(Press-News.org) DENVER (Feb. 4, 2013) – Unfriending someone on Facebook may be as easy as clicking a button, but a new study from the University of Colorado Denver shows the repercussions often reach far beyond cyberspace.
"People think social networks are just for fun," said study author Christopher Sibona, a doctoral student in the Computer Science and Information Systems program at the University of Colorado Denver Business School. "But in fact what you do on those sites can have real world consequences."
Sibona found that 40 percent of people surveyed said they would avoid in real life anyone who unfriended them on Facebook. Some 50 percent said they would not avoid the person and the remaining 10 percent were unsure. Women said they would avoid contact more than men.
The study, published this month by the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, was based on 582 survey responses gathered via Twitter. Sibona found six factors that predicted whether someone would avoid a person who unfriended them.
If the person discussed the event after it happened.
If the emotional response to the unfriending was extremely negative.
If the person unfriended believed the action was due to offline behavior.
The geographical distance between the two.
If the troubled relationship was discussed prior to the unfriending.
How strong the person valued the relationship before the unfriending.
"The number one predictor was whether the person who said the relationship was over talked about it to someone else," Sibona said. "Talking to someone is a public declaration that the friendship is over."
Those who felt they had behaved badly offline and were being punished for that through unfriending also tended to avoid future contact.
"The gender finding that showed women tended to avoid the person who unfriended them more than men was interesting," Sibona. "But we really don't know why this is."
The study highlights how relationships are changing as the world becomes increasingly connected by the Internet. Americans now spend about 25 percent of their time online using social networks like Facebook which has over a billion members. The result is that traditional face-to-face communication is giving way to more remote online interactions which have their own rules, language and etiquette.
"The cost of maintaining online relationships is really low, and in the real world, the costs are higher," Sibona said. "In the real world, you have to talk to people, go see them to maintain face-to-face relationships. That's not the case in online relationships. "
Also, in the real world when a friendship ends it usually just fades away, Sibona said. On Facebook, it can be abruptly terminated with one party declaring the friendship over.
"Since it's done online there is an air of unreality to it but in fact there are real life consequences," he said. "We are still trying to come to grips as a society on how to handle elements of social media. The etiquette is different and often quite stark."
In 2010, Sibona authored a study on why people are unfriended on Facebook. He found the following top four reasons.
Frequent, unimportant posts.
Polarizing posts usually about politics or religion.
Inappropriate posts involving sexist, racist remarks
Boring everyday life posts about children, food, spouses etc.
Sibona said his current study demonstrates the power of being ostracized on social media.
He cited one experiment showing that subjects who experienced such ostracism had lower moods, less feeling of belonging, less sense of control and reduced self-esteem.
"People who are unfriended may face similar psychological effects…because unfriending may be viewed as a form of social exclusion," Sibona said. "The study makes clear that unfriending is meaningful and has important psychological consequences for those to whom it occurs."
### END
Study shows Facebook unfriending has real life consequences
Many avoid 'unfrienders' in real life
2013-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In a fight to the finish, Saint Louis University research aims knockout punch at hepatitis B
2013-02-04
ST. LOUIS – In research published in the Jan. 24 edition of PLOS Pathogens, Saint Louis University investigators together with collaborators from the University of Missouri and the University of Pittsburgh report a breakthrough in the pursuit of new hepatitis B drugs that could help cure the virus. Researchers were able to measure and then block a previously unstudied enzyme to stop the virus from replicating, taking advantage of known similarities with another major pathogen, HIV.
John Tavis, Ph.D., study author and professor of molecular microbiology and immunology ...
University of Leicester announces discovery of King Richard III
2013-02-04
UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER REVEALS:
Wealth of evidence, including radiocarbon dating, radiological evidence, DNA and bone analysis and archaeological results, confirms identity of last Plantagenet king who died over 500 years ago
DNA from skeleton matches TWO of Richard III's maternal line relatives. Leicester genealogist verifies living relatives of Richard III's family
Individual likely to have been killed by one of two fatal injuries to the skull – one possibly from a sword and one possibly from a halberd
10 wounds discovered on skeleton - Richard III killed ...
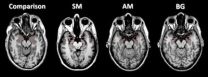
Human brain is divided on fear and panic
2013-02-04
When doctors at the University of Iowa prepared a patient to inhale a panic-inducing dose of carbon dioxide, she was fearless. But within seconds of breathing in the mixture, she cried for help, overwhelmed by the sensation that she was suffocating.
