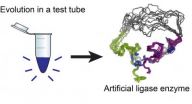
(Press-News.org) There's a wobbly new biochemical structure in Burckhard Seelig's lab at the University of Minnesota that may resemble what enzymes looked like billions of years ago, when life on earth began to evolve – long before they became ingredients for new and improved products, from detergents to foods and fuels.
Seelig created the fledgling enzyme by using directed evolution in the laboratory. Working with colleague Gianluigi Veglia, graduate student Fa-An Chao, and other team members, he subsequently determined its structure, which made its debut December 9 as an advance online publication in Nature Chemical Biology. Lab tests show that the enzyme (a type of RNA ligase, which connects two RNA molecules) functions like natural enzymes although its structure looks very different and it is flexible rather than rigid. Seelig speculates the new protein resembles primordial enzymes, before their current structures evolved.
Seelig and Veglia are professors in the College of Biological Sciences, where Fa-An Chao is a graduate student. Both faculty members have appointments in the Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics and Seelig is member of the BioTechnology Institute.
While a handful of groups worldwide are developing artificial enzymes, they use rational design to construct the proteins on computers. Instead, the Seelig lab employs directed evolution. "To my knowledge, our enzyme is the only entirely artificial enzyme created in a test tube by simply following the principles of natural selection and evolution," he says.
Rational enzyme design relies on preconceived notions of what a new enzyme should look like and how it should function. In contrast, directed evolution involves producing a large quantity of candidate proteins and screening several generations to produce one with the desired function. With this approach, the outcome isn't limited by current knowledge of enzyme structure.
"Just as in nature, only the fittest survive after each successive generation," Seelig explains. The process continues until it produces an enzyme that efficiently catalyzes a desired biochemical reaction. In this case, the new enzyme joins two pieces of RNA together.
"It's kind of like giving typewriters to monkeys," he says. "One monkey and one typewriter won't produce anything clever. But if you have enough monkeys and typewriters, eventually one of them will write 'to be or not to be'." The lottery provides another analogy. "If you buy more tickets, you're more likely to win," Seelig says.
Like all proteins, the new RNA ligase enzyme is a chain of amino acids folded into a 3D structure, but the resemblance stops there. Natural enzymes, like all proteins, are made from alpha helices and beta strands. Seelig's artificial enzyme lacks those structures. Instead, it forms around two metal ions and is not rigid. "Compared to enzymes we know from nature, the artificial enzyme has a rather unusual structure and dynamics," Seelig says.
For decades, naturally occurring enzymes have been tweaked by industry to make industrial processes and products more effective. The ability to create enzymes from scratch using a natural process opens the door to a vast array of new products that provide business opportunities and improve quality of life without harmful environmental effects.
Going forward, Seelig plans to create enzymes with useful applications while he continues to explore the underlying basic science of enzyme structure and function, aiming to learn more about the origin of enzymes and how proteins evolve.
"Enzymes have always fascinated me," he says. "It's rewarding to do work that has practical applications yet provides the opportunity to better understand how life on earth evolved."
INFORMATION:
U. of Minn. researchers unveil first artificial enzyme created by evolution in a test tube
2013-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers develop model for identifying habitable zones around star
2013-01-30
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Researchers searching the galaxy for planets that could pass the litmus test of sustaining water-based life must find whether those planets fall in a habitable zone, where they could be capable of having liquid water and sustaining life. New work, led by a team of Penn State researchers, will help scientists in that search.
Using the latest data, the Penn State Department of Geosciences team has developed an updated model for determining whether discovered planets fall within a habitable zone. The work builds on a prior model by James Kasting, ...
Reconcilable differences: Study uncovers the common ground of scientific opposites
2013-01-30
Searching for common elements in seemingly incompatible scientific theories may lead to the discovery of new ones that revolutionize our understanding of the world.
Such is the idea behind a mathematical framework Princeton University researchers developed that strips away the differences between scientific laws and theories to reveal how the ideas are compatible. In a recent report in the journal Physical Review Letters, the authors explain how the mathematical model finds common ground between the famously at-odds physics equations that govern classical and quantum ...
