(Press-News.org) TORONTO, Jan. 23, 2013—Smokers who quit when they are young adults can live almost as long as people who never smoked, groundbreaking new research has found.
Smoking cuts at least 10 years off a person's lifespan. But a comprehensive analysis of health and death records in the United States found that people who quit smoking before they turn 40 regain almost all of those lost years.
"Quitting smoking before age 40, and preferably well before 40, gives back almost all of the decade of lost life from continued smoking," said Dr. Prabhat Jha, head of the Centre for Global Health Research at St. Michael's Hospital and a professor in the Dalla Lana School of Public Health at the University of Toronto.
"That's not to say, however, that it is safe to smoke until you are 40 and then stop," said Dr. Jha. "Former smokers still have a greater risk of dying sooner than people who never smoked. But the risk is small compared to the huge risk for those who continue to smoke."
His findings were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Jha's team found that people who quit smoking between ages 35 and 44 gained about nine years and those who quit between ages 45-54 and 55-64 gained six and four years of life, respectively.
The study is unique as it examines the risks of smoking and the benefits of stopping among a representative sample of Americans. Earlier studies had examined specific groups such as nurses or volunteers who are healthier than average Americans overall. Importantly, the study is among the first to document the generation of women who started smoking when they were young and kept smoking through their adult lives.
"Women who smoke like men, die like men," Dr. Jha said. For women, the risks of dying from smoking-related causes are 50 per cent greater than found in the studies conducted in the 1980s.
Women and men who smoke both lost a decade of life. Current male or female smokers ages 25-79 had a mortality rate three times higher than people who had never smoked. Never smokers were about twice more likely to live to age 80 than were smokers.
This study adds to recent evidence from Britain, Japan and the United States that smoking risks involve about a decade of life lost worldwide. This includes a review of 50 years of smoking mortality in the United States published in the same issue of the New England Journal of Medicine and led by Dr. Michael J. Thun and other researchers from the American Cancer Society.
While about 40 million Americans and 4 million Canadians smoke, most of the world's estimated 1.3 billion smokers live in low- and middle-income countries. Worldwide about 30 million young adults begin smoking each year (about half of all young men and 10 per cent of young women) and most do not stop.
In many high-income countries more than half of people who ever smoked have quit, cessation remains uncommon in most low- and middle-income people. On current trends, smoking will kill about 1 billion people in the 21st century as opposed to 'only' 100 million in the 20th century.
Professor Amartya Sen, the noted Harvard University economist who won the 1998 Nobel Prize in economics, said "the inability to develop an appropriate public policy about smoking has been one of the bigger failures of public action in India, China and most other developing countries, in contrast to strong tobacco control in most western countries.
"This study brings out how great the threat actually is, and shows that risks of death from smoking are even larger than previously thought," said Professor Sen, who was not involved in the study. "The result is of great global significance."
Dr. Jha noted that smoking rates in the United States, China and India would decline much faster if their governments levied high taxes on tobacco, as seen in Canada and France. Taxation is the single most effective step to get adults to quit and to prevent children from starting, he said.
Dr. Jha's research used data from the U.S. National Health Interview Survey in which a representative cross-section of the population is surveyed every year about a broad range of health topics. More than 200,000 survey participants were linked to the National Death Index, which includes death certificate information for all Americans since 1986. The researchers related about deaths of about 16,000 people to their past reported smoking.
Dr. Jha advises various governments around the world on disease control strategies. He is the principal investigator of the Million Death Study in India, one of the largest studies of premature deaths in the world.
###The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Disease Control Priorities-3 project of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
About St. Michael's Hospital
St. Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in more than 23 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, care of the homeless and global health are among the Hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Center, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
For more information, to obtain video clips of Dr. Jha discussing this paper or to interview Dr. Jha, please contact:
Leslie Shepherd
Manager, Media Strategy
Phone: 416-864-6094
shepherdl@smh.ca
St. Michael's Hospital
Inspired Care. Inspiring Science.
www.stmichaelshospital.com
Follow us on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/stmikeshospital
Asian media can contact Prabha Sati, Phone: +91 971 196 4550 email: satip@smh.ca to arrange interviews with Dr. Jha.
See PowerPoint slides, Frequently Asked Questions and other materials at www.cghr.org/tobacco
Smokers who quit before age 40 have lifespan almost as long as people who never smoked
Study also finds women who smoke like men, die like men
2013-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Estrogen fights urinary infection in mouse study
2013-01-24
Estrogen levels drop dramatically in menopause, a time when the risk of urinary tract infections increases significantly.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found new evidence in mice that the two phenomena are connected by more than just timing. If further research confirms these links, boosting estrogen levels may get a second look as an approach for reducing urinary infections in menopausal women.
"Scientists tested estrogen as a treatment for post-menopausal women with urinary tract infections in the 1990s, but the results ...
