(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
Motor development in children under five years of age can now be tested reliably: Together with colleagues from Lausanne, researchers from the University Children's Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich have determined normative data for different exercises such as hopping or running. This enables parents and experts to gage the motor skills of young children for the first time objectively and thus identify abnormalities at an early stage.
My child still can't stand on one leg or walk down the stairs in alternating steps while all the other children already can. Are my child's motor skills normal or does he need therapy? Parents of children of a pre-school age often ask questions like these and experts wonder from which age a child should really be able to perform certain motor tasks.
Until now, there has been a lack of reliable data that describes the age from which children are able to stand on one leg, hop on one leg, climb stairs or run. Such standards have been lacking as it was assumed that motor performance in children under the age of five could not be measured reliably. For children aged between five and eighteen, however, there is an instrument called the Zurich Motor Assessment created by Remo Largo and his team at the University Children's Hospital Zurich in 2001. This test procedure is used by many experts to examine neuromotor skills in children of a school age.
New tests for young children
Neurophysiologist Tanja Kakebeeke and developmental pediatrician Oskar Jenni from the University Children's Hospital Zurich have now extended this test, simplified it for pre-school children aged between three and five and collected normative data for this age group. The test contains gross and fine motor exercises and additional tasks where children are supposed to run, hop, climb stairs and balance.
The tests described in their study reveal that young pre-school children are not yet able to perform certain tasks such as hopping or standing on one leg for longer than two seconds. "Children develop these skills between the age of three and five but very quickly and they are able to at the age of five," explains Kakebeeke.
At the age of three, only forty percent of the children were able to stand on one leg briefly. At five years of age, they all could. As soon as a child was able to do a task and his or her performance was measurable, it was classified on a five-point scale. The best performance, for example, was thus: The child can stand on one leg – the right and the left – for longer than five seconds. The normative data then developed from the proportion of children who can perform a skill and the actual performance of these children. With the normative data, motor development abnormalities can now be diagnosed at an early stage and therapeutic measures initiated.
### END
The age from when children can hop on one leg
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists unveil secrets of important natural antibiotic
2013-02-21
An international team of scientists has discovered how an important natural antibiotic called dermcidin, produced by our skin when we sweat, is a highly efficient tool to fight tuberculosis germs and other dangerous bugs.
Their results could contribute to the development of new antibiotics that control multi-resistant bacteria.
Scientists have uncovered the atomic structure of the compound, enabling them to pinpoint for the first time what makes dermcidin such an efficient weapon in the battle against dangerous bugs.
Although about 1700 types of these natural antibiotics ...
In rich and poor nations, giving makes people feel better than getting, research finds
2013-02-21
WASHINGTON - Feeling good about spending money on someone else rather than for personal benefit may be a universal response among people in both impoverished countries and rich nations, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Our findings suggest that the psychological reward experienced from helping others may be deeply ingrained in human nature, emerging in diverse cultural and economic contexts," said lead author Lara Aknin, PhD, of Simon Fraser University in Canada.
The findings provide the first empirical evidence that "the ...
Cell therapy a little more concrete thanks to VIB research
2013-02-21
Cell therapy is a promising alternative to tissue and organ transplantation for diseases that are caused by death or poor functioning of cells. Considering the ethical discussions surrounding human embryonic stem cells, a lot is expected of the so-called 'induced pluripotent stem cells' (iPS cells). However, before this technique can be applied effectively, a lot of research is required into the safety and efficacy of such iPS cells. VIB scientists associated to the UGent have developed a mouse model that can advance this research to the next step.
Lieven Haenebalcke ...
VHA plays leading role in health information technology implementation and research
2013-02-21
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2013) - The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is aiming to become a leader in using health information technology (HIT) to change the way patients experience medical care, to decrease medical mistakes, and to improve health outcomes. A special March supplement of Medical Care highlights new research into the many and varied types of HIT projects being explored to improve the quality of patient care throughout the VHA system. Medical Care is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The special issue ...
Antibacterial protein's molecular workings revealed
2013-02-21
On the front lines of our defenses against bacteria is the protein calprotectin, which "starves" invading pathogens of metal nutrients.
Vanderbilt investigators now report new insights to the workings of calprotectin – including a detailed structural view of how it binds the metal manganese. Their findings, published online before print in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could guide efforts to develop novel antibacterials that limit a microbe's access to metals.
The increasing resistance of bacteria to existing antibiotics poses a severe threat to ...
When water speaks
2013-02-21
Why certain catalyst materials work more efficiently when they are surrounded by water instead of a gas phase is unclear. RUB chemists have now gleamed some initial answers from computer simulations. They showed that water stabilises specific charge states on the catalyst surface. "The catalyst and the water sort of speak with each other" says Professor Dominik Marx, depicting the underlying complex charge transfer processes. His research group from the Centre for Theoretical Chemistry also calculated how to increase the efficiency of catalytic systems without water by ...
Sniffing out the side effects of radiotherapy may soon be possible
2013-02-21
Researchers at the University of Warwick and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust have completed a study that may lead to clinicians being able to more accurately predict which patients will suffer from the side effects of radiotherapy.
Gastrointestinal side effects are commonplace in radiotherapy patients and occasionally severe, yet there is no existing means of predicting which patients will suffer from them. The results of the pilot study, published in the journal Sensors, outline how the use of an electronic nose and a newer technology, FAIMS (Field Asymmetric ...
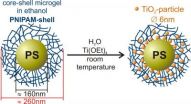
Titanium dioxide nanoreactor
2013-02-21
This press release is available in German.
Now, Dr. Katja Henzler and a team of chemists at the Helmholtz Centre Berlin have developed a synthesis to produce nanoparticles at room temperature in a polymer network. Their analysis, conducted at BESSY II, Berlin's synchrotron radiation source, has revealed the crystalline structure of the nanoparticles. This represents a major step forward in the usage of polymeric nanoreactors since, until recently, the nanoparticles had to be thoroughly heated to get them to crystallize. The last synthesis step can be spared due ...
Wanted: A life outside the workplace
2013-02-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A memo to employers: Just because your workers live alone doesn't mean they don't have lives beyond the office.
New research at Michigan State University suggests the growing number of workers who are single and without children have trouble finding the time or energy to participate in non-work interests, just like those with spouses and kids.
Workers struggling with work-life balance reported less satisfaction with their lives and jobs and more signs of anxiety and depression.
"People in the study repeatedly said I can take care of my job demands, ...
Research discovers gene mutation causing rare eye disease
2013-02-21
New Orleans, LA – Research conducted by Dr. Jayne S. Weiss, Professor and Chair of Ophthalmology at LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, and colleagues has discovered a new mutation in a gene that causes Schnyder corneal dystrophy (SCD.) The gene was found to be involved in vitamin K metabolism suggesting the possibility that vitamin K may eventually be found useful in its treatment. The findings are published in the February 2013 issue of the peer-reviewed journal, Human Mutation.
Schnyder corneal dystrophy is a rare hereditary eye disease that results in progressive ...