A middle class that copes by shopping secondhand
2010-10-20
(Press-News.org) Conventional wisdom holds that people try to mimic the behavior of the next social class above their own.
Except when it comes to shopping at secondhand stores and yard sales, concludes a new study by Brigham Young University sociology students and faculty.
The study found that high-income shoppers scour the secondhand market for antiques, but everyone else is trying to stretch the family dollar.
"Middle-class shoppers were looking for furniture, some appliances, clothes, things that you could argue are necessities," said BYU sociology professor Ralph Brown. "There's a different sensibility now about how things work."
Brown and a group of undergrads gathered the data in a community that suffered the closure of a major employer several years before the national recession began in 2008. Brown mentored student Spencer James in this analysis of shopping behavior in the "thrift economy." James, who is now pursuing a Ph.D. at Penn State, is the lead author of the report in the current issue of the journal Family Relations.
James said in an email that thrift shopping plays a role in communities that is sometimes overlooked. Besides helping families get more for their money, neighborhood events like yard sales may also establish a sense of community.
BYU professor Todd Goodsell co-authored the study and found it noteworthy that thrift stores were used to cope financially at a time when 75 percent of the area's homes were considered affordable to families with a median income.
"It's got to be even worse now," Goodsell said.
And for that reason, the researchers are applying for grants to conduct a follow-up study.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-10-20
Seeing a child or a dog play is not a foreign sight. But what about a turtle or even a wasp?
Apparently, they play, too.
In fact, according to Gordon Burghardt, a psychology professor at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, many animals -- not just dogs, cats, and monkeys -- need a little play time.
"I studied the behavior of baby and juvenile reptiles for many years and never saw anything that I thought was play. Then I had an epiphany when I saw Pigface, a Nile softshell turtle, batting around a basketball at the National Zoo in Washington, D.C. I realized ...
2010-10-20
CLEVELAND – In a first-of-its-kind clinical trial, physicians at University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center who are Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine researchers are exploring the role of Vitamin D in preventing esophageal cancer. Principal Investigator Linda Cummings, MD, along with Amitabh Chak, MD, and Gregory Cooper, MD, from the UH Digestive Health Institute, is recruiting patients with Barrett's esophagus to measure the effects of Vitamin D on protein levels that may influence the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
"Vitamin D is being studied ...
2010-10-20
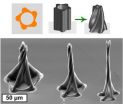
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Twisting spires, concentric rings, and gracefully bending petals are a few of the new three-dimensional shapes that University of Michigan engineers can make from carbon nanotubes using a new manufacturing process.
The process is called "capillary forming," and it takes advantage of capillary action, the phenomenon at work when liquids seem to defy gravity and travel up a drinking straw of their own accord.
The new miniature shapes, which are difficult if not impossible to build using any material, have the potential to harness the exceptional mechanical, ...
2010-10-20
SEATTLE, Wash.—October 18, 2010—Researchers at the Allen Institute for Brain Science have found that the same genes have different activity patterns in the brain in individuals with different genetic backgrounds. These findings may help to explain individual differences in the effectiveness and side-effect profiles of therapeutic drugs and thus have implications for personalized medicine. The study is available in this week's online early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (www.pnas.org).
In this study, the authors compared where in the brain ...
2010-10-20
Scientists at The Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital – The Neuro, McGill University have discovered that our brains have the ability to determine the shape of an object simply by processing specially-coded sounds, without any visual or tactile input. Not only does this new research tell us about the plasticity of the brain and how it perceives the world around us, it also provides important new possibilities for aiding those who are blind or with impaired vision.
Shape is an inherent property of objects existing in both vision and touch but not sound. Researchers ...
2010-10-20
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — University of Illinois chemists have developed a simple sensor to detect an explosive used in shoe bombs. It could lead to inexpensive, easy-to-use devices for luggage and passenger screening at airports and elsewhere.
Triacetone triperoxide (TATP) is a high-powered explosive that in recent years has been used in several bombing attempts. TATP is easy to prepare from readily available components and has been difficult to detect. It defies most standard methods of chemical sensing: It doesn't fluoresce, absorb ultraviolet light or readily ionize.
The ...
2010-10-20
A study published Oct. 19 in the open access journal Public Library of Science (PLoS) ONE, shows that not just human memories fade. Scientists from Arizona State University and the Norwegian University of Life Sciences examined how aging impacts the ability of honey bees to find their way home.
While bees are typically impressive navigators, able to wend their way home through complex landscapes after visits to flowers far removed from their nests, the study reveals that aging impairs the bees' ability to extinguish the memory of an unsuitable nest site even after the ...
2010-10-20
The United States and many other heavily populated countries face a growing threat of severe and prolonged drought in coming decades, according to results of a new study by National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) scientist Aiguo Dai.
The detailed analysis concludes that warming temperatures associated with climate change will likely create increasingly dry conditions across much of the globe in the next 30 years.
The drought may reach a scale in some regions by the end of the century that has rarely, if ever, been observed in modern times.
Using an ensemble ...
2010-10-20
Procedural sedation and analgesia is an essential element of care for children requiring painful procedures in the emergency department. The practice of combining ketamine and propofol, two common medications used in emergency departments, has become more popular. However, until recently, it was unclear whether this practice was superior to the use of either agent alone, especially in children.
Research led by Drs. Amit Shah, Gregory Mosdossy and Michael Rieder of the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at The University of Western Ontario and Lawson Health Research ...
2010-10-20
AMES, Iowa – The eyes of sheep infected with scrapie – a neurological disorder similar to mad cow disease – return an intense, almost-white glow when they're hit with blue excitation light, according to a research project led by Iowa State University's Jacob Petrich.
The findings suggest technologies and techniques can be developed to quickly and noninvasively test for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, progressive and fatal neurological diseases such as mad cow disease in cattle and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans. Petrich, in fact, is working to develop ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A middle class that copes by shopping secondhand