(Press-News.org) Boston – More than 100 million Americans suffer from chronic pain. But treating and studying chronic pain is complex and presents many challenges. Scientists have long searched for a method to objectively measure pain and a new study from Brigham and Women's Hospital advances that effort. The study appears in the January 2013 print edition of the journal Pain.
"While we need to be cautious in the interpretation of our results, this has the potential to be an exciting discovery for anyone who suffers from chronic pain," said Marco Loggia, PhD, the lead author of the study and a researcher in the Pain Management Center at BWH and the Department of Radiology at Massachusetts General Hospital. "We showed that specific brain patterns appear to track the severity of pain reported by patients, and can predict who is more likely to experience a worsening of chronic back pain while performing maneuvers designed to induce pain. If further research shows this metric is reliable, this is a step toward developing an objective scale for measuring pain in humans."
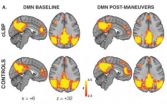
Specifically, researchers studied 16 adults with chronic back pain and 16 adults without pain and used a brain imaging technique called arterial spin labeling to examine patterns of brain connectivity (that is, to examine how different brain regions interact, or "talk to each other"). They found that when a patient moved in a way that increased their back pain, a network of brain regions called Default Mode Network exhibited changes in its connections. Regions within the network (such as the medial prefrontal cortex) became less connected with the rest of the network, whereas regions outside network (such as the insula) became connected with this network. Some of these observations have been noted in previous studies of fibromyalgia patients, which suggests these changes in brain connectivity might reflect a general feature of chronic pain, possibly common to different patient populations.
"This is the first study using arterial spin labeling to show common networking properties of the brain are affected by chronic pain," said study author Ajay Wasan, MD, MSc, Director of the Section of Clinical Pain Research at BWH. "This novel research supports the use of arterial spin labeling as a tool to evaluate how the brain encodes and is affected by clinical pain, and the use of resting default mode network connectivity as a potential neuroimaging biomarker for chronic pain perception."
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by grant numbers K23-DA020681, R01-AT004714, P01-AT002048, R01-AT 005280, R01-AT006146 and P01-AT006663 from the National Institutes of Health.
Discovery could eventually help diagnose and treat chronic pain
2012-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Field Museum studies rare meteorite possibly from the outer asteroid belt
2012-12-21
On April 22, 2012 a very fast-moving fireball was observed over large parts
of California and Nevada. Equivalent to four kilotons of TNT, the fireball was photographed, and recorded by video and by weather Doppler-radars. The photographs and videos helped to trace back its orbit to the far reaches of the outer part of the asteroid belt. The radar data helped meteorite hunters to recover a total of 77 specimens, with the first ones found only two days after the fall. The meteorite was named Sutter's Mill, after the location where it fell. (Interestingly, Sutter's Mill ...
Better stroke care, everywhere: NIH-funded study boosts local hospitals' clotbuster use
2012-12-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — From the moment a stroke occurs, patients must race against the clock to get treatment that can prevent lasting damage. Now, a new study shows the promise – and the challenges – of getting them state-of-the-art treatment safely at their local hospital, saving precious minutes.
The results come from an effort that tested methods to improve delivery of a time-sensitive, clot-busting drug in stroke patients at 24 community hospitals across Michigan. To date, clot-busting treatment has been mostly used at larger hospitals.
The research effort was coordinated ...
Peacock love songs lure eavesdropping females from afar
2012-12-21
Durham, NC — Deep in the scrublands of Keoladeo National Park in northwest India, one thing was hard for biologist Jessica Yorzinski to ignore: It wasn't the heat. It wasn't the jackals. It was the squawks of peacocks in the throes of passion.
From behind the trees in the distance, she could hear a loud two-part whoop, the distinctive call that male peacocks make right before mating.
During the peacock courtship dance, a male announces that he's ready to make his move by dashing towards the object of his affection and emitting a singular squawk before mounting his ...
Not all gamers are low scorers on friendships, relationships
2012-12-21
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Not all video game players are destined for lives filled with failing relationships and dwindling friendships, according to Penn State researchers, who say that a lot depends on the role of the game-playing activity in the gamer's life.
"There's a common stereotype that if you play video games, then you are a loner," said Benjamin Hickerson, assistant professor of recreation, parks and tourism management. "But it may have more to do with how a person is involved in gaming that determines how their social support is affected."
In a study of people ...
Steering stem cells to become 2 different building blocks for new blood vessels
2012-12-21
Growing new blood vessels in the lab is a tough challenge, but a Johns Hopkins engineering team has solved a major stumbling block: how to prod stem cells to become two different types of tissue that are needed to build tiny networks of veins and arteries.
The team's solution is detailed in an article appearing in the January 2013 print edition of the journal Cardiovascular Research. The article also was published recently in the journal's online edition. The work is important because networks of new blood vessels, assembled in the lab for transplanting into patients, ...
2 novel treatments for retinitis pigmentosa move closer to clinical trials
2012-12-21
New York, NY (December 20, 2012) — Two recent experimental treatments — one involving skin-derived induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell grafts, the other gene therapy — have been shown to produce long-term improvement in visual function in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa (RP), according to the Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) scientists who led the studies. At present, there is no cure for RP, the most common form of inherited blindness.
"While these therapies still need to be refined, the results are highly encouraging," said Stephen H. Tsang, MD, PhD, associate ...
NASA sees Cyclone Evan blown apart by wind shear
2012-12-21
Cyclone Evan is no more than a remnant low pressure area in the South Pacific Ocean now. NOAA's GOES-15 satellite captured an image of the remnants from its fixed orbit in space on Dec. 20 that showed strong wind shear had basically blown the storm apart.
The last official bulletin by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center was issued on Dec. 19 at 2100 UTC (4 p.m. EST/U.S. or 12:56 a.m. Fiji local time on Dec. 20). At that time, Evan's maximum sustained winds were still near 35 knots (40 mph/64.8 kph) and it had transitioned into an extra-tropical storm. It was located 400 ...
Eighth Landsat satellite arrives at launch site
2012-12-21
An oversized semi-trailer truck carrying NASA's Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) has arrived at its launch site at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California in preparation for launch. This NASA and U.S. Geological Survey mission will continue a 40-year record of measuring change on the planet from space.
LDCM is the eighth satellite in the Landsat series, which began in 1972. It will extend and expand global land observations that are critical in many sectors, including energy and water management, forest monitoring, human and environmental health, urban planning, ...
Protein kinase Akt identified as arbiter of cancer stem cell fate
2012-12-21
PHILADELPHIA — The protein kinase Akt is a key regulator of cell growth, proliferation, metabolism, survival, and death. New work on Akt's role in cancer stem cell biology from the lab of senior author Honglin Zhou, MD, PhD and Weihua Li, co-first author, both from the Center for Resuscitation Sciences, Department of Emergency Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, and Xiaowei Xu, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, appears in Molecular Cell. The findings were also highlighted in Nature and Science reviews.
This new research shows ...
Discovery of Africa moth species important for agriculture, controlling invasive plants
2012-12-21
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — In the rain forests of the Congo, where mammals and birds are hunted to near-extinction, an impenetrable sound of buzzing insects blankets the atmosphere.
Because it is a fairly inaccessible region with political unrest, much of the Congo's insect biodiversity remains largely undiscovered. In a new monographic book published this week in Zootaxa, researchers at the University of Florida and the Royal Museum of Central Africa in Belgium provide insect biodiversity information for this area in Central Africa that increasingly undergoes habitat destruction. ...