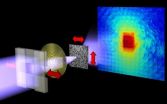
(Press-News.org) For more than 100 years radiography meant: don't move! In order to visualize nanostructures such as biological cells, the porous structure of cement or storage fields of magnetic disks, the experimentators had to avoid any kind of vibration of X-ray microscope and sample. In addition, only a small percentage fraction of the incoming X-ray radiation could be used. Using special filters, they had to select exactly the fraction with the right properties – for example, the right wavelength.
Contributions of different wavelengths separated
Pierre Thibault of the Technische Universitaet Muenchen and Andreas Menzel, scientist at the Paul Scherrer Institute (Villigen, Switzerland) have now developed an interpretation method that produces reliable images in spite of vibrations or fluctuations. The method is based on a technique called "ptychography", developed in the 1960s for electron microscopy. Thibault and Menzel's advancements now make it possible to distinguish effects originating from the contribution of different types of X-ray waves.
Fluctuations visualized
Probably the most significant result of the study is that it gives access to a whole class of objects that previously could hardly be investigated. "We now not only can compensate for the vibrations in the microscope," says Andreas Menzel. "We can even characterize fluctuations of the sample itself, even if they are much too fast to be seen with individual snapshots."
"We needed to convince ourselves that the images we produced did indeed reflect accurately the samples and their dynamics," says Pierre Thibault. "So we carried out computer simulations. They confirmed that effects of the instrument as well as of the sample itself, such as flows, switching events or mixed quantum states, can be characterized."
Microscopic view inside
The new method combines the characterization of dynamical states with high-resolution X-ray microscopy. One possible application is to analyze the changing magnetization of individual bits in magnetic storage media with high storage density. The interactions of such single magnetic bits or their thermal fluctuations, which ultimately determine the lifetime of magnetic data storage, could be visualized.
"In addition to its use in imaging," explains Pierre Thibault, "our analysis method also reveals a fundamental relationship to other disciplines: Microscopy and scientific disciplines such as quantum computing, previously regarded as independent, can benefit from each other here."
INFORMATION:
Publication:
Reconstructing state mixtures from diffraction measurements
Pierre Thibault & Andreas Menzel, Nature, 7 February 2013, DOI: 10.1038/nature11806
Improved X-ray microscopic imaging
X-ray microscopy technique makes fluctuations visible
2013-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breast milk reduces risk of sepsis and intensive care costs in very-low-birth-weight infants
2013-02-07
CHICAGO -- Feeding human breast milk to very-low-birth-weight infants greatly reduces risk for sepsis and significantly lowers associated neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) costs, according to a study by Rush University Medical Center researchers.
The study, published Jan. 31 in the advance online version of the Journal of Perinatology, showed that every 10 milliliters of human milk per kilogram that a very low birth weight infant received during the first 28 days of life decreased the odds of sepsis by almost 20 percent.
A daily dose of 25 to 49.99 milliliters of ...
Sensing the light, but not to see
2013-02-07
WOODS HOLE, MASS. -- Among the animals that are appealing "cover models" for scientific journals, lancelets don't spring readily to mind. Slender, limbless, primitive blobs that look pretty much the same end to end, lancelets "are extremely boring. I wouldn't recommend them for a home aquarium," says Enrico Nasi, adjunct senior scientist at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL). Yet Nasi and his collaborators managed to land a lancelet on the cover of the Journal of Neuroscience last December. These simple chordates, they discovered, offer insight into our own biological ...
Scientists identify genetic mechanism that contributed to Irish Famine
2013-02-07
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — When a pathogen attacks a plant, infection usually follows after the plant's immune system is compromised. A team of researchers at the University of California, Riverside focused on Phytophthora, the pathogen that triggered the Irish Famine of the 19th century by infecting potato plants, and deciphered how it succeeded in crippling the plant's immune system.
The genus Phytophthora contains many notorious pathogens of crops. Phytophthora pathogens cause worldwide losses of more than $6 billion each year on potato (Phytophthora infestans) and about ...
The deep roots of catastrophe
2013-02-07
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 7, 2013 – A University of Utah seismologist analyzed seismic waves that bombarded Earth's core, and believes he got a look at the earliest roots of Earth's most cataclysmic kind of volcanic eruption. But don't worry. He says it won't happen for perhaps 200 million years.
"What we may be detecting is the start of one of these large eruptive events that – if it ever happens – could cause very massive destruction on Earth," says seismologist Michael Thorne, the study's principal author and an assistant professor of geology and geophysics at the University ...
2 antibodies are better than 1
2013-02-07
Cancer drugs of the new, molecular generation destroy malignant breast tumors in a targeted manner: They block characteristic molecules on tumor cells - receptors for the hormones estrogen or progesterone, or a co-receptor, called HER2, that binds to many growth factors. But about one in every six breast tumors has none of these receptors. Such cancers, called triple-negative, are particularly aggressive and notoriously difficult to treat.
Some of these therapy-resistant cancers have a potential molecular target for cancer drugs, a growth-factor receptor called EGFR, ...
A genetic device performs DNA diagnosis
2013-02-07
Scientists hope that one day in the distant future, miniature, medically-savvy computers will roam our bodies, detecting early-stage diseases and treating them on the spot by releasing a suitable drug, without any outside help. To make this vision a reality, computers must be sufficiently small to fit into body cells. Moreover, they must be able to "talk" to various cellular systems. These challenges can be best addressed by creating computers based on biological molecules such as DNA or proteins. The idea is far from outrageous; after all, biological organisms are capable ...
Going along means getting along -- and that's not always good, Baylor study finds
2013-02-07
Caving in to social pressure — such as saying that you love a movie because friends do — makes for good vibes about being part of a group and can produce more of the same conduct, according to a Baylor University sociological study. The finding has implications for people ranging from philanthropists to gangs, researchers said.
"The punch line is very simple: Conformity leads to positive feelings, attachments, solidarity — and these are what motivate people to continue their behavior," said Kyle Irwin, Ph.D., an assistant professor of sociology at Baylor and lead author. ...
Observed: The outburst before the blast
2013-02-07
Before they go all-out supernova, certain large stars undergo a sort of "mini-explosion," throwing a good-sized chunk of their material off into space. Though several models predict this behavior and evidence from supernovae points in this direction, actually observations of such pre-explosion outbursts have been rare. In new research led by Dr. Eran Ofek of the Weizmann Institute, scientists found such an outburst taking place a short time – just one month – before a massive star underwent a supernova explosion.
The findings, which recently appeared in Nature, help ...
How to improve communication between parents and children after divorce
2013-02-07
How to improve communication between parents and children after divorce
Article provided by Law Office of Rebecca Garren Parker Visit us at http://www.rebeccaparkerlaw.com
Most people understand that divorce takes a toll on the finances and emotions of a family. However, some may not realize the burden a divorce can place on communication between family members, including communication between former spouses and between parents and children. By following a few simple tips, everyone can improve communication and help redefine and heal relationships after a divorce.
Communication ...
How parenting plans work in California
2013-02-07
How parenting plans work in California
Article provided by The Law Offices of Daniel S. Frank Visit us at http://www.danielfrankattorney.com
A parenting plan, also called a custody and visitation agreement, is a written agreement that where and with whom the child of divorcing parents will and defines the times the child will spend with the non-custodial parent. The main purpose of creating a parenting plan is to agree on how to share time with the child and how the parents will make important decisions regarding the child's welfare, such as education and health. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Improved X-ray microscopic imagingX-ray microscopy technique makes fluctuations visible