(Press-News.org) You may have to be over a certain age to be a contestant on "Deal or No Deal", but children as young as five start to maximize their profits - in cookies - when making decisions similar to those on the show, according to research published January 9 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Valerie Dufour and colleagues from the National Center for Scientific Research in France.
Children aged 3-9 were given a cookie and presented the option to either keep it or exchange it for one of 6 identical cups containing cookies. The cookies in the cups could be larger, smaller or equal in size to what they already had. The chances of winning a larger cookie were altered by presenting different combinations of cookie sizes in the cups (3 large, 2 equal and 1 small, for example). In each case, the children were told how many cups had a 'winning' cookie before they made their decision.
Three to four-year-olds could not distinguish between the profits to be had by choosing to exchange their cookie when the odds of winning were greater. Kids aged five and up were better at understanding the odds of winning, and their decisions were affected by chances of losing. They also framed their decisions in the context of previous wins or losses.
The researchers found that though children over the age of five were risk-seekers, they also exhibited an aversion to loss typically seen in adults. This aversion arises from a 'better safe than sorry' choice but can also lead to judgment errors in adults, causing a loss of potential profits. The results of this study suggest that this is a decision-making pattern that we begin to learn as early as age five.
###
Citation: Steelandt S, Broihanne M-H, Romain A, Thierry B, Dufour V (2013) Decision-Making under Risk of Loss in Children. PLoS ONE 8(1): e52316. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052316
Financial Disclosure: The research was supported by a grant from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-08-412 BLAN-0042-01). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interest Statement: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
PLEASE LINK TO THE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE IN ONLINE VERSIONS OF YOUR REPORT (URL goes live after the embargo ends): http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052316
Deal or no deal: 5 year olds make smart decisions in games of risk
Children aged 5 and over start to make decisions to maximize profits under risky situations
2013-01-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic form of anemia offers new avenue to treating drug-resistant tumors
2013-01-10
VIDEO:
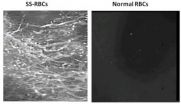
This is an intravital microscopy of the skin window of tumors in mice injected with
SSRBCs or NLRBCs.
Click here for more information.
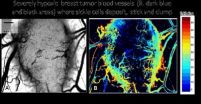
The genetic mutation that causes sickle cell anemia also turns red blood cells into potent tumor killers and may offer a new way to treat some cancers that are resistant to existing treatments, according to research published January 9 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by David S. Terman of Jenomic Research Institute and colleagues ...
Brown eyes appear more trustworthy than blue
2013-01-10
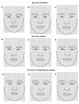
People view brown-eyed faces as more trustworthy than those with blue eyes, except if the blue eyes belong to a broad-faced man, according to research published January 9 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Karel Kleisner and colleagues from Charles University in the Czech Republic.
The study's results attempt to answer a larger question: What makes us think a person's face looks trustworthy? The authors asked study participants to rate male and female faces for trustworthiness based on two features: eye color and face shape. A significant number of participants found ...
Sickle cells show potential to attack aggressive cancer tumors
2013-01-10
DURHAM, N.C. – By harnessing the very qualities that make sickle cell disease a lethal blood disorder, a research team led by Duke Medicine and Jenomic, a private cancer research company in Carmel, Calif., has developed a way to deploy the misshapen red blood cells to fight cancer tumors.
Reporting in the Jan. 9, 2013, edition of the on-line journal, PLOS ONE, the researchers describe a process of exploiting sickle-shaped red blood cells to selectively target oxygen deprived cancer tumors in mice and block the blood vessels that surround them.
"Sickle cells appear ...
Johns Hopkins scientists use Pap test fluid to detect ovarian, endometrial cancers
2013-01-10
Using cervical fluid obtained during routine Pap tests, scientists at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have developed a test to detect ovarian and endometrial cancers. In a pilot study, the "PapGene" test, which relies on genomic sequencing of cancer-specific mutations, accurately detected all 24 (100 percent) endometrial cancers and nine of 22 (41 percent) ovarian cancers. Results of the experiments are published in the January 9 issue of the journal, Science Translational Medicine.
The investigators note that larger scale studies are needed before clinical implementation ...
Mapping the Milky Way: Radio telescopes give clues to structure, history
2013-01-10
Astronomers have discovered hundreds of previously-unknown sites of massive star formation in the Milky Way, including the most distant such objects yet found in our home Galaxy. Ongoing studies of these objects promise to give crucial clues about the structure and history of the Milky Way.
The scientists found regions where massive young stars or clusters of such stars are forming. These regions, which astronomers call HII (H-two) regions, serve as markers of the Galaxy's structure, including its spiral arms and central bar.
"We're vastly improving the census of our ...
Mount Sinai researchers foresee new therapies and diagnostics for deadly fibrotic diseases
2013-01-10
A team of scientists has developed a playbook for ending the devastating impact of fibrotic diseases of the liver, lung, kidney, and other organs, which are responsible for as many as 45 percent of all deaths in the industrialized world. Despite the prevalence of these illnesses, which are caused by buildup of scar tissue, there are no approved antifibrotic drugs on the market in the U.S. A top fibrosis expert from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and three other institutions have described drug targets and compounds they hope will prove broadly effective in ...
Drug-resistant melanoma tumors shrink when therapy is interrupted
2013-01-10
Researchers in California and Switzerland have discovered that melanomas that develop resistance to the anti-cancer drug vemurafenib (marketed as Zelboraf), also develop addiction to the drug, an observation that may have important implications for the lives of patients with late-stage disease.
The team, based at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), the Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research (NIBR) in Emeryville, Calif., and University Hospital Zurich, found that one mechanism by which melanoma cells become resistant to vemurafenib also renders them ...
The farthest supernova yet for measuring cosmic history
2013-01-10
What if you had a "Wayback Television Set" and could watch an entire month of ancient prehistory unfold before your eyes in real time? David Rubin of the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) presented just such a scenario to the American Astronomical Society (AAS) meeting in Long Beach, CA, when he announced the discovery of a striking astronomical object: a Type Ia supernova with a redshift of 1.71 that dates back 10 billion years in time. Labeled SN SCP-0401, the supernova is exceptional for its detailed spectrum and precision ...
Spin and bias in published studies of breast cancer trials
2013-01-10
Spin and bias exist in a high proportion of published studies of the outcomes and adverse side-effects of phase III clinical trials of breast cancer treatments, according to new research published in the cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Thursday).
In the first study to investigate how accurately outcomes and side-effects are reported in breast cancer trials, researchers at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre and University of Toronto (Toronto, Canada) found that in a third of all trials that failed to show a statistically significant benefit for the treatment ...
Particles of crystalline quartz wear away teeth
2013-01-10
This press release is available in German.
Dental microwear, the pattern of tiny marks on worn tooth surfaces, is an important basis for understanding the diets of fossil mammals, including those of our own lineage. Now nanoscale research by an international multidisciplinary group that included members of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig has unraveled some of its causes. It turns out that quartz dust is the major culprit in wearing away tooth enamel. Silica phytoliths, particles produced by plants, just rub enamel, and thus have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Deal or no deal: 5 year olds make smart decisions in games of riskChildren aged 5 and over start to make decisions to maximize profits under risky situations