A new genre of 'intelligent' micro- and nanomotors
2013-01-30
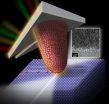
(Press-News.org) Enzymes, workhorse molecules of life that underpin almost every biological process, may have a new role as "intelligent" micro- and nanomotors with applications in medicine, engineering and other fields. That's the topic of a report in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, showing that single molecules of common enzymes can generate enough force to cause movement in specific directions.
Peter J. Butler, Ayusman Sen and colleagues point out that enzymes — proteins that jump-start chemical reactions — are the basis of natural biological motors essential to life. Scientists long have wondered whether a single enzyme molecule, the smallest machine that could possibly exist, might be able to generate enough force to cause its own movement in a specific direction. "Positive answers to these questions," they explain, "have important implications in areas ranging from biological transport to the design of 'intelligent,' enzyme-powered, autonomous nano- and micromotors, which are expected to find applications in bottom-up assembly of structures, pattern formation, cargo (drug) delivery at specific locations, roving sensors and related functions."
They provide the positive answers in experiments with two common enzymes called catalase and urease. Catalase protects the body from harmful effects of hydrogen peroxide formed naturally in the course of life. Urease, found in many plants, converts urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. The researchers show that these two enzymes, in the presence of their respective substrate (hydrogen peroxide or urea, which acts as fuel), show movement. More significantly, the movement becomes directional through the imposition of a substrate gradient, a form of chemotaxis. Chemotaxis is what attracts living things toward sources of food. The researchers also show that movement causes chemically interconnected enzymes to be drawn together; a form of predator-prey behavior at the nanoscale.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from The Pennsylvania State University Materials Research Science and Engineering Center supported by the National Science Foundation.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 163,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2013-01-30
PHILADELPHIA — Wear is a fact of life. As surfaces rub against one another, they break down and lose their original shape. With less material to start with and functionality that often depends critically on shape and surface structure, wear affects nanoscale objects more strongly than it does their macroscale counterparts.
Worse, the mechanisms behind wear processes are better understood for things like car engines than nanotech devices. But now, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania's School of Engineering and Applied Science have experimentally demonstrated ...
2013-01-30
ITHACA, N.Y. – In hospitals, poor floor design, storage closet clutter and crowded corridors can contribute to nurse and medical staff fatigue. These distractions can hurt patient care quality and result in higher medical costs.
Now, a new Cornell University study offers a spatial solution.
Rana Zadeh, Cornell assistant professor of design and environmental analysis in the College of Human Ecology, analyzed the floor plans and work patterns within five medical-surgical units at U.S. hospitals and found numerous opportunities to boost nurses' efficiency through better ...
2013-01-30
New research suggests that dual-identity immigrants — first-generation immigrants and their descendants who identify with both their cultural minority group and the society they now live in — may be more prone to political radicalism if they perceive their two cultural identities to be incompatible.
The new research is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Psychological scientist Bernd Simon from Kiel University in Germany and colleagues hypothesized that perceived incompatibility between the two cultural identities ...
2013-01-30
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Even in our DNA there is no refuge from rogues that prey on the elderly. Parasitic strands of genetic material called transposable elements — transposons — lurk in our chromosomes, poised to wreak genomic havoc. Cells have evolved ways to defend themselves, but in a new study, Brown University researchers describe how cells lose this ability as they age, possibly resulting in a decline in their function and health.
Barbara McClintock, awarded the Nobel Prize in 1983, made the original discovery of transposons in maize. Since then ...
2013-01-30
Boulder, Colo., USA - Geology content posted online 4 through 25 January 2013 cover topics from greenhouse gas emissions to video observations of erupting geysers in Russia and from the age of Earth to the age of Grand Canyon. Highlights and detailed information about each article are listed below.
1. Earth is mostly flat
2. Age maps of early Earth
3. Sagaing fault, Indo-Burmese wedge
4. Anthropogenic lead
5. The growth of a newly born submarine volcano
6. The Hemlo gold deposit, Ontario, Canada
7. Reptile and mammal fossils in the Karoo Basin, South Africa
8. ...
2013-01-30
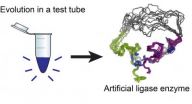
There's a wobbly new biochemical structure in Burckhard Seelig's lab at the University of Minnesota that may resemble what enzymes looked like billions of years ago, when life on earth began to evolve – long before they became ingredients for new and improved products, from detergents to foods and fuels.
Seelig created the fledgling enzyme by using directed evolution in the laboratory. Working with colleague Gianluigi Veglia, graduate student Fa-An Chao, and other team members, he subsequently determined its structure, which made its debut December 9 as an advance online ...
2013-01-30
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Researchers searching the galaxy for planets that could pass the litmus test of sustaining water-based life must find whether those planets fall in a habitable zone, where they could be capable of having liquid water and sustaining life. New work, led by a team of Penn State researchers, will help scientists in that search.
Using the latest data, the Penn State Department of Geosciences team has developed an updated model for determining whether discovered planets fall within a habitable zone. The work builds on a prior model by James Kasting, ...
2013-01-30
Searching for common elements in seemingly incompatible scientific theories may lead to the discovery of new ones that revolutionize our understanding of the world.
Such is the idea behind a mathematical framework Princeton University researchers developed that strips away the differences between scientific laws and theories to reveal how the ideas are compatible. In a recent report in the journal Physical Review Letters, the authors explain how the mathematical model finds common ground between the famously at-odds physics equations that govern classical and quantum ...
2013-01-30
EUGENE, Ore. -- (Jan. 30, 2013) -- When De'Anthony Thomas returned the opening kickoff for a touchdown in the 2013 Fiesta Bowl, says University of Oregon researcher Frank Diaz, Thomas put Ducks fans into a heightened zone of engagement for watching the game, not unlike what was experienced by music students who were first exposed to a brief session of mindfulness meditation before hearing an opera passage.
As a high school orchestra and band educator in Florida, Diaz had flirted with yoga and light meditation in a quest to heighten music engagement. He noticed, anecdotally, ...
2013-01-30
A new study from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium (CKD-PC) found that in general chronic kidney disease is similarly associated with a higher risk of death and end stage renal disease for both women and men. The findings were released online in advance of publication in BMJ.
Chronic kidney disease affects 10 to 16 percent of adults worldwide. Current thresholds for chronic kidney disease are based on two kidney measures, estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albuminuria, a measure of protein ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new genre of 'intelligent' micro- and nanomotors