Right target, but missing the bulls-eye for Alzheimer's
2013-01-24
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of late-life dementia. The disorder is thought to be caused by a protein known as amyloid-beta, or Abeta, which clumps together in the brain, forming plaques that are thought to destroy neurons. This destruction starts early, too, and can presage clinical signs of the disease by up to 20 years.
For decades now, researchers have been trying, with limited success, to develop drugs that prevent this clumping. Such drugs require a "target" — a structure they can bind to, thereby preventing the toxic actions of Abeta.
Now, ...
Discovery of new class of damage-prone DNA regions could lead to better cancer treatments
2013-01-24
Cancer is thought to arise from DNA damage at fragile sites in the genome. A study published by Cell Press on January 24th in the journal Cell reveals a new class of fragile sites that contributes to DNA alterations in a type of blood cancer called B cell lymphoma The findings could lead to the development of more effective treatments for B cell lymphoma and potentially other cancers.
"This study describes an underlying mechanism of genome instability in B cell lymphoma that could not be previously explained," says senior study author André Nussenzweig of the National ...
Dung beetles follow the Milky Way
2013-01-24
You might expect dung beetles to keep their "noses to the ground," but they are actually incredibly attuned to the sky. A report published online on January 24 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, shows that even on the darkest of nights, African ball-rolling insects are guided by the soft glow of the Milky Way.
While birds and humans are known to navigate by the stars, the discovery is the first convincing evidence for such abilities in insects, the researchers say. It is also the first known example of any animal getting around by the Milky Way as opposed to ...
Dung beetles use stars for orientation
2013-01-24
An insect with a tiny brain and minimal computing power has become the first animal proven to use the Milky Way for orientation. Scientists from South Africa and Sweden have published findings showing the link between dung beetles and the spray of stars which comprises our galaxy.
Although their eyes are too weak to distinguish individual constellations, dung beetles use the gradient of light to dark provided by the Milky Way to ensure they keep rolling their balls in a straight line and don't circle back to competitors at the dung pile.
"The dung beetles don't care which ...
Discovering the secrets of tumor growth
2013-01-24
Scientists at the University of Copenhagen's Center for Healthy Ageing have identified a compound that blocks the expression of a protein without which certain tumours cannot grow. This compound has the potential as an anticancer agent according to the research published in the journal CHBIOL: Chemistry and Biology this week.
The BLM protein is also known to be important in maintaining stability in cells when they multiply, thus preventing cancer. However, certain types of tumour need BLM to grow. This is typical of osteosarcomas - aggressive malignant tumours often seen ...
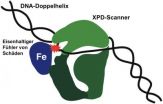
A scanner for hereditary defects
2013-01-24
Our DNA is constantly under attack from UV light, toxins and metabolic processes. Proteins and enzymes continually repair the damaged DNA. Unrecognized and therefore unrepaired damage to the genetic material, however, accelerates aging and causes cancer and genetic disorders. A team headed by veterinary pharmacologist and toxicologist Hanspeter Nägeli has now discovered that the protein XPD plays a key role in locating damaged DNA.
XPD protein as scanner
Genetic information is stored on approximately three billion base pairs of adenine/thymine or cytosine/guanine in ...
Research ties lightning to onset of headache, migraines
2013-01-24
CINCINNATI—University of Cincinnati (UC) researchers have found that lightning may affect the onset of headache and migraines.
These results, published in the Jan. 24, 2013 online edition of the journal Cephalalgia, are the first tying lightning to headache and could help chronic sufferers more efficiently anticipate headache and migraine arrival and begin preventive treatment immediately.
Geoffrey Martin, fourth-year medical student at UC, and his father Vincent Martin, MD, professor in the division of general internal medicine, UC Health physician and headache expert, ...
False beliefs persist, even after instant online corrections
2013-01-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio - It seems like a great idea: Provide instant corrections to web-surfers when they run across obviously false information on the Internet.
But a new study suggests that this type of tool may not be a panacea for dispelling inaccurate beliefs, particularly among people who already want to believe the falsehood.
"Real-time corrections do have some positive effect, but it is mostly with people who were predisposed to reject the false claim anyway," said R. Kelly Garrett, lead author of the study and assistant professor of communication at Ohio State University.
"The ...
Liquid crystal's chaotic inner dynamics
2013-01-24
Liquid crystal displays are ubiquitous. Now, Polish physicists have demonstrated that the application of a very strong alternating electric field to thin liquid crystal cells leads to a new distinct dynamic effect in the response of the cells. The theory of spatio-temporal chaos explains this effect. It was elucidated by Wojciech Jeżewski and colleagues from the Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, in Poznań, Poland, and is about to be published in EPJ E. This effect has implications for the operation of liquid-crystal devices because their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Smokers who quit before age 40 have lifespan almost as long as people who never smokedStudy also finds women who smoke like men, die like men