(Press-News.org) Researchers have identified a microRNA liver gene, miR-27b, which regulates lipid (cholesterol or fat) levels in the blood. This regulator gene controls multiple genes involved in dyslipidemia—abnormal blood cholesterol levels that can contribute to heart disease. Study details published in the February issue of Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), describe a new in silico approach to identify the significance of microRNAs in regulating disease-related gene pathways.
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed in April, 2003 and the world had a map of the 3 billion DNA letters making up the human genome. One of the HGP leaders was Dr. Francis Collins, currently NIH Director and contributor to the present study. "The HGP provided the basic instruction book for human biology," explains Dr. Collins. "Further genomic studies, such as the investigation of microRNAs, have built upon the efforts of the HGP to explain how the genome carries out its functions, and helps identify genes involved in the development of disease."
For the present study, lead author Dr. Kasey Vickers from the NIH/NHLBI Lipoprotein Metabolism Section (presently at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine) and colleagues performed high-throughput small RNA sequencing of mouse liver and detected roughly 150 microRNAs. The team used a novel in silico approach to identify microRNA regulatory hub genes involved in lipid metabolism. In human and mouse livers miR-27b was determined to be the strongest hub with 27 predicted targets.
"We found liver miR-27b levels to be sensitive to high triglycerides (hyperlipidemia) in the blood and liver," said Dr. Vickers. The team reported a nearly 3-fold increase in miR-27b levels in the liver of mice on a high-fat diet, with 42% of calories from fat. In human liver tissue cells, researchers determined that miR-27b regulates mRNA and protein expression of key lipid-metabolism genes (Angptl3 and Gpam). Vickers added, "Using a mouse model of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis, we found hepatic miR-27b and its target genes to be inversely altered, and thus contributing to risk for cardiovascular disease."
The senior author of the study, Dr. Praveen Sethupathy from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, leads an interdisciplinary laboratory that weaves together computational and experimental approaches to understand the role of microRNAs in complex metabolic diseases. "MicroRNAs are thought to impart stability to gene networks, particularly in the face of changes to the environment, such as diet," he says. "MicroRNAs represent promising therapeutic targets for a variety of metabolic diseases, but a lot more work remains to be done in order to fully appreciate how and when they function."
In a related editorial published in this month's issue of Hepatology, Dr. Carlos Fernández-Hernando from the New York University School of Medicine confirms the emergence of microRNAs in regulating cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism. He writes, "Altogether these data (by Vickers et al.) strongly suggest that miR-27b regulates lipid metabolism, but its role in regulating lipid levels in other cells, such as macrophages and neurons, remains unclear." Dr. Fernández-Hernando highlights the importance of the new in silico approach used by the researchers to identify microRNAs in regulating genes involved in the same bodily process, suggesting this method could be used to identify microRNAs in controlling genetic networks.
INFORMATION:
This study and editorial are published in Hepatology. Media wishing to receive a PDF of the articles may contact sciencenewsroom@wiley.com.
Full citations: "MicroRNA-27b is a Regulatory Hub in Lipid Metabolism and is Altered in Dyslipidemia." Kasey C. Vickers, Bassem M. Shoucri, Michael G. Levin, Han Wu, Daniel S. Pearson, David Osei-Hwedieh, Francis S. Collins, Alan T. Remaley and Praveen Sethupathy. Hepatology; (DOI: 10.1002/hep.25846); Print Issue Date: February, 2013.
URL: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/hep.25846
Editorial: "The Emerging Role of miRNAs in the Regulation of Lipid Metabolism." Carlos Fernández-Hernando. Hepatology; (DOI: 10.1002/hep.25960); Print Issue Date: February, 2013.
URL: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/hep.25960
Author Contact: To arrange an interview with Dr. Praveen Sethupathy, please contact Les Lang with UNC at llang@med.unc.edu or at 919-966-9366.
About the Journal
Hepatology is the premier publication in the field of liver disease, publishing original, peer-reviewed articles concerning all aspects of liver structure, function and disease. Each month, the distinguished Editorial Board monitors and selects only the best articles on subjects such as immunology, chronic hepatitis, viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, genetic and metabolic liver diseases and their complications, liver cancer, and drug metabolism. Hepatology is published on is published by Wiley on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). For more information, please visit http://wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/hep.
About Wiley
Founded in 1807, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. has been a valued source of information and understanding for more than 200 years, helping people around the world meet their needs and fulfill their aspirations. Wiley and its acquired companies have published the works of more than 450 Nobel laureates in all categories: Literature, Economics, Physiology or Medicine, Physics, Chemistry, and Peace.
