(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON - Feeling good about spending money on someone else rather than for personal benefit may be a universal response among people in both impoverished countries and rich nations, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Our findings suggest that the psychological reward experienced from helping others may be deeply ingrained in human nature, emerging in diverse cultural and economic contexts," said lead author Lara Aknin, PhD, of Simon Fraser University in Canada.
The findings provide the first empirical evidence that "the warm glow" of spending on someone else rather than on oneself may be a widespread component of human psychology, the authors reported in the study published online in APA's Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Researchers found a positive relationship between personal well-being and spending on others in 120 of 136 countries covered in the 2006-2008 Gallup World Poll. The survey comprised 234,917 individuals, half of whom were male, with an average age of 38. The link between well-being and spending on others was significant in every region of the world, and it was not affected by other factors among those surveyed, such as income, social support, perceived freedom and perceived national corruption, the study said.
The results were similar in several experiments the researchers themselves conducted with participants in wealthy and poor countries. For one analysis, they compared responses from 820 individuals recruited mostly from universities in Canada and Uganda. The participants wrote about a time they had either spent money on themselves or on others, after which they were asked to report how happy they felt. They were also asked if they spent money on another person to build or strengthen a relationship. People who remembered spending money on someone else felt happier than those who recalled spending money on themselves, even when the researchers controlled for the extent to which people built or strengthened a relationship, according to the study.
The researchers obtained the same results when they conducted an online survey of 101 adults in India. Some respondents were asked to recall recently spending money on themselves or someone else, while others were tested for their happiness level without recalling past spending. Those who recalled spending on someone else said they had a greater feeling of well-being than those who remembered spending on themselves or those who weren't asked about spending.
In another experiment, 207 university students in Canada and South Africa reported higher levels of well-being after purchasing a goody bag for a sick child rather than buying one for themselves. Both groups went to labs where they were given a small amount of money and told to buy a bag of treats for themselves or one for a child at a local hospital.
"From an evolutionary perspective, the emotional benefits that people experience when they help others acts to encourage generous behavior beneficial to long-term human survival," said Aknin.
###
Article: "Pro-social Spending and Well-Being: Cross-Cultural Evidence for a Psychological Universal," Lara B. Aknin, PhD, Simon Fraser University; Christopher P. Barrington-Leigh, PhD, McGill University; Elizabeth W. Dunn, PhD, and John F. Helliwell, PhD, University of British Columbia; Justine Burns, PhD, University of Cape Town; Robert Biswas-Diener, PhD; Imelda Kemeza, MS, Mbarara University of Science and Technology; Paul Nyende, MS, Makerere University; Claire E. Ashton-James, PhD, University of Groningen; Michael I. Norton, PhD, Harvard University; online Feb. 18, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology
Contact: Lara B. Aknin at laknin@sfu.ca or 604-729-9571.
The American Psychological Association, in Washington, D.C., is the largest scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the United States and is the world's largest association of psychologists. APA's membership includes more than 137,000 researchers, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. Through its divisions in 54 subfields of psychology and affiliations with 60 state, territorial and Canadian provincial associations, APA works to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve people's lives. END
In rich and poor nations, giving makes people feel better than getting, research finds
People worldwide may experience 'warm glow' from spending on others
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cell therapy a little more concrete thanks to VIB research
2013-02-21
Cell therapy is a promising alternative to tissue and organ transplantation for diseases that are caused by death or poor functioning of cells. Considering the ethical discussions surrounding human embryonic stem cells, a lot is expected of the so-called 'induced pluripotent stem cells' (iPS cells). However, before this technique can be applied effectively, a lot of research is required into the safety and efficacy of such iPS cells. VIB scientists associated to the UGent have developed a mouse model that can advance this research to the next step.
Lieven Haenebalcke ...
VHA plays leading role in health information technology implementation and research
2013-02-21
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 21, 2013) - The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is aiming to become a leader in using health information technology (HIT) to change the way patients experience medical care, to decrease medical mistakes, and to improve health outcomes. A special March supplement of Medical Care highlights new research into the many and varied types of HIT projects being explored to improve the quality of patient care throughout the VHA system. Medical Care is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The special issue ...
