UAlberta medical researchers discover new potential chemotherapy
Researchers find Achilles heel of some cancers
2012-12-13
(Press-News.org) Medical researchers at the University of Alberta have discovered that knocking out a particular "partner" gene is the Achilles' heel of some cancers.
Cancer causing genes often have a partner in crime, meaning when either of the two genes is active in cancer cells, the tumour grows. The challenge for researchers has been pinpointing the genes’ “lethal partners.” Loss of one of the partners alone isn’t deadly to the cell, but if both are gotten rid of, the cancer cells are destroyed.
Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry researcher Michael Weinfeld and his collaborators, Edan Foley and graduate student Todd Mereniuk, took cells and artificially removed a particular gene known as PKNP. Then the team knocked out 7,000 other genes, one at a time, all in an effort to find PKNP's "lethal partners" that trigger cell death.
And the team found it—a deadly partner gene, a rare type of cancer suppressor typically missing in lymphomas.
The team confirmed their findings by examining tumours that lacked this specific cancer suppressor. They then inactivated PKNP, which caused the cancer cells to die. Their findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Cancer Research.
Developing cancer drugs that inactivate PKNP will result in only the cancer cells that lack this gene being eradicated, not healthy, normal cells, says Weinfield, who works in the Department of Oncology at the U of A.
"Lots of work in the cancer research field is to try and come up with ways to attack cancer cells and leave normal cells intact," he says. "You need to take advantage of whatever you can to defeat cancer, which can be extremely difficult."
Weinfeld and his colleagues are now working with Dennis Hall in the Department of Chemistry at the U of A and the Centre for Drug Research and Development in British Columbia to improve this potential drug they've discovered. They are also partnering with John Lewis, the Frank and Carla Sojonky Chair in Prostate Cancer Research in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, to work with his cancer-targeting nanotechnology theories.
INFORMATION:
The team's research was funded by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-12-13
DETROIT – Urologists at Henry Ford Hospital have developed a new technique that could make minimally invasive robotic partial nephrectomy procedures the norm, rather than the exception for kidney cancer patients. The technique spares the kidney, eliminates long hospital stays and provides better outcomes by giving the surgeon more time to perform the procedure.
Dubbed ICE for Intracorporeal Cooling and Extraction, the technique may allow more kidney cancer patients to avoid conventional open surgery – now used in the vast majority of cases – and its possible complications, ...
2012-12-13
INDIANAPOLIS -- Despite U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulations requiring generic medications to carry identical warnings to those on corresponding brand-name products, a study by Regenstrief Institute researchers has found that more than two-thirds of generic drugs have safety-warning labels that differ from the equivalent brand-name drug.
The investigators reviewed 9,105 product labels for over 1,500 drugs available on DailyMed, an online repository of labeling information maintained by the FDA and the National Library of Medicine. Of the 1,040 drugs with more ...
2012-12-13
A research group at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed a relatively simple, fast and effective method of depositing uniform, ultrathin layers of platinum atoms on a surface.* The new process exploits an unexpected feature of electrodeposition of platinum—if you drive the reaction much more strongly than usual, a new reaction steps in to shuts down the metal deposition process, allowing an unprecedented level of control of the film thickness.
Platinum is a widely used industrial catalyst—in automobile catalytic converters and hydrogen ...
2012-12-13
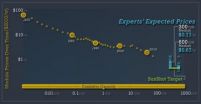
Prices for solar modules—the part of solar panels that produce electricity—will continue to fall, in line with the long-term trend since 1980, according to a survey of experts by Near Zero, , a nonprofit energy research organization. However, for prices to keep falling for the long term will require continued committment to research, such as on materials used for making solar modules.
To get a sense of what future prices for solar power are likely to be, as well as other challenges and bottlenecks that the industry faces, Near Zero conducted a formal, quantitative survey ...
2012-12-13
A new Northwestern University study of professors in STEM fields at top research universities across the country shows that bias against women is ingrained in the workforce, despite a societal desire to believe workplace equality exists.
The quantitative study of the complete publication records of more than 4,200 professors in seven STEM fields (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) confirms that, for some disciplines, female faculty do publish fewer papers than male faculty but not for lack of talent or effort.
The researchers found the "productivity ...
2012-12-13
BOSTON--When people with a family history of colorectal cancer develop the disease, their tumors often carry a molecular sign that the cancer could be life-threatening and may require aggressive treatment, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists report in a new study.
The finding, reported in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, draws on data from studies that have tracked the health of tens of thousands of people over several decades. It suggests that colorectal cancer patients could one day have their tumor tissue tested for the molecular sign, and, if necessary, ...
2012-12-13
COLUMBIA, Mo. — Heart disease is a leading cause of death throughout the world. Doctors say that it is important to detect heart disease early before it becomes too serious. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have found a way that they believe could help detect heart disease before it progresses too far as well as identify patients who are at risk for strokes.
In a study published in Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, Isabelle Masseau, an assistant teaching professor in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, found that she could use targeted micro-bubbles ...
2012-12-13
SEATTLE – Younger women who wait at least 15 years after their first menstrual period to give birth to their first child may reduce their risk of an aggressive form of breast cancer by up to 60 percent, according to a Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center study. The findings, by Christopher I. Li, M.D., Ph.D., a member of the Public Health Sciences Division at Fred Hutch, are published online in Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.
"We found that the interval between menarche and age at first live birth is inversely associated with the risk of triple-negative breast ...
2012-12-13
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have uncovered seven primitive galaxies from a distant population that formed more than 13 billion years ago. In the process, their observations have put forward a candidate for the record for the most distant galaxy found to date (at redshift 11.9), and have shed new light on the earliest years of cosmic history. The galaxies are seen as they were when the Universe was less than 4 percent of its present age.
A team of scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope has made new observations of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field ...
2012-12-13
Research by University of Notre Dame biochemist Anthony S. Serianni is providing new insights that could have important implications for understanding and treating diabetes.
Serianni points out that biological compounds known as dicarbonyl sugars are produced inside the human body from the natural breakdown of the simple sugar, glucose. The formation of these sugars is enhanced in diabetic patients because glucose concentrations in the blood and plasma of diabetics are significantly elevated.
"We investigated, under laboratory conditions that approximate those in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] UAlberta medical researchers discover new potential chemotherapy
Researchers find Achilles heel of some cancers