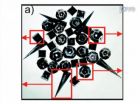
(Press-News.org) Government limits on mold toxins present naturally in grain crops should be expanded to include so-called "masked mycotoxins" that change from harmless to potentially harmful forms in the body, a new study concludes. It appears in ACS' journal Chemical Research in Toxicology.
Chiara Dall'Asta and colleagues explain that molds growing naturally on wheat, corn and other plants produce toxic substances termed mycotoxins. Some health experts regard mycotoxins as the most serious chronic dietary risk factor, greater than the potential health threats from pesticides and insecticides. Government regulations thus limit levels of mycotoxins that are permissible in food and animal feed. Plants protect themselves by binding or "conjugating" glucose, sulfur or other substances to the mycotoxin, producing conjugated mycotoxins that are not harmful.
Dall'Asta explains that these "masked mycotoxins" are not included in current safety regulations because of uncertainty about what happens when people and animals eat them. The new study focused on two of the most widespread mycotoxin contaminants of grain crops — deoxynivalenol (DON) and zearalenone (ZEN). The authors say their results show, for the first time, that bacteria present in the large intestine in people deconjugate or "unmask" DON and ZEN, releasing the original toxic forms. "For this reason, masked mycotoxins should be considered when evaluating population exposure," the study concludes.
###The authors acknowledge funding from the Basic Research Investment Fund (FIRB), the Italian Ministry of University and Research and the AGER Project "From Seed to Pasta."
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 163,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
'Masked' mold toxins in food should be included in safety regulations
2013-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Origami meets chemistry in scholarly video-article
2013-02-13
February 13, 2013
Cambridge, MA: The nanotechnology research space is rapidly growing, with vast implications for the healthcare, consumer electronics, surveillance, and defense industries. However, a major limitation to this research is the ability to create particles that vary in shape and function on a micrometer or nanometer scale.
To overcome these limitations, chemical engineers at Johns Hopkins University have developed self-assembling particles that are inspired by origami, the traditional Japanese art of folding paper into complex three-dimensional shapes. ...
A cooler way to protect silicon surfaces
2013-02-13
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Silicon, the material of high-tech devices from computer chips to solar cells, requires a surface coating before use in these applications. The coating "passivates" the material, tying up loose atomic bonds to prevent oxidation that would ruin its electrical properties. But this passivation process consumes a lot of heat and energy, making it costly and limiting the kinds of materials that can be added to the devices.
Now a team of MIT researchers has found a way to passivate silicon at room temperature, which could be a significant boon to solar-cell ...
Protein central to cancer stem cell formation provides new potential target
2013-02-13
HOUSTON - Researchers have identified a pivotal protein in a cellular transformation that makes a cancer cell more resistant to treatment and more capable of growing and spreading, making it an inviting new target for drug development.
Additionally, the international team led by scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center found the cancer drug sunitinib potentially has a new role in treating triple-negative, claudin-low breast cancer, a particularly resistant version of a type of cancer that is already difficult to treat.
"We found that FOXC2 lies ...
NASA's Chandra suggests rare explosion created our galaxy's youngest black hole
2013-02-13
New data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory suggest a highly distorted supernova remnant may contain the most recent black hole formed in the Milky Way galaxy. The remnant appears to be the product of a rare explosion in which matter is ejected at high speeds along the poles of a rotating star.
The remnant, called W49B, is about a thousand years old as seen from Earth and located about 26,000 light-years away.
"W49B is the first of its kind to be discovered in the galaxy," said Laura Lopez, who led the study at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. "It appears ...
By guessing, clinicians may miss 3/4 of alcohol problems
2013-02-13
SAN ANTONIO, Texas (Feb. 13, 2013) — By relying on hunches rather than posing a few screening questions, primary care clinicians may be missing three-fourths of the alcohol problems in their patients, a newly released analysis shows.
"It's often off the radar — people come in for hypertension and are not asked how much they drink," said study co-author Barbara J. Turner, M.D., M.S.Ed., M.A., M.A.C.P., of UT Medicine San Antonio. Primary care offices typically don't have good systems to administer questionnaires to screen for certain problems, including alcohol consumption, ...
Tube versus IV feeding in malnourished pediatric cancer patients
2013-02-13
About 60 percent of pediatric cancer patients experience malnourishment during treatment. At that point, patients and families have a choice: tube feeding or IV nutrition supplement. Which would you choose? A study published this week in the Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing shows that families' perceptions, especially of the discomfort of tube feeding, leads to choosing IV over tube – despite the fact that tube feeding is usually the better choice, associated with better gut function and lower rates of infection.
"Despite the benefits of tube feeding, we found a ...
Key molecule suppresses growth of cancerous liver tumors, Mayo study finds
2013-02-13
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A molecule already implicated in a number of diverse cellular functions can suppress the growth of tumors in the liver, a Mayo Clinic Cancer Center study has found. Its name is IQGAP1, and when the molecule is active in the cells that surround a tumor cell, this "tumor microenvironment" becomes less hospitable to cancer growth. When the molecule is deficient, cancer thrives.
Results of the study appear in the Journal of Clinical Investigation. The findings give new insight into cancer metastasis, the ability of a tumor to spread from its primary site ...
Engineers show feasibility of superfast materials
2013-02-13
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 13, 2013 – University of Utah engineers demonstrated it is feasible to build the first organic materials that conduct electricity on their edges, but act as an insulator inside. These materials, called organic topological insulators, could shuttle information at the speed of light in quantum computers and other high-speed electronic devices.
The study published this week in the journal Nature Communications will help pioneer a new field of research in materials science, in the same way organic materials lowered the cost and eased production of light-emitting ...
Epigenetics shapes fate of brain vs. brawn castes in carpenter ants
2013-02-13
PHILADELPHIA — The recently published genome sequences of seven well-studied ant species are opening up new vistas for biology and medicine. A detailed look at molecular mechanisms that underlie the complex behavioral differences in two worker castes in the Florida carpenter ant, Camponotus floridanus, has revealed a link to epigenetics. This is the study of how the expression or suppression of particular genes by chemical modifications affects an organism's physical characteristics, development, and behavior. Epigenetic processes not only play a significant role in many ...
Discovering cell surface proteins' behavior
2013-02-13
Contact:
Bingyun Sun, 778.782.9097, bingyun_sun@sfu.ca
Carol Thorbes, PAMR, 778.782.3035, cthorbes@sfu.ca
Simon Fraser University is Canada's top-ranked comprehensive university and one of the top 50 universities in the world under 50 years old. With campuses in Vancouver, Burnaby and Surrey, B.C., SFU engages actively with the community in its research and teaching, delivers almost 150 programs to more than 30,000 students, and has more than 120,000 alumni in 130 countries.
Simon Fraser University: Engaging Students. Engaging Research. Engaging Communities.
...