Mindfulness meditation heightens a listener's musical engagement
2013-01-30
EUGENE, Ore. -- (Jan. 30, 2013) -- When De'Anthony Thomas returned the opening kickoff for a touchdown in the 2013 Fiesta Bowl, says University of Oregon researcher Frank Diaz, Thomas put Ducks fans into a heightened zone of engagement for watching the game, not unlike what was experienced by music students who were first exposed to a brief session of mindfulness meditation before hearing an opera passage.
As a high school orchestra and band educator in Florida, Diaz had flirted with yoga and light meditation in a quest to heighten music engagement. He noticed, anecdotally, ...
Chronic kidney disease increases risk of death for both women and men
2013-01-30
A new study from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium (CKD-PC) found that in general chronic kidney disease is similarly associated with a higher risk of death and end stage renal disease for both women and men. The findings were released online in advance of publication in BMJ.
Chronic kidney disease affects 10 to 16 percent of adults worldwide. Current thresholds for chronic kidney disease are based on two kidney measures, estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albuminuria, a measure of protein ...
Researchers help confirm value of flow-diverting device for most challenging aneurysms
2013-01-30
CINCINNATI—A multi-center study supports the effectiveness of the newest technology available for the treatment of difficult, life-threatening brain aneurysms. The technology, the Pipeline embolization device, is a flow diverter that redirects blood flow away from wide-necked or giant aneurysms that cannot be treated in more conventional ways.
Andrew Ringer, MD, director of the division of cerebrovascular surgery and professor of neurosurgery and radiology at the University of Cincinnati (UC) College of Medicine, led the Cincinnati portion of the study, which was published ...
Scientists uncover previously unknown mechanism of memory formation
2013-01-30
JUPITER, FL, January 30, 2013 – It takes a lot to make a memory. New proteins have to be synthesized, neuron structures altered. While some of these memory-building mechanisms are known, many are not. Some recent studies have indicated that a unique group of molecules called microRNAs, known to control production of proteins in cells, may play a far more important role in memory formation than previously thought.
Now, a new study by scientists on the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute has for the first time confirmed a critical role for microRNAs in the ...
Study: Alternate walking and running to save energy, maintain endurance
2013-01-30
COLUMBUS, Ohio—Forget "slow and steady wins the race." A new study shows that, at least sometimes, the best way to conserve energy and reach your destination on time is to alternate between walking and running—whether your goal is the bus stop or a marathon finish line.
In the January 30, 2013 issue of the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, researchers examined how people budget their time as they travel on foot to reach a destination at a particular appointed time. The study found that when people have neither too much time nor too little time to reach their destination, ...
In-brain monitoring shows memory network
2013-01-30
Working with patients with electrodes implanted in their brains, researchers at the University of California, Davis, and The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) have shown for the first time that areas of the brain work together at the same time to recall memories. The unique approach promises new insights into how we remember details of time and place.
"Previous work has focused on one region of the brain at a time," said Arne Ekstrom, assistant professor at the UC Davis Center for Neuroscience. "Our results show that memory recall involves ...
New study shows 'just a bite' will satisfy
2013-01-30
How much chocolate would you need to eat to be satisfied? Less than half as much as you think, according to this recently published Cornell University snacking study. Using chocolate chips, apple pie, and potato chips, researchers Ellen van Kleef, Mitsuru Shimizu, and Brian Wansink designed a study to determine if people who were given smaller portions of snack foods would feel hungrier or satisfied fifteen minutes after eating.
Two groups with different portion sizes were tested. The larger portion size group was given 100g of chocolate, 200g of apple pie, and 80g ...
Cornell engineers solve a biological mystery and boost artificial intelligence
2013-01-30
ITHACA, N.Y. – By simulating 25,000 generations of evolution within computers, Cornell University engineering and robotics researchers have discovered why biological networks tend to be organized as modules – a finding that will lead to a deeper understanding of the evolution of complexity. (Proceedings of the Royal Society, Jan. 30, 2013.)
The new insight also will help evolve artificial intelligence, so robot brains can acquire the grace and cunning of animals.
From brains to gene regulatory networks, many biological entities are organized into modules – dense clusters ...