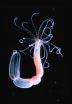
(Press-News.org) In many animals, the brain is located in a specific structure, the head, together with sensory organs and often together with the mouth. However, there are even more distantly related animals, which have a nervous system, but no brain, like sea anemones and corals.
In this collaborative study between a research group led by Fabian Rentzsch (Sars Centre Bergen) and Ulrich Technau from the Dept. of Molecular Evolution and Development the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis was used to find out if one of the ends of the sea anemone corresponds to the head of higher animals. To do this they studied the function of genes that control head development in higher animals during the embryonic development of the starlet sea anemone.
"Despite looking completely different, it has become clear over the last decade, that all animals have a similar repertoire of genes, including those that are required to make the head of higher animals", says Ulrich Technau from the Dept. of Molecular Evolution and Development.
Stands on its head
When the sea anemones are in the larval stage they swim and search for a suitable site for settlement and metamorphosis into a polyp. During this metamorphosis, it is the front end of the larva, which senses the environment and attaches to the ground, while the other end, transforms into the oral side of the animal with mouth and tentacles.
In contrast to everyone's expectation, the researchers found that the differentiation of the aboral (anterior) front of the sea anemone larva is governed by a hierarchy of genes, controlled by the upstream master control gene Six3/6. Notably, this gene as well its downstream dependent genes, also play a crucial role in setting up the field for making the brain of flies, fish and men. Hence, the function of the "head genes" is located at the end that corresponds to the "foot" of the adult animals. "The anterior end of the swimming larva carries their main sense organ, so at this stage it looks more like this might be their head", says Rentzsch, the leader of the Norwegian research team. And indeed, the "head genes" function on this side of the animals, yet they are not (yet) used to form a full brain.
Sea anemones and all higher animals, including humans, share a common brainless ancestor, which lived between 600 and 700 million years ago. By revealing the function of "head genes" in Nematostella, the authors believe that they now understand better how and from where the head and brain of higher animals evolved. Definitely, the gene network that formed a sensory centre has been evolved in this common ancestor some 600 million years ago.
"Based on the appearance of the adult animals, the aboral end of these animals has traditionally been called the foot and the upper end the head, while in fact it is basically turned upside down", explains Technau. "Or we..." he adds with a smile.
INFORMATION:
Publication in PLoS Biology:
Chiara Sinigaglia, Henriette Busengdal, Lucas Leclere, Ulrich Technau and Fabian Rentzsch (2013) The bilaterian head patterning gene six3/6 controls aboral domain development in a cnidarian. PLoS Biology
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001488
Scientific Contact:
Dr. Ulrich Technau
Department of Molecular
Evolution and Development
University of Vienna
1090 Wien, Althanstraße 14 (UZA I)
T +43-1-4277-570 00
M +43-664-60277-570 00
ulrich.technau@univie.ac.at
Press Contact:
Mag. Veronika Schallhart
Public Relations
Research and teaching
1010 Wien, Universitätsring 1
T +43-1-4277-175 30
M +43-664-60277-175 30
veronika.schallhart@univie.ac.at
The brainless origin of our head
2013-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
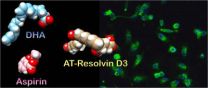
Aspirin and omega-3 fatty acids work together to fight inflammation
2013-02-21
Experts tout the health benefits of low-dose aspirin and omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like flax seeds and salmon, but the detailed mechanisms involved in their effects are not fully known. Now researchers reporting in the February 21 issue of the Cell Press journal Chemistry & Biology show that aspirin helps trigger the production of molecules called resolvins that are naturally made by the body from omega-3 fatty acids. These resolvins shut off, or "resolve," the inflammation that underlies destructive conditions such as inflammatory lung disease, heart disease, ...
Why living against the clock is a risky business
2013-02-21
Living against the clock—working late-night shifts or eating at inappropriate times, for example—can come with real health risks, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and diabetes among them. Now, researchers reporting in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, on February 21 have new evidence to explain why it matters not just what mice (or by extension, people) eat, but also when they eat it.
Insulin action rises and falls according to a 24-hour, circadian rhythm, the researchers found. What's more, mice unable to keep the time for one reason or another get stuck in an insulin-resistant ...
