(Press-News.org) Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of late-life dementia. The disorder is thought to be caused by a protein known as amyloid-beta, or Abeta, which clumps together in the brain, forming plaques that are thought to destroy neurons. This destruction starts early, too, and can presage clinical signs of the disease by up to 20 years.
For decades now, researchers have been trying, with limited success, to develop drugs that prevent this clumping. Such drugs require a "target" — a structure they can bind to, thereby preventing the toxic actions of Abeta.
Now, a new study out of UCLA suggests that while researchers may have the right target in Abeta, they may be missing the bull's-eye. Reporting in the Jan. 23 issue of the Journal of Molecular Biology, UCLA neurology professor David Teplow and colleagues focused on a particular segment of a toxic form of Abeta and discovered a unique hairpin-like structure that facilitates clumping.
"Every 68 seconds, someone in this country is diagnosed with Alzheimer's," said Teplow, the study's senior author and principal investigator of the NIH-sponsored Alzheimer's Disease Research Center at UCLA. "Alzheimer's disease is the only one of the top 10 causes of death in America that cannot be prevented, cured or even slowed down once it begins. Most of the drugs that have been developed have either failed or only provide modest improvement of the symptoms. So finding a better pathway for these potential therapeutics is critical."
The Abeta protein is composed of a sequence of amino acids, much like "a pearl necklace composed of 20 different combinations of different colors of pearl," Teplow said. One form of Abeta, Abeta40, has 40 amino acids, while a second form, Abeta42, has two extra amino acids at one end.
Abeta42 has long been thought to be the toxic form of Abeta, but until now, no one has understood how the simple addition of two amino acids made it so much more toxic then Abeta40.
In his lab, Teplow and his colleagues used computer simulations in which they looked at the structure of the Abeta proteins in a virtual world. The researchers first created a virtual Abeta peptide that only contained the last 12 amino acids of the entire 42–amino-acid-long Abeta42 protein. Then, said Teplow, "we just let the molecule move around in a virtual world, letting the laws of physics determine how each atom of the peptide was attracted to or repulsed by other atoms."
By taking thousands of snapshots of the various molecular structures the peptides created, the researchers determined which structures formed more frequently than others. From those, they then physically created mutant Abeta peptides using chemical synthesis.
"We studied these mutant peptides and found that the structure that made Abeta42 Abeta42 was a hairpin-like turn at the very end of the peptide of the whole Abeta protein," Teplow said.
The hairpin turn structure was not previously known in the detail revealed by the researchers, "so we feel our experiments were novel," he said. "Our lab is the first to show that it is this specific turn that accounts for the special ability of Abeta42 to aggregate into clumps that we think kills neurons. Abeta40, the Abeta protein with two less amino acids at the end of the protein, did not do the same thing."
Hopefully, the work of the Teplow laboratory presents what may the most relevant target yet for the development of drugs to fight Alzheimer's disease, the researchers said.
### Other authors on the study included Robin Roychaudhuri, Mingfeng Yang, Atul Deshpande, Gregory M. Cole and Sally Frautschy, all of UCLA, and Aleksey Lomakin and George B. Benedek of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Funding for the study was provided by grants from the State of California Alzheimer's Disease Research Fund, a UCLA Faculty Research Grant, the National Institutes of Health (AG027818, NS038328) and the James Easton Consortium for Alzheimer's Drug Discovery and Biomarkers.
The Mary S. Easton Center for Alzheimer's Disease Research at UCLA is part of the UCLA Department of Neurology, which encompasses more than 20 disease-related research programs, along with large clinical and teaching programs. These programs cover brain mapping and neuroimaging, movement disorders, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, neurogenetics, nerve and muscle disorders, epilepsy, neuro-oncology, neurotology, neuropsychology, headaches and migraines, neurorehabilitation, and neurovascular disorders. The department ranked first among its peers nationwide in National Institutes of Health funding (2002).
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
Right target, but missing the bulls-eye for Alzheimer's
UCLA researchers discover new point of attack for drug therapy
2013-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discovery of new class of damage-prone DNA regions could lead to better cancer treatments
2013-01-24
Cancer is thought to arise from DNA damage at fragile sites in the genome. A study published by Cell Press on January 24th in the journal Cell reveals a new class of fragile sites that contributes to DNA alterations in a type of blood cancer called B cell lymphoma The findings could lead to the development of more effective treatments for B cell lymphoma and potentially other cancers.
"This study describes an underlying mechanism of genome instability in B cell lymphoma that could not be previously explained," says senior study author André Nussenzweig of the National ...