The patient, a woman in her 40s known as SM, has an extremely rare condition called Urbach-Wiethe disease that has caused extensive damage to the amygdala, an almond-shaped area in the brain long known for its role in fear. She had not felt terror since getting the disease when she was an adolescent.
In a paper published ...
New criteria for automated preschool vision screening
2013-02-04
San Francisco, CA, February 4, 2012 – The Vision Screening Committee of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, the professional organization for pediatric eye care, has revised its guidelines for automated preschool vision screening based on new evidence. The new guidelines are published in the February issue of the Journal of AAPOS.
Approximately 2% of children develop amblyopia, sometimes known as "lazy eye" – a loss of vision in one or both eyes caused by conditions that impair the normal visual input during the period of development of ...
A little tag with a large effect
2013-02-04
February 4, 2013, New York, NY and Oxford, UK – Nearly every cell in the human body carries a copy of the full human genome. So how is it that the cells that detect light in the human eye are so different from those of, say, the beating heart or the spleen?
The answer, of course, is that each type of cell selectively expresses only a unique suite of genes, actively silencing those that are irrelevant to its function. Scientists have long known that one way in which such gene-silencing occurs is by the chemical modification of cytosine—one of the four bases of DNA that ...
Shop King Jewelers 2013 Valentine's Day Jewelry Sale for Savings on Unique Valentine's Gifts & Valentine's Day Presents for Men and Women
2013-02-04
Searching for the perfect Valentine's Day gift doesn't have to be a stressful experience. King Jewelers believes that the pursuit of a unique valentine's gift for the one you love can be an enjoyable and extremely personal experience, even online. That's why for this Valentine's Day King Jewelers has put together an exclusive selection of fine jewelry, watches, diamond studs, diamond pendants and accessories for men and women that will make ideal Valentine's Day gift ideas for your loved one.
Valentines Day Gift Ideas for Him and Her
Online shoppers will find a wide ...
DNA reveals mating patterns of critically endangered sea turtle
2013-02-04
New University of East Anglia research into the mating habits of a critically endangered sea turtle will help conservationists understand more about its mating patterns.
Research published today in Molecular Ecology shows that female hawksbill turtles mate at the beginning of the season and store sperm for up to 75 days to use when laying multiple nests on the beach.
It also reveals that these turtles are mainly monogamous and don't tend to re-mate during the season.
Because the turtles live underwater, and often far out to sea, little has been understood about their ...
Changes to DNA on-off switches affect cells' ability to repair breaks, respond to chemotherapy
2013-02-04
PHILADELPHIA - Double-strand breaks in DNA happen every time a cell divides and replicates. Depending on the type of cell, that can be pretty often. Many proteins are involved in everyday DNA repair, but if they are mutated, the repair system breaks down and cancer can occur. Cells have two complicated ways to repair these breaks, which can affect the stability of the entire genome.
Roger A. Greenberg, M.D., Ph.D., associate investigator, Abramson Family Cancer Research Institute and associate professor of Cancer Biology at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of ...
Researchers discover mutations linked to relapse of childhood leukemia
2013-02-04
After an intensive three-year hunt through the genome, medical researchers have pinpointed mutations that leads to drug resistance and relapse in the most common type of childhood cancer—the first time anyone has linked the disease's reemergence to specific genetic anomalies.
The discovery, co-lead by William L. Carroll, MD, director of NYU Langone Medical Center's Cancer Institute, is reported in a study published online February 3, 2013, in Nature Genetics.
"There has been no progress in curing children who relapse, in spite of giving them very high doses of chemotherapy ...
Pioneering research helps to unravel the brain's vision secrets
2013-02-04
A new study led by scientists at the Universities of York and Bradford has identified the two areas of the brain responsible for our perception of orientation and shape.
Using sophisticated imaging equipment at York Neuroimaging Centre (YNiC), the research found that the two neighbouring areas of the cortex -- each about the size of a 5p coin and known as human visual field maps -- process the different types of visual information independently.
The scientists, from the Department of Psychology at York and the Bradford School of Optometry & Vision Science established ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Study shows Facebook unfriending has real life consequencesMany avoid 'unfrienders' in real life