For monarchs to fly north, first they've got to chill
2013-02-21
Monarch butterflies are well known for their ability to fly 2,000 miles south from North America to Mexico each fall and back again in the spring. Now, researchers reporting in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, on February 21 have evidence to show that the butterflies would just keep on heading south if it weren't for the chilly weather.
The findings help to explain why the butterflies spend the winter on frosty mountaintops. They also imply that global climate change could profoundly influence the monarchs' migrations, the researchers say.
"The monarchs need ...
Biomarker may identify neuroblastomas with sensitivity to BET bromodomain inhibitors
2013-02-21
PHILADELPHIA — Neuroblastoma, the most common malignant tumor of early childhood, is frequently associated with the presence of MYCN amplification, a genetic biomarker associated with poor prognosis. Researchers have determined that tumors containing MYCN amplification are sensitive to a new class of drugs, BET bromodomain inhibitors.
The researchers made this discovery in a preclinical study, which was funded in part by a Stand Up To Cancer Innovative Research Grant and was published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"BET ...
Life's tiniest architects pinpointed by Yale researchers
2013-02-21
If a genome is the blueprint for life, then the chief architects are tiny slices of genetic material that orchestrate how we are assembled and function, Yale School of Medicine researchers report Feb. 21 in the journal Developmental Cell.
The study pinpoints the molecular regulators of epigenetics – the process by which unchanging genes along our DNA are switched on and off at precisely right time and place.
"Our genome is like a landscape with lakes, mountains, and rivers, but it is not yet a community or a city full of buildings," said Haifan Lin, director of the ...
Research shows that coldness triggers northward flight in migrating monarch butterflies
2013-02-21
WORCESTER, MA – Each fall millions of monarch butterflies from across the eastern United States begin a southward migration in order to escape the frigid temperatures of their northern boundaries, traveling up to 2,000 miles to an overwintering site in a specific grove of fir trees in central Mexico. Surprisingly, a new study by scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School published in Current Biology, suggests that exposure to coldness found in the microenvironment of the monarch's overwintering site triggers their return north every spring. Without this ...
New study indicates avocado consumption may be associated with better diet quality
2013-02-21
IRVINE, Calif. (February 20, 2013) – New analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) , a program of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), indicates that consuming avocados may be associated with better diet quality and nutrient intake level, lower intake of added sugars, lower body weight, BMI and waist circumferences, higher "good cholesterol" levels and lower metabolic syndrome risk. These results were published in the January 2013 issue of Nutrition Journal.
Specifically, the survey data (NHANES 2001-2008, ...
Early human burials varied widely but most were simple
2013-02-21
DENVER (Feb. 21, 2013) – A new study from the University of Colorado Denver shows that the earliest human burial practices in Eurasia varied widely, with some graves lavish and ornate while the vast majority were fairly plain.
"We don't know why some of these burials were so ornate, but what's striking is that they postdate the arrival of modern humans in Eurasia by almost 10,000 years," said Julien Riel-Salvatore, Ph.D., assistant professor of anthropology at CU Denver and lead author of the study. "When they appear around 30,000 years ago some are lavish but many aren't ...
Circadian clock linked to obesity, diabetes and heart attacks
2013-02-21
Disruption in the body's circadian rhythm can lead not only to obesity, but can also increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
That is the conclusion of the first study to show definitively that insulin activity is controlled by the body's circadian biological clock. The study, which was published on Feb. 21 in the journal Current Biology, helps explain why not only what you eat, but when you eat, matters.
The research was conducted by a team of Vanderbilt scientists directed by Professor of Biological Sciences Carl Johnson and Professors of Molecular Physiology ...
Bees attracted to contrasting colors when looking for nectar
2013-02-21
Flower colors that contrast with their background are more important to foraging bees than patterns of colored veins on pale flowers according to new research, by Heather Whitney from the University of Cambridge in the UK, and her colleagues. Their observation of how patterns of pigmentation on flower petals influence bumblebees' behavior suggests that color veins give clues to the location of the nectar. There is little to suggest, however, that bees have an innate preference for striped flowers. The work is published online in Springer's journal, Naturwissenschaften - ...