(Press-News.org) Public relations professionals who have provided ethics counsel to senior management are at least as fervent about serving the public interest — sometimes even more so — as they are about their duty to their organizations, according to a Baylor University researcher.
A new study of 30 senior public relations professionals, most of whom had served as an "organizational conscience," showed the individuals viewed themselves as an "independent voice" in the organization and not "mired by its perspective or politics," said study author Marlene S. Neill, Ph.D., a lecturer in the department of journalism, public relations and new media in Baylor's College of Arts & Sciences.
The study, published in Journal of Mass Media Ethics: Exploring Questions of Media Morality, was co-authored by Minette Drumwright, Ph.D. , an associate professor of advertising at the University of Texas at Austin, and may be viewed here: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08900523.2012.746108
Researchers did in-depth interviews with senior public relations professionals in the United States and Australia, with an average of 27 years of experience. All but three had served as the chief public relations officers in their organizations, which included corporations, nonprofit organizations and government entities; and two of those also provided counsel in their roles in PR agencies for their clients as external counselors.
Study participants said they often were in the "kill the messenger" predicament, making it tricky to give criticism to people who outranked them and to persuade those people to agree with them, Neill said.
Speaking up on sensitive ethical issues required courage, study participants said. A few were fired or demoted for refusing to do something that was blatantly unethical; two resigned when their advice was rejected, including one who refused to include false information in a press release.
One participant noted that "I can't afford to lose my credibility . . . As PR professionals, it's all we have. And if I lose my credibility here, it's not like I can just go start over with someone else, somewhere else."
One individual said that the " 'yes man' has no value, no value whatsoever" in PR. Another said one reason for her good relationship with her company CEO is that "he can count on me to not always agree with him."
Another major barrier was a common misperception among senior executives that public relations is nothing more than a tool of marketing, which limits PR professionals' roles as problem solvers.
Crucial to their jobs is a sound relationship with their organizations' legal counsels, informants said. So is access to key decision makers, the better to ensure "fire prevention" instead of "fire fighting" — damage control in a crisis.
Neill said that participants were resourceful about how to communicate to management without seeming judgmental, using such approaches as mock news conferences and the "headline test," in which managers were asked to imagine a good headline and a bad headline that might result from an approach they advocated.
One participant contrasted her experience at an iron-fisted company — in which senior managers' attitude was one of "Do what I say, and don't question me" — with a more effective and positive experience at another company. There, she said, "Nobody is belittled; the managers and executives don't feel like you're questioning their authority. They're very much into a learning mode. They ask a lot of questions; they very much are information gathering."
### END
ANN ARBOR -- A review of the available evidence underscores the safety of the federal childhood immunization schedule, according to a report released today by the Institute of Medicine. University of Michigan population ecologist Pejman Rohani served on the 13-person committee that wrote the report.
Roughly 90 percent of American children receive most childhood vaccines advised by the federal immunization schedule by the time they enter kindergarten, the committee noted. However, some parents choose to spread out their children's immunizations over a different time frame ...
WASHINGTON -- A review of the available evidence underscores the safety of the federal childhood immunization schedule, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine. Should signals indicate the need for investigation of the schedule, however, the report offers a framework for conducting safety research using existing or new data collection systems.
Roughly 90 percent of American children receive most childhood vaccines advised by the federal immunization schedule by the time they enter kindergarten, noted the committee that wrote the report. However, some parents ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (January 16, 2013) – With the rapidly expanding use of brain and spinal cord stimulation therapy (neuromodulation), new "remote presence" technologies may help to meet the demand for experts to perform stimulator programming, reports a study in the January issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The preliminary study by Dr. Ivar Mendez of Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, supports ...
PHILADELPHIA -- In the first study to examine discussion of drug side effects on Internet message boards, researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found that breast cancer survivors taking the commonly prescribed adjuvant therapy known as aromatase inhibitors (AIs) often detailed in these forums troublesome symptoms resulting from the drugs, and they were apt to report discontinuing the treatment or switching to a different drug in the same class. The findings are published online this week in the journal Pharmacoepidemiology and ...
Fashionable people may turn up their noses at jute — the cheap fiber used to make burlap, gunny sacks, twine and other common products — but new research is enhancing jute's appeal as an inexpensive, sustainable reinforcement for mortar and concrete. The study appears in ACS' journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
Subhasish B Majumder and colleagues note that there has been a resurgence of interest in using economical, sustainable natural fibers, rather than steel or synthetic fibers, to reinforce the cement compositions used to make concrete and mortar, ...
Scientists are reporting development of the first practical way to make large amounts of a promising new anti-cancer substance that kills cancer cells differently than existing medicines. Their article on synthesis of the substance, and tests demonstrating its effectiveness in the laboratory, appears in ACS' Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Isamu Shiina and colleagues explain that the substance, AMF-26, showed promise against certain forms of cancer in laboratory studies, fostering excitement about its potential for development as a new anti-cancer drug. That excitement ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (January 16, 2012) – Efforts to correct false beliefs about health care reform may backfire, depending on individuals' political views and level of knowledge, suggests a study in the February issue of Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
In the study, more politically knowledgeable people with positive views of Sarah Palin were likely to harden their opposition to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) when presented with information debunking Palin's "death panel" claim, according to the study ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (January 16, 2013) – Researchers using sophisticated genetic testing techniques have identified a promising new biomarker for diagnosis of glioma—the most common type of malignant brain tumor, reports the January issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The biomarker ELTD1 "may serve as an additional biomarker for gliomas in preclinical and clinical diagnosis of gliomas," according to the study by Rheal A. Towner of Oklahoma ...
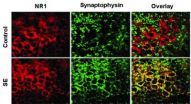
LOS ANGELES (Jan. 16, 2013) – In a promising finding for epileptic patients suffering from persistent seizures known as status epilepticus, researchers reported today that new medication could help halt these devastating seizures. To do so, it would have to work directly to antagonize NMDA receptors, the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic activity and memory function in the brain.
"Despite the development of new medications to prevent seizures, status epilepticus remains a life-threatening condition that can cause extensive brain damage in the patients ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (www.ucr.edu) — An assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering is using the teeth of a marine snail found off the coast of California to create less costly and more efficient nanoscale materials to improve solar cells and lithium-ion batteries.
The most recent findings by David Kisailus, an assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering, details how the teeth of chiton grow. The paper was published today (Jan. 16) in the journal Advanced Functional Materials. It was co-authored by several ...