide could reduce crop yields
2012-11-30
This press release is available in German.
The carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere continues to climb and heat up the climate. The gas is, however, indispensable for plants, as they use the carbon it provides to form glucose and other important substances. Therefore, the more carbon dioxide the better? The equation is unfortunately not as simple as that. The plants, which ensure our basic food supply today, have not been bred for vertical growth but for short stalks and high grain yields. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology ...
The Counter Terrorist Magazine Will Be Easy to Find During the 2013 Shot Show in Las Vegas - January 15th, Through the 18th, 2013 - Now In Its Fifth Year!
2012-11-30
The Counter Terrorist Magazine's 28th issue will be available at several events including the NRA Life of Duty ATACTV Law Enforcement & Military Range Day and the 3 Gun Nation Pro Series Event. In addition to these key shooting events you can pick up your copy on the show floor at exhibitor booths throughout the Shot Show.
As part of the continuous commitment to make sure that The Counter Terrorist Magazine has the best distribution in the industry, we've partnered with some of the best names in the business to have free copies of the magazine available at their ...
Adapting fish defenses to block human infections
2012-11-30
Worcester, Mass. -- Living in an environment teaming with bacteria and fungi, fish have evolved powerful defenses against waterborne pathogens, including antimicrobial peptides located in their gills. Undergraduate researchers at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) are studying the biology and the mechanics of one of those peptides with the hope they can use that knowledge to create engineered surfaces that kill bacteria responsible for foodborne illnesses and hospital-acquired infections.
The research team, led by Terri Camesano, professor of chemical engineering, ...
Which group of Asian-American children is at highest risk for obesity?
2012-11-30
New Rochelle, NY, November 29, 2012—Asian-American children have been at low risk for being overweight or obese compared to other racial and ethnic groups in the U.S., but that may be changing. Yet as rates of overweight and obesity rise, the risk appears to vary depending on the Asian country of origin, according to an article in Childhood Obesity, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Childhood Obesity website at http://www.liebertpub.com/chi.
In the article "Prevalence of Obesity among Young Asian-American ...
Scientists describe the genetic signature of a vital set of neurons
2012-11-30
Scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center have identified two genes involved in establishing the neuronal circuits required for breathing. They report their findings in a study published in the December issue of Nature Neuroscience. The discovery, featured on the journal's cover, could help advance treatments for spinal cord injuries and neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), which gradually kill neurons that control the movement of muscles needed to breathe, move, and eat.
The study identifies a molecular code that distinguishes a group ...
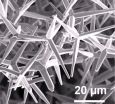
Predicting material fatigue
2012-11-30
The scientists of Kiel University, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg and the Technische Universität München (TUM) have published their results in the current issue of the journal Advanced Materials.
"The luminescent features of zinc oxide tetrapod crystals are well established. According to our work hypothesis, these characteristics showed pronounced variations under a mechanical load, and we realised that it could help to detect internal damages of composite materials", says Dr. Yogendra Mishra of Kiel University's Technical Faculty. In one experiment, the scientists ...
Young surgeons face special concerns with operating room distractions
2012-11-30
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A study has found that young, less-experienced surgeons made major surgical mistakes almost half the time during a "simulated" gall bladder removal when they were distracted by noises, questions, conversation or other commotion in the operating room.
In this analysis, eight out of 18, or 44 percent of surgical residents made serious errors, particularly when they were being tested in the afternoon. By comparison, only one surgeon made a mistake when there were no distractions.
Exercises such as this in what scientists call "human factors engineering" ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Penn Study finds residents believe vacant land threatens community, physical and mental healthResident perspectives provide essential insight on how vacant land affects neighborhood health