Dung beetles follow the Milky Way
2013-01-24
You might expect dung beetles to keep their "noses to the ground," but they are actually incredibly attuned to the sky. A report published online on January 24 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, shows that even on the darkest of nights, African ball-rolling insects are guided by the soft glow of the Milky Way.
While birds and humans are known to navigate by the stars, the discovery is the first convincing evidence for such abilities in insects, the researchers say. It is also the first known example of any animal getting around by the Milky Way as opposed to ...
Dung beetles use stars for orientation
2013-01-24
An insect with a tiny brain and minimal computing power has become the first animal proven to use the Milky Way for orientation. Scientists from South Africa and Sweden have published findings showing the link between dung beetles and the spray of stars which comprises our galaxy.
Although their eyes are too weak to distinguish individual constellations, dung beetles use the gradient of light to dark provided by the Milky Way to ensure they keep rolling their balls in a straight line and don't circle back to competitors at the dung pile.
"The dung beetles don't care which ...
Discovering the secrets of tumor growth
2013-01-24
Scientists at the University of Copenhagen's Center for Healthy Ageing have identified a compound that blocks the expression of a protein without which certain tumours cannot grow. This compound has the potential as an anticancer agent according to the research published in the journal CHBIOL: Chemistry and Biology this week.
The BLM protein is also known to be important in maintaining stability in cells when they multiply, thus preventing cancer. However, certain types of tumour need BLM to grow. This is typical of osteosarcomas - aggressive malignant tumours often seen ...
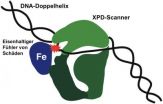
A scanner for hereditary defects
2013-01-24
Our DNA is constantly under attack from UV light, toxins and metabolic processes. Proteins and enzymes continually repair the damaged DNA. Unrecognized and therefore unrepaired damage to the genetic material, however, accelerates aging and causes cancer and genetic disorders. A team headed by veterinary pharmacologist and toxicologist Hanspeter Nägeli has now discovered that the protein XPD plays a key role in locating damaged DNA.
XPD protein as scanner
Genetic information is stored on approximately three billion base pairs of adenine/thymine or cytosine/guanine in ...
Research ties lightning to onset of headache, migraines
2013-01-24
CINCINNATI—University of Cincinnati (UC) researchers have found that lightning may affect the onset of headache and migraines.
These results, published in the Jan. 24, 2013 online edition of the journal Cephalalgia, are the first tying lightning to headache and could help chronic sufferers more efficiently anticipate headache and migraine arrival and begin preventive treatment immediately.
Geoffrey Martin, fourth-year medical student at UC, and his father Vincent Martin, MD, professor in the division of general internal medicine, UC Health physician and headache expert, ...
False beliefs persist, even after instant online corrections
2013-01-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio - It seems like a great idea: Provide instant corrections to web-surfers when they run across obviously false information on the Internet.
But a new study suggests that this type of tool may not be a panacea for dispelling inaccurate beliefs, particularly among people who already want to believe the falsehood.
"Real-time corrections do have some positive effect, but it is mostly with people who were predisposed to reject the false claim anyway," said R. Kelly Garrett, lead author of the study and assistant professor of communication at Ohio State University.
"The ...
Liquid crystal's chaotic inner dynamics
2013-01-24
Liquid crystal displays are ubiquitous. Now, Polish physicists have demonstrated that the application of a very strong alternating electric field to thin liquid crystal cells leads to a new distinct dynamic effect in the response of the cells. The theory of spatio-temporal chaos explains this effect. It was elucidated by Wojciech Jeżewski and colleagues from the Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, in Poznań, Poland, and is about to be published in EPJ E. This effect has implications for the operation of liquid-crystal devices because their ...
Adolescent sexual and reproductive health priorities identified
2013-01-24
Quality sexual and reproductive health care is an essential component of public health. However, there are insufficient evidence-based policies related to adolescent sexual and reproductive health in low- and middle-income countries. In an effort to address the research gap, faculty from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health led a project to identify research priorities for adolescent sexual and reproductive health in these countries. The results, which are based on input from nearly 300 experts and highlight key focus areas, are featured in the January issue ...
Some minority students may fare better than whites when working part time, new research finds
2013-01-24
WASHINGTON - African-American and Hispanic students may be less likely than non-Hispanic white students to hold a job during the school year, but when they do, they tend to work somewhat longer hours and seem less likely to see their grades suffer than non-Hispanic white students with jobs, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
A study involving nearly 600,000 students from around the country also found that among high school students who work long hours at a part-time job, black and Hispanic students from lower income households ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] Right target, but missing the bulls-eye for Alzheimer'sUCLA researchers discover new point of attack for drug therapy