(Press-News.org) A drug developed at Linköping University in Sweden protects against the side effects of cancer treatments while strengthening the effects on the tumour. An international drug evaluation is now starting up on a larger group of patients.
The results of the studies with the compound, known as calmangafodipir, were published in the latest issue of the cancer journal Translational Oncology with Professor Rolf G. G. Andersson as the main author.
The research was initiated on a substance called mangafodipir, which was used as a contrast media in magnetic resonance scans. But pharmacologists at LiU discovered that it also protected healthy cells in connection with cancer treatments.
"We found that the substance could affect the formation of oxygen radicals, which are a cause of side effects in chemotherapy," says Professor Andersson.
For example, the number of white blood cells decreases drastically in almost all the patients, which opens the door to infections that could even be fatal.
The researchers began with cell tests, and then went on to mice infected with cancer cells. The mice were treated with chemotherapy and were administered mangafodipir at the same time. Tumour formation decreased while white blood cells were protected.
One problem was that a large portion of the manganese in the substance was released; as a consequence, the positive effect subsided. The free manganese can also be poisonous and cause brain damage.
"We remade the substance and replaced a lot of the manganese with calcium. This yielded a more stable complex, which turned out to be even better at protecting cells, thereby increasing the anti-cancer effect," says Professor Andersson.
The effect of mangafodipir was confirmed in a smaller study on patients with colon cancer, which was published in Translational Oncology in February 2012.
Jan Olof G. Karlsson is a senior lecturer at Linköping University and a senior researcher at PledPharma AB who is developing the drug, which will be marketed under the brand name PledOx®. An international Phase 2 study, involving patients with cancer of the large intestine, has recently been initiated. The results are expected at the end of the year.INFORMATION:
Article: Superior therapeutic index of calmangafodipir in comparison to mangafodipir as a chemotherapy adjunct by Jan Olof G. Karlsson, Tino Kurz, Susanne Fleichsig, Jacques Näsström and Rolf G.G. Andersson. Translational Oncology, Vol. 5 No. 6, December 2012.
This press release is available in German. Image sensors are at the core of every digital camera. Before a snapshot appears on the display, the sensors first convert the light from the lens to electrical signals. The image processor then uses these to create the final photo.
Many compact and cellphone cameras contain silicon-based image sensors produced using CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) technology. Prof. Paolo Lugli and Dr. Daniela Baierl from TUM have developed a cost-effective process to improve the performance of these CMOS sensors. Their approach ...
Public acceptance of climate change's reality may have been influenced by the rate at which words moved from scientific journals into the mainstream, according to anthropologist Michael O'Brien, dean of the College of Arts and Science at the University of Missouri. A recent study of word usage in popular literature by O'Brien and his colleagues documented how the usage of certain words related to climate change has risen and fallen over the past two centuries. Understanding how word usage affects public acceptance of science could lead to better science communication and ...
New Orleans, LA – Research led by Dr. Suresh Alahari, the Fred Brazda Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans and its Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center, details exactly how the Her2 cancer gene promotes the progression and spread of breast cancer cells. The inactivation of a tumor suppression gene called Nischarin is among the mechanisms identified. The findings provide a new therapeutic target to block the function of Her2. The research was published in Cancer Research, OnlineFirst on January 21, 2013.
About 30% of breast ...
(Garrison, NY) Arguing that obesity "may be the most difficult and elusive public health problem the United States has ever encountered" and that anti-obesity efforts having made little discernible difference, Daniel Callahan, co-founder and President Emeritus of The Hastings Center, proposes a bold and controversial approach to fighting the epidemic.
Callahan says that the public health community can learn from one of the most successful public health campaigns: the anti-smoking campaign. A primary strategy has been to stigmatize smokers, he says, making it clear that ...
The kindness of mankind most likely developed from our more sinister and self-serving tendencies, according to Princeton University and University of Arizona research that suggests society's rules against selfishness are rooted in the very exploitation they condemn.
The report in the journal Evolution proposes that altruism — society's protection of resources and the collective good by punishing "cheaters" — did not develop as a reaction to avarice. Instead, communal disavowal of greed originated when competing selfish individuals sought to control and cancel out one ...
NEW YORK - January 22, 2013 - In 2009, the Securities and Exchange Commission mandated that public companies submit portions of annual (10-K) and quarterly (10-Q) reports—in a digitized format known as eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL). The goal of this type of data was to provide more relevant, timely, and reliable "interactive" data to investors and analysts. The XBRL-formatted data is meant to allow users to manipulate and organize the financial information according to their own purposes faster, cheaper, and more easily than current alternatives.
But how ...
Using a brain-imaging technique that examines the entire infant brain, researchers have found that the anatomy of certain brain areas – the hippocampus and cerebellum – can predict children's language abilities at 1 year of age.
The University of Washington study is the first to associate these brain structures with future language skills. The results are published in the January issue of the journal Brain and Language.
"The brain of the baby holds an infinite number of secrets just waiting to be uncovered, and these discoveries will show us why infants learn languages ...
1. Evidence Review: Some Behavioral Interventions May Reduce Child Abuse and Neglect
Risk assessment and behavioral interventions in pediatric clinics may reduce child abuse and neglect, according to a recent evidence review. Researchers reviewed studies published since 2004 when the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force last published recommendations on child abuse and neglect to determine the effectiveness of primary care relevant interventions on child abuse and neglect outcomes. The researchers also sought to determine adverse effects of interventions. Physicians and ...
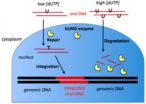
A team of researchers based at Johns Hopkins has decoded a system that makes certain types of immune cells impervious to HIV infection. The system's two vital components are high levels of a molecule that becomes embedded in viral DNA like a code written in invisible ink, and an enzyme that, when it reads the code, switches from repairing the DNA to chopping it up into unusable pieces. The researchers, who report the find in the Jan. 21 early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, say the discovery points toward a new approach to eradicating HIV ...
CHICAGO --- How do you annihilate lymphoma without using any drugs?
Starve it to death by depriving it of what appears to be a favorite food: HDL cholesterol.
Northwestern Medicine® researchers discovered this with a new nanoparticle that acts like a secret double agent. It appears to the cancerous lymphoma cell like a preferred meal -- natural HDL. But when the particle engages the cell, it actually plugs it up and blocks cholesterol from entering. Deprived of an essential nutrient, the cell eventually dies.
A new study by C. Shad Thaxton, M.D., and Leo I. Gordon, ...