Wiley is a global provider of content and content-enabled workflow solutions in areas of scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly research; professional development; and education. Our core businesses produce scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly journals, reference works, books, database services, and advertising; professional books, subscription products, certification and training services and online applications; and education content and services including integrated online teaching and learning resources for undergraduate and graduate students and lifelong learners. Wiley's global headquarters are located in Hoboken, New Jersey, with operations in the U.S., Europe, Asia, Canada, and Australia. The Company's Web site can be accessed at http://www.wiley.com. The Company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbols JWa and JWb.
END
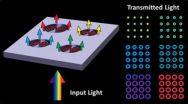
CHESTNUT HILL, MA (February 7, 2013) – Using the geometric and material properties of a unique nanostructure, Boston College researchers have uncovered a novel photonic effect where surface plasmons interact with light to form "plasmonic halos" of selectable output color. The findings appear in the journal Nano Letters.
The novel nanostructure proved capable of manipulating electron waves known as surface plasmon polaritons, or SPPs, which were discovered in the 1950s but of late have garnered the attention of scientists for their potential applications in fields that ...
Chicago (February 7, 2013): Colorectal surgical patients are often discharged from the hospital with vague guidance on how to recognize complications, but researchers at the Michael DeBakey Veterans Administration (VA) Medical Center and Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, aim to change that scenario. A health services research team convened a panel of surgical experts to develop a list of postoperative complication signs that should prompt colorectal surgical patients to call their surgeons or go to an emergency room. The study on the development of this early patient-centered ...
The hippocampus – a structure of the brain whose shape resembles that of a seahorse – is also called the "gateway" to memory. This is where information is stored and retrieved. Its performance relies on new neurons being continually formed in the hippocampus over the entire lifetime. "However, in old age, production of new neurons dramatically decreases. This is considered to be among the causes of declining memory and learning ability", Prof. Dr. Ana Martin-Villalba, a neuroscientist, explains.
Martin-Villalba, who heads a research department at the German Cancer Research ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Scientists have long puzzled over why "bad" bacteria such as E. coli can thrive in the guts of those with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), causing serious diarrhea. Now UC Davis researchers have discovered the answer—one that may be the first step toward finding new and better treatments for IBD.
The researchers discovered a biological mechanism by which harmful bacteria grow, edge out beneficial bacteria and damage the gut in IBD. This new understanding, published in the Feb. 8 issue of Science, may help researchers develop new treatments for ...
Jacob Rutt is a bright 11-year-old who likes to draw detailed maps in his spare time. But the budding geographer has a hard time with physical skills most children take for granted -- running and climbing trees are beyond him, and even walking can be difficult. He was diagnosed with a form of muscular dystrophy known as Duchenne when he was two years old.
The disease affects about 1 in 3,500 newborns -- mostly boys -- worldwide. It usually becomes apparent in early childhood, as weakened skeletal muscles cause delays in milestones such as sitting and walking. Children ...
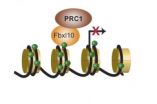
A single embryonic stem cell can develop into more than 200 specialized cell types that make up our body. This maturation process is called differentiation and is tightly regulated. If the regulation is lost, specialized cells cannot develop correctly during development. In adulthood, the specialized cells may forget their identity and develop into cancer cells. Research from BRIC, University of Copenhagen, has identified a crucial role of the molecule Fbxl10 in differentiation of embryonic stem cells and suggests the molecule as a new potential target for cancer therapy.
"Our ...
Highlights of this news release:
Six-month study finds that progestin-releasing contraceptives show a slight negative impact on metabolic markers, raising the risk for type 2 diabetes.
Contraceptive implants under the skin increase the risk more than uterine implants.
Longer and larger studies are needed to see if metabolic changes are temporary or long-term.
LOS ANGELES – A first-of-its-kind study by researchers at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California (USC) indicates that healthy, obese, reproductive-age women who use long-acting ...
Fishing communities living on the islands of Indonesia's Karimunjawa National Park have found an important balance, improving their social well-being while reducing their reliance on marine biodiversity, according to the Wildlife Conservation Society and the University of Western Australia.
Over the past 5 years, the Government of Indonesia has turned Karimunjawa National Park—a marine paradise of turquoise seas and mangrove-ringed islands in the Java Sea just south of Borneo—into a model of co-management for the country, largely by increasing community participation ...
ARGONNE, Ill. – Although scientists have been aware that magnetism and electricity are two sides of the same proverbial coin for almost 150 years, researchers are still trying to find new ways to use a material's electric behavior to influence its magnetic behavior, or vice versa.
Thanks to new research by an international team of researchers led by the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory, physicists have developed new methods for controlling magnetic order in a particular class of materials known as "magnetoelectrics."
Magnetoelectrics get their ...
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer that has few treatment options;
This large-scale study shows that abnormal levels of small molecules called microRNA can be used to classify this malignancy into four subtypes;
The findings could lead to new ways to identify the best therapy for individual patients and to more effective therapies in the future.
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new, large-scale study of triple-negative breast cancer shows that small molecules called microRNA can be used to define four subtypes of this aggressive malignancy.
The ...