(Press-News.org) Many nations battling malaria face an economic dilemma: spend money indefinitely to control malaria transmission or commit additional resources to eliminate transmission completely. A review of malaria elimination conducted by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute and other institutions suggests stopping malaria transmission completely has longlasting benefits for many countries and that once eliminated, the disease is unlikely to reemerge over time. Furthermore, total eradication of malaria may not be necessary before countries that eliminate the disease within their own borders can rely on their health systems to control cases. The study is published in the February 22 edition of Science.
"Our research identified a number of changes that could explain the stability of malaria elimination. The key for us now is to determine whether elimination caused some of these changes, and to identify other countries where elimination could become a stable endpoint," said the study's senior author, David Smith, PhD, MS, professor in the Department of Epidemiology and the Malaria Research Institute at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
For the analysis, the researchers examined outcomes of the Global Malaria Eradication Programme, with activities starting in the late 1940s. When the program was defunded in 1969, the majority of countries that had achieved elimination stayed that way, while most countries that did not eliminate the disease continue to battle malaria today. The study analyzed data from countries that eliminated malaria, describing nearly a quarter of a million imported malaria cases−usually acquired during travel–compared with only about five thousand malaria cases transmitted in-country. Malaria transmission in elimination countries is rare today.
The researchers developed six hypotheses as to why malaria elimination remains stable over time. Among the reasons, researchers question whether economic development spurs a reduction in malaria transmission, independent of disease control measures, or if economic development is a byproduct of reduced illness from malaria. Other hypotheses consider benefits of mosquito control measures, effectiveness of outbreak management, and population travel patterns as reasons for keeping importation of new malaria infections low.
"If malaria elimination helps cause its own stability, then eradication may benefit from regional coordination, but it does not require a globally coordinated campaign. Malaria elimination can proceed like a ratchet, country-by-country and region-by-region, culminating in global eradication," explained Smith.
###
"The Stability of Malaria Elimination" was written by C. Chiyaka, A.J. Tatem, J.M. Cohen, P.W. Gething, G. Johnston, R. Gosling, R. Laxminarayan, S.I. Hay, and D.L. Smith.
The researchers were funded by grants from the Bloomberg Family Foundation, the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases at NIH, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, the Fogarty International Center at NIH, and the Wellcome Trust.
Eliminating malaria has longlasting benefits for many countries
2013-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scale-up of HIV treatment in rural South Africa dramatically increases adult life expectancy
2013-02-22
Boston, MA — The large antiretroviral treatment (ART) scale-up in a rural community in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, has led to a rapid and dramatic increase in population adult life expectancy—a gain of 11.3 years over eight calendar years (2004-2011)—and the benefit of providing ART far outweighs the cost, according to new research from Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH).
While previous studies have shown that ART significantly improves survival in clinical cohorts of HIV patients receiving ART, this is the first study to directly measure the full population-level ...
Caves point to thawing of Siberia
2013-02-22
Evidence from Siberian caves suggests that a global temperature rise of 1.5 degrees Celsius could see permanently frozen ground thaw over a large area of Siberia, threatening release of carbon from soils, and damage to natural and human environments.
A thaw in Siberia's permafrost (ground frozen throughout the year) could release over 1000 giga-tonnes of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, potentially enhancing global warming.
The data comes from an international team led by Oxford University scientists studying stalactites and stalagmites ...
Should grandma join Facebook? It may give her a cognitive boost, study finds
2013-02-22
For older adults looking to sharpen their mental abilities, it might be time to log on to Facebook.
Preliminary research findings from the University of Arizona suggest that men and women older than 65 who learn to use Facebook could see a boost in cognitive function.
Janelle Wohltmann, a graduate student in the UA department of psychology, set out to see whether teaching older adults to use the popular social networking site could help improve their cognitive performance and make them feel more socially connected.
Her preliminary findings, which she shared this month ...
Geoengineering by coalition
2013-02-22
Washington, D.C.—Solar geoengineering is a proposed approach to reduce the effects of climate change due to greenhouse gasses by deflecting some of the sun's incoming radiation. This type of proposed solution carries with it a number of uncertainties, however, including geopolitical questions about who would be in charge of the activity and its goals.
New modeling work from Carnegie's Katharine Ricke and Ken Caldeira shows that if a powerful coalition ever decided to deploy a geoengineering system, they would have incentive to exclude other countries from participating ...
Brown University researchers build robotic bat wing
2013-02-22
VIDEO:
The strong, flapping flight of bats offers great possibilities for the design of small aircraft, among other applications. By building a robotic bat wing, Brown researchers have uncovered flight secrets...
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Researchers at Brown University have developed a robotic bat wing that is providing valuable new information about dynamics of flapping flight in real bats.
The robot, which mimics the wing ...
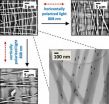
Researchers 'nanoweld' by applying light to aligned nanorods in solid materials
2013-02-22
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a way to melt or "weld" specific portions of polymers by embedding aligned nanoparticles within the materials. Their technique, which melts fibers along a chosen direction within a material, may lead to stronger, more resilient nanofibers and materials.
Physicists Jason Bochinski and Laura Clarke, with materials scientist Joe Tracy, placed specifically aligned gold nanorods within a solid material. Gold nanorods absorb light at different wavelengths, depending upon the size and orientation of the nanorod, ...
Scientists make older adults less forgetful in memory tests
2013-02-22
Toronto, Canada – Scientists at Baycrest Health Sciences' Rotman Research Institute (RRI) and the University of Toronto's Psychology Department have found compelling evidence that older adults can eliminate forgetfulness and perform as well as younger adults on memory tests.
Scientists used a distraction learning strategy to help older adults overcome age-related forgetting and boost their performance to that of younger adults. Distraction learning sounds like an oxymoron, but a growing body of science is showing that older brains are adept at processing irrelevant and ...
Immigration among Latin-American countries fails to improve income
2013-02-22
Although immigration to the United States from Latin American countries, particularly Mexico, has captured much public attention, immigrants who move between countries in Latin America have more difficulty than those moving to the United States.
Donald Bogue, professor emeritus in sociology and a distinguished scholar of demography, has found that unlike immigrants to the United States, immigrants between nations in Latin America frequently do not improve their lives by moving.
A popular theory on immigration contends that immigrants are self-selected achievers who ...
Why some soldiers develop PTSD while others don't
2013-02-22
Pre-war vulnerability is just as important as combat-related trauma in predicting whether veterans' symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) will be long-lasting, according to new research published in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Researcher Bruce Dohrenwend and colleagues at Columbia's Mailman School of Public Health and the New York State Psychiatric Institute found that traumatic experiences during combat predicted the onset of the full complement of symptoms, known as the PTSD "syndrome," in Vietnam ...
Why sourdough bread resists mold
2013-02-22
Sourdough bread resists mold, unlike conventionally leavened bread. Now Michael Gaenzle and colleagues of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, show why. During sourdough production, bacteria convert the linoleic acid in bread flour to a compound that has powerful antifungal activity. The research, which could improve the taste of bread, is published online ahead of print in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
The major benefits from the research are twofold: better tasting bread, says Gaenzle, because "preservatives can be eliminated from the recipes, ...