(Press-News.org) A newly-released study on early adoptees of the Primary Care Network initiative proposes that their success lies with three key elements: strong leadership, a redefined, inclusive workspace and allowance for creative discord.
In a paper published in Health Care Management Review, lead researcher Trish Reay of the Alberta School of Business and colleagues from the U of A, University of Calgary and Florida Atlantic University state that of eight centres that agreed to the government proposal to design and deliver comprehensive family health care, five were able to thrive by engaging in and adopting changes in standard practice.
Reay says that this reorganization of patient care into more comprehensive services reaps positive benefits for all parties – the patients, the doctors and other healthcare practitioners involved in the networks, and the healthcare system itself. And with over 2500 doctors now signed on the initiative, it is a system that holds promise for improved healthcare delivery in the province.
"What the doctors I've spoken to find attractive about the PCN model is, that by bringing other professionals and creating a team, it allows the physicians to practice medicine in the way they really want to," she said.
Follow the leader: healthcare managers guide successful integration
Reay noted that healthcare managers who were hired to organize the PCNs were an important catalyst of change. They facilitated group decision-making regarding the re-organization and re-allocation of work, such as counseling diabetes patients on lifestyles, from doctors to other healthcare professionals, such as nurses. The physicians were able to focus on the aspects of the practice for which they were solely qualified. Under this framework, the care and treatment of patients truly became a team approach.
"We found that the managers had to find ways to get the physicians and those around them to actually try these new, multidisciplinary mechanisms," said Reay. "These managers had a positive attitude and they set up a number of different ways that almost made them keep trying it for awhile. As they kept trying it, they made them talk about it and really think through how it was going."
Communication, space key components
Reay says that a re-organization and re-allocation of physical space was critical in developing teamwork and facilitating communication. But, the ability to communicate – and to disagree – also seemed to make the successful PCNs. Those who had not made successful transition were pleasant, but she said they constantly claimed to be "almost ready" to make the change, a sign that perhaps hid underlying communications issues. Those leaders that had managed the difficult conversations and found the ability to compromise and move forward were models of success.
"(Managers) encouraged people to disagree so that you could have a more full discussion about what was going on and really think through how to manage it," she said.
PCNS provide benefit for all
Reay said the doctors she spoke with are sold on PCNs because they allow them greater freedom to practice medicine the way they want, provide for maintained contact with their patients and offer them great work-life balance. As economic issues mean that healthcare has to do more with less, she says this model permits the PCNs to focus on healthcare needs of their patient community – areas such as mental health, diabetes, cardiac care, etc – and work preventatively providing counseling and information to people at-risk for chronic diseases.
"Patients actually like this model. They like the fact that they see their physicians still, but they don't have to rely on those quick office visits in order to ask questions and get more information and learn about whatever it may be that they have, said Reay. "In a business world, we'd say that this model is more 'user-friendly.'
"The client has a better and, I think, more effective experience in terms of learning to manage their own life and be healthy."
INFORMATION: END
(Boston) – A new study from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) shows that tissues derived from induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells in an experimental model were not rejected when transplanted back into genetically identical recipients. The study, published online in Cell Stem Cell, demonstrates the potential of utilizing iPS cells to develop cell types that could offer treatment for a wide range of conditions, including diabetes, liver and lung diseases, without the barrier of immune rejection.
Ashleigh Boyd, DPhil, and Neil Rodrigues, DPhil, the study's senior ...
Every day scientists learn more about how the world works at the smallest scales. While this knowledge has the potential to help others, it's possible that the same discoveries can also be used in ways that cause widespread harm.
A new article in the journal Nanomedicine, born out of a Federal Bureau of Investigation workshop held at the University of Notre Dame in September 2012, tackles this complex "dual-use" aspect of nanotechnology research.
"The rapid pace of breakthroughs in nanotechnology, biotechnology, and other fields, holds the promise of great improvements ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Dairy cows that are fed flaxseed produce more nutritious milk, according to a new study by Oregon State University.
