(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - The increasing incidence of allergic skin diseases, and the accompanying economic burden and heightened risk of developing other allergic conditions, have spurred researchers to look for better ways to control these immune system-based disorders.
Atopic dermatitis, more commonly called eczema, now affects 10 to 20 percent of children in the United States and direct health-care costs exceed $3 billion, according to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. What's more, up to 50 percent of children with atopic dermatitis will develop other allergic diseases, including asthma, a phenomenon termed the "allergic march," the gradual acquisition of co-existing allergic diseases.
David Artis, Ph.D., associate professor of Microbiology, and Brian Kim, M.D., clinical instructor of Dermatology, from the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, have identified a previously unknown critical role for a recently identified immune cell population in the progression of atopic dermatitis. They describe their findings in the latest issue of Science Translational Medicine.
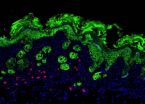
The team found an accumulation of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in the active lesions of patients with atopic dermatitis. Using a mouse model of atopic dermatitis they also showed that mouse ILCs contribute to disease progression. These studies suggest innate lymphoid cells may be a new therapeutic target in treating the development and severity of atopic dermatitis.
Under the Skin
"Like foot soldiers protecting the skin barrier from onslaught, innate lymphoid cells are present in healthy skin and we would predict that these cells play a role in maintaining normal tissue function and perhaps in protecting against microbes on this barrier," says Artis. "However, in chronic inflammatory diseases like atopic dermatitis, unchecked innate lymphoid cell responses can promote inflammation."
Kim adds, "A potential consequence of our more hygienic environment is that immune cells may be left somewhat redundant and so contribute to the increasing incidence of allergic diseases like eczema."
Many studies before the current one in STM have identified immune pathways that activate ILCs in such other tissues as the intestine and lung. "An unexpected finding of the current study is that innate lymphoid cells in the skin appear to be activated and regulated by different pathways," says Kim. "These findings suggest that tissue-specific local signals may regulate their function. This finding may also offer therapeutic potential to selectively target innate lymphoid cells in certain tissues, especially for limiting disease severity."
At present, the first-line therapy for atopic dermatitis remains topical steroids. Unlike other inflammatory diseases like psoriasis and arthritis that can be treated with modern biologic-based therapies, there are no targeted biologic therapies that are approved for use to treat atopic dermatitis.
"Our findings give us hope that new biologic therapies may be designed to treat atopic dermatitis in the future," says Artis.
These studies are part of a new collaboration between basic scientists in Penn's Department of Microbiology and Institute for Immunology, along with clinicians at Penn's Department of Dermatology. These studies are supported by the National Institutes of Health's Clinical and Translational Science Award program, which is administered through Penn's Institute for Translational Medicine and Therapeutics.
INFORMATION:
Research in the Artis lab is supported by the National Institutes of Health (AI061570, AI087990, AI074878, AI083480, AI095466, AI095608, AI097333, AI102942) and the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Investigator in Pathogenesis of Infectious Disease Award. Kim is funded by NIH grant KL2-RR024132. The study was also funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation Prospective Research Fellowship, the NCI Comprehensive Cancer Center Support Grant (2-P30 CA016520); the NIH/NIDDK P30 Center for Molecular Studies in Digestive and Liver Diseases (P30-DK050306), the National Center for Research Resources and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (KL2TR000139), and the Skin Disease Research Center (SDRC 5-P30-AR-057217).
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $479.3 million awarded in the 2011 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital — the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2011, Penn Medicine provided $854 million to benefit our community.
Itching for new help for eczema: Recently identified immune cells possible therapeutic target
Implications from Penn study for treating the development and severity of atopic dermatitis
2013-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists may have received millions in duplicate funding
2013-01-31
Big Data computation at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute at Virginia Tech reveals that over the past two decades funding agencies may have awarded millions and possibly billions of dollars to scientists who submitted the same grant request multiple times — and accepted duplicate funding.
An analysis led by Harold R. Garner, a professor at Virginia Tech, not only indicates that millions in funding may have been granted and used inappropriately, it points to techniques to uncover existing instances of duplicate funding and ways to prevent it in the future. The analysis ...
Setting the stage for a new paradigm in treatment of heart failure
2013-01-31
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Despite a substantial increase in the number of people suffering the debilitating and often deadly effects of heart failure, treatments for the condition have not advanced significantly for at least 10 years. An analysis by researchers at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine shows new breakthroughs could be closer than we thought.
