(Press-News.org) West Orange, NJ. February 4, 2013. The final phase of the SCIRehab Project (Phase 3) was published in the November 2012 issue of the Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine (JSCM). Nine papers comprised the Special Issue: Relationship of Inpatient Rehabilitation Interventions to Outcomes Following Spinal Cord Injury. Guest editors: J. Scott Richards, Gale Whiteneck, Daniel Lammertse, Marcel Dijkers, and Julie Gassaway. Key article available for free download via ingentaconnect.com: Whiteneck G, Gassaway J. The SCIRehab Project: What rehabilitation interventions are most strongly associated with positive outcomes after spinal cord injury? Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine 2012;35(6): 482-483.
The SCIRehab Project Phase 1 and Phase 2 articles were published in JSCM in June 2009 and March 2011, respectively. The Project was funded by the National Institute on Disability and Rehabilitation, Research Office of Rehabilitative Services, US Department of Education, to Craig Hospital (H133A060103 and H133N060005), The Mount Sinai School of Medicine (H133N060027), the National Rehabilitation Hospital (H133N060028), Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (H133N060014) and to Shepherd Center (H133N060009), and Carolinas Rehabilitation.
The SCIRehab Project used practice-based evidence research methodology to investigate inpatient rehabilitation practices for acute spinal cord injury. The objective was to inform clinical decision-making by determining what interventions are associated with positive outcomes at discharge and one-year followup. More than 1000 clinicians collected detailed data on 460,000 interventions for 1376 patients at six sites in the US. Seven components of SCI rehabilitation were studied: psychology, nursing, physical, occupational and recreational therapy, speech-language pathology, and social work/case management. Each was defined and classified in Phase 1; treatment times were analyzed in Phase 2. Phase 3 details the associations between the interventions and patient outcomes at discharge and one-year post injury. The results provide an in-depth look at practice-based rehabilitation practices that can inform the direction of further research and guide clinicians in selecting interventions for patients with acute SCI.
###
The Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine (JSCM) serves the international community of professionals dedicated to improving the lives of people with injuries/disorders of the spinal cord. JSCM is the peer-reviewed official journal of the Academy of Spinal Cord Injury Professionals, a US-based multidisciplinary organization serving scientists, physicians, psychologists, nurses, therapists and social workers in the field of spinal cord injury care and research. The editor is Donald Bodner, MD, of the School of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio. JSCM is published 6 times a year by Maney Publishing.
JSCM publishes issue on NIDRR-funded project on practice-based evidence in SCI rehabilitation
Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine publishes Phase 3 articles for NIDRR-funded multi-site SCIRehab Project on practice-based evidence in spinal cord injury rehabilitation
2013-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enigmatic 'ribbon' of energy discovered by NASA satellite explained
2013-02-05
DURHAM, N.H. -- After three years of puzzling over a striking "ribbon" of energy and particles discovered by NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) at the edge of our solar system, scientists may be on the verge of cracking the mystery.
In a paper published Feb. 4, 2013, in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers, including lead author Nathan Schwadron of the University of New Hampshire, propose a "retention theory" that for the first time explains all the key observations of this astrophysical enigma.
"If the theory is correct," Schwadron notes, "the ribbon can ...
Scientists discover protein that allows safe recycling of iron from old red blood cells
2013-02-05
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – Humans survive by constantly recycling iron, a metal that is an essential component of red blood cells, but which is toxic outside of those cells. More than 90 percent of the iron in an adult human's 25 trillion life-sustaining red blood cells is recycled from worn-out cells.
Almost 50 years ago scientists first began hypothesizing that our bodies must have a special protein 'container' to safely transport heme -- the form of iron found in living things – during the breakdown and recycling of old red blood cells and other types of heme metabolism. ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Feb. 5, 2013
2013-02-05
1. Being Physically Fit Earlier in Life May Lower Risk for Dementia Later in Life
Having a higher fitness level at midlife seems to be associated with lower hazards of developing Alzheimer disease and other types of dementia later in life. Between 1970 and 2009, researchers at a community health clinic utilized an exercise treadmill test to assess the baseline fitness levels of 19,458 non-elderly, community-dwelling adults who were in generally good health. The researchers reviewed Medicare data for the patients who became eligible to receive benefits between January ...