Antibacterial protein's molecular workings revealed
2013-02-21
On the front lines of our defenses against bacteria is the protein calprotectin, which "starves" invading pathogens of metal nutrients.
Vanderbilt investigators now report new insights to the workings of calprotectin – including a detailed structural view of how it binds the metal manganese. Their findings, published online before print in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could guide efforts to develop novel antibacterials that limit a microbe's access to metals.
The increasing resistance of bacteria to existing antibiotics poses a severe threat to ...
When water speaks
2013-02-21
Why certain catalyst materials work more efficiently when they are surrounded by water instead of a gas phase is unclear. RUB chemists have now gleamed some initial answers from computer simulations. They showed that water stabilises specific charge states on the catalyst surface. "The catalyst and the water sort of speak with each other" says Professor Dominik Marx, depicting the underlying complex charge transfer processes. His research group from the Centre for Theoretical Chemistry also calculated how to increase the efficiency of catalytic systems without water by ...
Sniffing out the side effects of radiotherapy may soon be possible
2013-02-21
Researchers at the University of Warwick and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust have completed a study that may lead to clinicians being able to more accurately predict which patients will suffer from the side effects of radiotherapy.
Gastrointestinal side effects are commonplace in radiotherapy patients and occasionally severe, yet there is no existing means of predicting which patients will suffer from them. The results of the pilot study, published in the journal Sensors, outline how the use of an electronic nose and a newer technology, FAIMS (Field Asymmetric ...
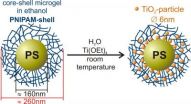
Titanium dioxide nanoreactor
2013-02-21
This press release is available in German.
Now, Dr. Katja Henzler and a team of chemists at the Helmholtz Centre Berlin have developed a synthesis to produce nanoparticles at room temperature in a polymer network. Their analysis, conducted at BESSY II, Berlin's synchrotron radiation source, has revealed the crystalline structure of the nanoparticles. This represents a major step forward in the usage of polymeric nanoreactors since, until recently, the nanoparticles had to be thoroughly heated to get them to crystallize. The last synthesis step can be spared due ...
Wanted: A life outside the workplace
2013-02-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A memo to employers: Just because your workers live alone doesn't mean they don't have lives beyond the office.
New research at Michigan State University suggests the growing number of workers who are single and without children have trouble finding the time or energy to participate in non-work interests, just like those with spouses and kids.
Workers struggling with work-life balance reported less satisfaction with their lives and jobs and more signs of anxiety and depression.
"People in the study repeatedly said I can take care of my job demands, ...
Research discovers gene mutation causing rare eye disease
2013-02-21
New Orleans, LA – Research conducted by Dr. Jayne S. Weiss, Professor and Chair of Ophthalmology at LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, and colleagues has discovered a new mutation in a gene that causes Schnyder corneal dystrophy (SCD.) The gene was found to be involved in vitamin K metabolism suggesting the possibility that vitamin K may eventually be found useful in its treatment. The findings are published in the February 2013 issue of the peer-reviewed journal, Human Mutation.
Schnyder corneal dystrophy is a rare hereditary eye disease that results in progressive ...
City layout key to predicting riots
2013-02-21
In the future police will be able to predict the spread of riots, and how they impact on cities, thanks to a new computer model.
Developed by researchers at UCL, the model highlights the importance of considering the layout of cities in order for police to suppress disorder as quickly as possible once a riot is in progress.
"As riots are rare events it is difficult to anticipate if and how they will evolve. Consequently, one of the main strategic issues that arose for the police during the 2011 London riots concerned when and where to deploy resources and how many ...
Rutgers neuroscientist sheds light on cause for 'chemo brain'
2013-02-21
It's not unusual for cancer patients being treated with chemotherapy to complain about not being able to think clearly, connect thoughts or concentrate on daily tasks. The complaint – often referred to as chemo-brain – is common. The scientific cause, however, has been difficult to pinpoint.
New research by Rutgers University behavioral neuroscientist Tracey Shors offers clues for this fog-like condition, medically known as chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment. In a featured article published in the European Journal of Neuroscience, Shors and her colleagues argue ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
[Press-News.org] In rich and poor nations, giving makes people feel better than getting, research findsPeople worldwide may experience 'warm glow' from spending on others