Their milk contained more omega-3 fatty acids and less saturated fat, the study found.
Diets high in saturated fat can increase cholesterol and cause heart disease, while those rich in omega-3 and other polyunsaturated fatty acids may reduce the risk of heart disease, studies have shown.
Traditional cattle feed mixtures of corn, grains, alfalfa hay and grass silage result in dairy products with low concentrations of omega-3 and other ...
Ex-tropical cyclone Oswald doesn't know when to stop causing problems for Queensland, Australia, and now teamed up with a low pressure area, it continues to bring heavy rainfall. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the remnants and saw Oswald hugging the southeastern Queensland coast.
Oswald has dropped a lot of rainfall throughout Queensland. An earlier rainfall analysis using NASA's TRMM satellite data showed Oswald and its remnants had dropped over 600 mm (~23.6 inches) of rain in areas of the Cape York Peninsula near the Gulf of Carpentaria. Higher rainfall totals have ...
VIDEO:
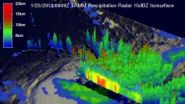
NASA's TRMM satellite saw tropical cyclone Garry moving through the open waters of the South Pacific Ocean on Jan. 25, 2013, at 0909 UTC. The heaviest rainfall (red) was occurring...
Click here for more information.
NASA's Aqua satellite identified powerful thunderstorms around the center of Cyclone Garry as the storm continued to intensify over warm waters of the South Pacific Ocean. Garry has prompted warnings for the southern group of the Cook Islands.
When NASA's ...
Railroad workers sue for asbestos and silica exposure injuries
In many respects, railroad work can be a dangerous job. Railroad workers are routinely exposed to risks that employees in other sectors do not encounter. The Federal Employers Liability Act aims to address these risks by providing injured railroad workers with the right to seek financial compensation for on-the-job injuries.
Occupational exposure claims -- for injuries or illnesses caused by repeated or prolonged exposure to hazardous substances -- are common FELA actions. Railroad workers who are injured ...
A felony conviction will haunt you
On May 23, 2012, 21-year-old University of Colorado Boulder graduate Zoey Ripple wandered drunk into a Boulder home at 3:30 a.m. The homeowners told police that Zoey came into their bedroom and approached their bed with some kind of light. They said she never said a word. The homeowners told her to leave several times and even warned her that they had a gun. When Zoey got about six feet from the couple, the husband shot her once in the hip.
Zoey not only suffered a fractured hip from the shot, but was charged with first-degree criminal ...
Freeh Report on Penn State Scandal Holds Corporate Governance Lessons
The recent indictment of former Penn State University President Graham Spanier alleges that Spanier engaged in a "conspiracy of silence" with other administrators to cover up the crimes of former football coach Jerry Sandusky. Although the media is likely to focus on the more salacious details of the Spanier indictment, it also holds important lessons for corporate boards.
One of the key points arising from the indictment of Spanier is the importance of the report of Judge Louis Freeh ...
Netflix Adopts Shareholder-Friendly Poison Pill
After Carl Icahn announced that he had acquired a 9.98 percent stake in Netflix, the company took steps to protect itself and its shareholders from a corporate takeover. The shareholder rights plan - also known as a poison pill - is intended to prevent Icahn from obtaining a controlling stake in the company. While the Netflix board sees its efforts as necessary to protect the company, Icahn claims that enacting the pill without a shareholder vote is an example of poor corporate governance.
The exact mechanism of the ...
An overview of workers' compensation in New York
It is an unfortunate reality that work can be dangerous. Of course, some professions are more hazardous than others, but nearly every job carries some risk of injury or illness.
A work-related injury can cause major disruptions in a person's life. At a minimum, there will be medical care to pay for. In some cases, the worker will need to take time off to recover. In others, he or she may be left with long-lasting disabilities.
When work injuries or illnesses happen, it is important for workers to avail themselves ...