New study shows that gases work with particles to promote cloud formation
2013-02-05
New York, NY—January 30, 2013—Researchers at Columbia Engineering and Georgia Institute of Technology have published a study in the online Early Edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) showing—for the first time—that certain volatile organic gases can promote cloud formation in a way never considered before by atmospheric scientists. The study will be published the week of February 4, 2013.
"This is the first time gases have been shown to affect cloud formation in this way," says V. Faye McNeill, Associate Professor in Chemical Engineering at ...
Hoodoos -- key to earthquakes?
2013-02-05
Please cite the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA) as the source of this information.
In the absence of long-term instrumental data, fragile rock formations, called hoodoos, may be key to understanding seismic hazard risk. In this study, researchers consider two hoodoos in Red Rock Canyon region to put limits on expected intensity of ground motion from earthquakes along the Garlock fault.
Hoodoos can be found in desert regions and are highly susceptible to erosion that makes their age uncertain. Despite that uncertainty, existing unfractured hoodoos, ...
Osaka Basin map: Identifies high-rise buildings at risk from quakes
2013-02-05
Please cite the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA) as the source of this information.
The Osaka Basin, Japan is home to many high-rise buildings that sit atop its thick soft sediments, vulnerable to long-period strong ground motions that last minutes. A new map created by Japanese researchers is intended to guide engineers and city planners in new construction and identifies existing buildings with the potential of resonance vibration.
The Osaka Basin in western Japan is surrounded by short mountain ranges, affected by large (M 8+) interplate earthquakes ...
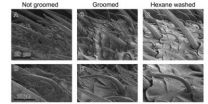
Grooming helps insects keep their senses sharpened
2013-02-05
Like a self-absorbed teenager, insects spend a lot of time grooming.
In a study that delves into the mechanisms behind this common function, North Carolina State University researchers show that insect grooming – specifically, antennal cleaning – removes both environmental pollutants and chemicals produced by the insects themselves.
The findings, published online this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that grooming helps insects maintain acute olfactory senses that are responsible for a host of functions, including finding food, ...
Antibody hinders growth of Gleevec-resistant gastrointestinal tumors in lab tests
2013-02-05
STANFORD, Calif. - An antibody that binds to a molecule on the surface of a rare but deadly tumor of the gastrointestinal tract inhibits the growth of the cancer cells in mice, according to researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The effect remains even when the cancer cells have become resistant to other treatments, and the findings may one day provide a glimmer of hope for people with the cancer, known as gastrointestinal stromal tumor, or GIST. The scientists hope to move into human clinical trials of the antibody within two years.
The antibody's ...
USC scientists design mouse with more human-like immune response
2013-02-05
LOS ANGELES — Medical scientists at the University of Southern California (USC) have bred a first-of-its-kind mouse model that possesses an immune response system more like a human's. The discovery makes way for quicker and more cost-effective development of next-generation drugs to treat human diseases like cancer, diabetes and tuberculosis.
Medical researchers have long used mice and rats to help formulate new drugs and vaccines, in part because their genetic and biological characteristics closely parallel human physiology. But mice are not humans, and many experimental ...
Cells predict onset of graft-versus-host disease in men receiving BMTs from female donors
2013-02-05
STANFORD, Calif. — Stanford University School of Medicine investigators have identified a clutch of cells that — if seen in a male patient's blood after receiving a brand-new immune system in the form of a bone-marrow transplant from a female donor — herald the onset of chronic graft-versus-host disease, or cGVHD. In this devastating syndrome, the patient's tissues come under a vicious and enduring assault by the transplanted cells.
"The overwhelming majority of patients who have these cells in their blood either have or will develop cGVHD within one to three months," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
[Press-News.org] JSCM publishes issue on NIDRR-funded project on practice-based evidence in SCI rehabilitationJournal of Spinal Cord Medicine publishes Phase 3 articles for NIDRR-funded multi-site SCIRehab Project on practice-based evidence in spinal cord injury rehabilitation