The analysis points to striking similarities between heart cells in patients with heart failure and brain cells in patients with Alzheimer's disease, raising the possibility that some treatment approaches being ...
Current evidence does not support selenium for preventing heart disease in well-nourished adults
2013-01-31
A systematic review published today in The Cochrane Library finds that in well-nourished adults current evidence does not support selenium for preventing heart disease. The review suggests that taking selenium supplements does not reduce a person's risk of developing heart disease, although most evidence is currently limited to healthy American adults.
Diet is a key factor influencing heart disease risk. Selenium is one dietary element that could potentially play a role in preventing heart disease by protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation. It is a common ...
Brain activity study lends insight into schizophrenia
2013-01-31
Magnetic fields produced by the naturally occurring electrical currents in the brain could potentially be used as an objective test for schizophrenia and help to better understand the disease, according to new research published today.
A team of researchers from Plymouth and Spain have used the non-invasive magnetoencephalogram (MEG) technique to find two spectral features that are significantly different in schizophrenia patients compared to healthy control subjects.
Furthermore, they found that there were four spectral features in the brain signals of schizophrenia ...
Dementia: Cerebrolysin shows promise
2013-01-31
Dementia patients may benefit from a promising new treatment called Cerebrolysin, according to the results of a systematic review published in The Cochrane Library. The authors brought together the most up-to-date evidence on Cerebrolysin as a treatment for vascular dementia.
Vascular dementia is a common form of dementia caused by damage to the network of blood vessels supplying the brain. Some of the symptoms are similar to those associated with Alzheimer's disease and stroke but in particular those with vascular dementia often experience difficulty thinking quickly, ...
Chronic hepatitis C: Interferon may be harmful in re-treatment
2013-01-31
People with hepatitis C and chronic liver disease who relapsed or failed to respond to initial treatment are unlikely to improve on interferon retreatment. In fact, they may face an increased risk of dying sooner, and are likely to experience a variety of adverse effects, according to an updated systematic review published in The Cochrane Library.
Hepatitis C affects around 170 million people worldwide. In some cases, infection leads to chronic liver disease, liver failure or liver cancer, eventually resulting in death. Treatment is based on antiviral drugs.
Interferon ...
Tuberculosis: WHO-endorsed test offers rapid detection
2013-01-31
A diagnostic test for tuberculosis (TB) can accurately and quickly detect both TB and drug-resistant strains, according to a new study. The authors of a new systematic review assessing the diagnostic accuracy of the Xpert® MTB/RIF test published in The Cochrane Library say their study can provide timely advice for clinicians and policymakers in countries where TB is a major public health problem.
Millions of people develop TB every year. Around 13% of cases occur in people living with HIV and more than a quarter of these people die as a result. Drug resistance is a major ...
New research shows complexity of global warming
2013-01-31
Global warming from greenhouse gases affects rainfall patterns in the world differently than that from solar heating, according to a study by an international team of scientists in the January 31 issue of Nature. Using computer model simulations, the scientists, led by Jian Liu (Chinese Academy of Sciences) and Bin Wang (International Pacific Research Center, University of Hawaii at Manoa), showed that global rainfall has increased less over the present-day warming period than during the Medieval Warm Period, even though temperatures are higher today than they were then. ...
Tuberculosis may lurk in bone marrow stem cells of infected patients, Stanford researchers say
2013-01-31
STANFORD, Calif. - Tuberculosis is a devastating disease that kills nearly 2 million people worldwide each year. Although antibiotics exist that can ameliorate the symptoms, the courses of therapy last for months and don't completely eradicate the disease, which frequently recurs years or decades after the initial treatment.
Now, in a classic case of bench-to-bedside research, scientists at the Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered a possible reason for the disease's resistance: The ability of the tuberculosis bacteria to infiltrate and settle down in ...
Arunachal contributes in detecting stem cells where dormant TB bacteria hide
2013-01-31
The Idu-Mishmi community and Arunachal Pradesh appeared on the world map today for its greatest contribution in studying dormant Mycobacterium in TB that has affected nearly 4 billion people in the world and causing 1.9 million deaths yearly. In India, one person is dying of TB every 3 minutes. The study details and the contribution of Idu-Mishmis of Arunachal Pradesh and RIWATCH (Research Institute of World's Ancient Traditions Cultures and Heritage) in accomplishing the study has been duly acknowledged in a research paper published in a reputed journal 'Science Translational ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
[Press-News.org] Itching for new help for eczema: Recently identified immune cells possible therapeutic targetImplications from Penn study for treating the development and severity of atopic dermatitis