(Press-News.org) Nearly 200 000 light-years from Earth, the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, floats in space, in a long and slow dance around our galaxy. Vast clouds of gas within it slowly collapse to form new stars. In turn, these light up the gas clouds in a riot of colours, visible in this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is ablaze with star-forming regions. From the Tarantula Nebula, the brightest stellar nursery in our cosmic neighbourhood, to LHA 120-N 11, part of which is featured in this Hubble image, the small and irregular galaxy is scattered with glowing nebulae, the most noticeable sign that new stars are being born.
The LMC is in an ideal position for astronomers to study the phenomena surrounding star formation. It lies in a fortuitous location in the sky, far enough from the plane of the Milky Way that it is neither outshone by too many nearby stars, nor obscured by the dust in the Milky Way's centre. It is also close enough to study in detail (less than a tenth of the distance of the Andromeda Galaxy, the closest spiral galaxy), and lies almost face-on to us [1], giving us a bird's eye view.
LHA 120-N 11 (known as N11 for short) is a particularly bright region of the LMC, consisting of several adjacent pockets of gas and star formation. NGC 1769 (in the centre of this image) and NGC 1763 (to the right, see [heic1011][1]) are among the brightest parts.
In the centre of this image, a dark finger of dust blots out much of the light. While nebulae are mostly made of hydrogen, the simplest and most plentiful element in the Universe, dust clouds are home to heavier and more complex elements, which go on to form rocky planets like the Earth. Much finer than household dust (it is more like smoke), this interstellar dust consists of material expelled from previous generations of stars as they died.
The data in this image were identified by Josh Lake, an astronomy teacher at Pomfret School in Connecticut, USA, in the [Hubble's Hidden Treasures][2] image processing competition. The competition invited members of the public to dig out unreleased scientific data from Hubble's vast archive, and to process them into stunning images.
Josh Lake won first prize in the competition with an [image][3] contrasting the light from glowing hydrogen and nitrogen in N11. The image above combines the data he identified with additional exposures taken in blue, green and near infrared light.
INFORMATION:
[1]: http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1011/
[2]: http://www.spacetelescope.org/announcements/ann1211/
[3]: http://www.spacetelescope.org/projects/fits_liberator/fitsimages/josh_lake_ngc_1763/
Notes
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA.
[1] Although the Large Magellanic Cloud is generally classified as an irregular galaxy, it shares some features with spiral galaxies, including a clearly visible bar, and a single spiral-arm-like structure. It is thought that the LMC may be a small spiral galaxy that was pulled out of shape by the Milky Way.
Links
[1]: [Hidden Treasures]
[2]: [Josh Lake's image of N11]
Contacts
Oli Usher
Hubble/ESA
Garching, Germany
A hidden treasure in the Large Magellanic Cloud
2013-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Potential new treatment for gastrointestinal cancers discovered
2013-01-17
Researchers have identified a complex of proteins that promotes the growth of some types of colon and gastric cancers, and shown that medications that block the function of this complex have the potential to be developed into a new treatment for these diseases.
The complex of proteins, known as mTorc1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1), has previously been implicated in the development of some other cancers but this is the first time it has been shown to promote the growth of colon and gastric cancers that are associated with inflammation.
Dr Stefan Thiem and ...
Amputations among people with diabetes can be reduced by 50 percent
2013-01-17
Every 30 seconds somebody in the world is amputated as a consequence of foot complication due to diabetes. A new study at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, confirmes that shoe inserts, podiatry, regular checkups and other simple interventions can reduce the number of amputations by more than 50%.
Orthotic researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, have studied diabetic foot complications ever since 2008. They have focused on protecting the foot from overloading the foot sole in order to minimize the risk of ulcers, which may eventually ...
The neurobiological consequence of predating or grazing
2013-01-17
This press release is available in German.
Researchers in the group of Ralf Sommer at the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology in Tuebingen, Germany, have for the first time been able to identify neuronal correlates of behaviour by comparing maps of synaptic connectivity, or "connectomes", between two species with different behaviour. They compared the pharyngeal nervous systems of two nematodes, the bacterial feeding Caenorhabditis elegans and the predator/omnivore Pristionchus pacificus and found large differences in how the neurons are "wired" together.
A ...
Study offers new insights into the mechanics of muscle fatigue
2013-01-17
A study in The Journal of General Physiology examines the consequences of muscle activity with surprising results, indicating that the extracellular accumulation of potassium that occurs in working muscles is considerably higher than previously thought.
Muscle excitation involves the influx of sodium ions and efflux of potassium ions. Although the fraction of ions that cross the muscle membrane with each contraction is minute, repeated activity can lead to substantial changes in the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of sodium and potassium ions. The extent ...
Pediatric coding top tips and pediatric CPT changes 2013
2013-01-17
Cyanobacteria belong to the Earth's oldest organisms. They are still present today in oceans and waters and even in hot springs. By producing oxygen and evolving into multicellular forms, they played a key role in the emergence of organisms that breathe oxygen. This has, now, been demonstrated by a team of scientists under the supervision and instruction of evolutionary biologists from the University of Zurich. According to their studies, cyanobacteria developed multicellularity around one billion years earlier than eukaryotes – cells with one true nucleus. At almost the ...
People with low risk for cocaine dependence have differently shaped brain to those with addiction
2013-01-17
People who take cocaine over many years without becoming addicted have a brain structure which is significantly different from those individuals who developed cocaine-dependence, researchers have discovered. New research from the University of Cambridge has found that recreational drug users who have not developed a dependence have an abnormally large frontal lobe, the section of the brain implicated in self-control. Their research was published in the journal Biological Psychiatry.
For the study, led by Dr Karen Ersche, individuals who use cocaine on a regular basis underwent ...
Cheating to create the perfect simulation
2013-01-17
(Jena) The planet Earth will die – if not before, then when the Sun collapses. This is going to happen in approximately seven billion years. In the universe however the death of suns and planets is an everyday occurance and our solar system partly consists of their remnants.
The end of stars – suns – rich in mass is often a neutron star. These "stars' liches" demonstrate a high density, in which atoms are extremely compressed. Such neutron stars are no bigger than a small town, but heavier than our sun, as physicist PD Dr. Axel Maas of the Jena University (Germany) points ...
Dietary shifts driving up phosphorus use
2013-01-17
Dietary changes since the early 1960s have fueled a sharp increase in the amount of mined phosphorus used to produce the food consumed by the average person over the course of a year, according to a new study led by researchers at McGill University.
Between 1961 and 2007, rising meat consumption and total calorie intake underpinned a 38% increase in the world's per capita "phosphorus footprint," the researchers conclude in a paper published online in Environmental Research Letters.
The findings underscore a significant challenge to efforts to sustainably manage the ...
Viagra converts fat cells
2013-01-17
Researchers from the University of Bonn treated mice with Viagra and made an amazing discovery: The drug converts undesirable white fat cells and could thus potentially melt the unwelcome "spare tire" around the midriff. In addition, the substance also decreases the risk of other complications caused by obesity. The results are now published in "The Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology" (FASEB).
Sildenafil – better known as Viagra – is used to treat erectile dysfunction. This substance prevents degradation of cyclic guanosine mono-phosphate ...
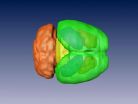
Is athleticism linked to brain size?
2013-01-17
VIDEO:
This movie shows running mice (bred-for-athleticism mouse on the left, regular mouse on the right).
Click here for more information.
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Is athleticism linked to brain size? To find out, researchers at the University of California, Riverside performed laboratory experiments on house mice and found that mice that have been bred for dozens of generations to be more exercise-loving have larger midbrains than those that have not been selectively bred ...