Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?
2013-02-22
(Press-News.org) Our ancestors evolutionarily split from those of rhesus monkeys about 25 million years ago. Since then, brain areas have been added, have disappeared or have changed in function. This raises the question, 'Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?'. Scientists have entertained the idea before but conclusive evidence was lacking. By combining different research methods, we now have a first piece of evidence that could prove that humans have unique cortical brain networks.
Professor Vanduffel explains: "We did functional brain scans in humans and rhesus monkeys at rest and while watching a movie to compare both the place and the function of cortical brain networks. Even at rest, the brain is very active. Different brain areas that are active simultaneously during rest form so-called 'resting state' networks. For the most part, these resting state networks in humans and monkeys are surprisingly similar, but we found two networks unique to humans and one unique network in the monkey."
"When watching a movie, the cortex processes an enormous amount of visual and auditory information. The human-specific resting state networks react to this stimulation in a totally different way than any part of the monkey brain. This means that they also have a different function than any of the resting state networks found in the monkey. In other words, brain structures that are unique in humans are anatomically absent in the monkey and there no other brain structures in the monkey that have an analogous function. Our unique brain areas are primarily located high at the back and at the front of the cortex and are probably related to specific human cognitive abilities, such as human-specific intelligence."
The study used fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans to visualise brain activity. fMRI scans map functional activity in the brain by detecting changes in blood flow. The oxygen content and the amount of blood in a given brain area vary according to a particular task, thus allowing activity to be tracked.
###
Contact person:
Professor Wim Vanduffel, Neurophysiology Research Group
Faculty of Medicine, KU Leuven
More information:
The full text of the study, "Evolutionary-Novel Functional Networks in the Human Brain?", is available on the website of The Journal of Neuroscience: http://www.jneurosci.org/content/33/8/3259.abstract. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2013-02-22
Researchers at Umeå University in Sweden conclude that public opposition to dam removal is not based on knowledge deficiency, as is sometimes argued in dam removal science. It is instead a case of different understandings and valuation of the environment and the functions it provides. The findings are now published in the journal Ecology and Society.
Dam removal is an increasingly common practice as old splash dams and small hydropower dams have become obsolete. Although the removal of these dams has ecological benefits by restoring rivers to their former courses, local ...
2013-02-22
PITTSBURGH—At a time when the U.S. government is contemplating changes to federal guidelines governing research with humans, serious questions are being raised about the role of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in overseeing such research. Particularly, vocal critics have cited lost time, money and even lives under a system that they claim consumes scarce resources and stifles academic freedom. In response, defenders of the IRB system point to the need to protect research participants from abuse.
Carnegie Mellon University's Alex John London, an internationally renowned ...
2013-02-22
Despite years of research, the genetic factors behind many human diseases and characteristics remain unknown. The inability to find the complete genetic causes of family traits such as height or the risk of type 2 diabetes has been called the "missing heritability" problem.
A new study by Princeton University researchers, however, suggests that missing heritability may not be missing after all — at least not in yeast cells, which the researchers used as a model for studying the problem. Published in the journal Nature, the results suggest that heritability in humans ...
2013-02-22
State supreme court justices who don't face voters are generally more effective than their elected counterparts, according to research led by Princeton University political scientists.
The research combines data about almost 6,000 state supreme court rulings nationwide between 1995 and 1998 with a new theoretical model to reach the conclusions that appointed justices generally bring a higher quality of information to the decision-making process, are more likely to change their preconceived opinions about a case, and are less likely to make errors than elected justices.
"Judges ...
2013-02-22
WASHINGTON, DC – With only one week left before sequestration is to take effect, America's research community sustained its call for an end to the across-the-board cuts to discretionary spending that will severely restrict the nation's ability to invest in the basic scientific research that drives innovation and produces economic growth. Sequestration will reduce federal funding for scientific research by nearly $95 billion over the next nine years, which will result in a reduction of U.S. GDP by at least $203 billion. The net impact will be 200,000 fewer jobs per year ...
2013-02-22
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 21, 2013 -- Rocket attacks in Sderot, Israel significantly increase the likelihood of miscarriages, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers.
The study, published in the January issue of Psychosomatic Medicine Journal of Bio-behavioral Medicine, compared 1,341 pregnancies of women (exposed group) who resided in Sderot, an area exposed to frequent rocket fire, with 2,143 pregnancies of women who lived in Kiryat Gat (unexposed group), which is out of range of missiles. Among women residing in the exposed ...
2013-02-22
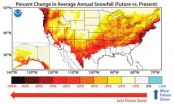
A new climate model predicts an increase in snowfall for the Earth's polar regions and highest altitudes, but an overall drop in snowfall for the globe, as carbon dioxide levels rise over the next century.
The decline in snowfall could spell trouble for regions such as the western United States that rely on snowmelt as a source of fresh water.
The projections are the result of a new climate model developed at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) and analyzed by scientists at GFDL and Princeton University. ...
2013-02-22
This press release is available in Spanish.
Studies at the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) are shedding some light on the microbes that dwell in cattle manure—what they are, where they thrive, where they struggle, and where they can end up.
This research, which is being conducted by Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientists at the agency's Agroecosystems Management Research Unit in Lincoln, Neb., supports the USDA priority of ensuring food safety. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency.
In one project, ARS microbiologist Lisa Durso ...
2013-02-22
Highlights
Dialysis patients using catheters to access the blood have the highest risks for death, infections, and cardiovascular events compared with patients using other types of vascular access.
Higher quality studies are needed to determine the true safety of different types of vascular access used for hemodialysis.
Worldwide, more than 1.5 million people are treated with hemodialysis.
Washington, DC (February 21, 2013) — Dialysis patients using catheters to access the blood have the highest risks for death, infections, and cardiovascular events compared with ...
2013-02-22
Highlights
Certain mutations and combinations of mutations in immune-related genes affect individuals' risk of developing a rare but serious kidney condition.
These mutations also affect patient prognosis following different treatments.About half of patients with the condition, called atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, develop kidney failure.
Washington, DC (February 21, 2013) — Certain gene mutations affect individuals' risk of developing a serious kidney condition, as well as their prognosis after being diagnosed with the disease, according to a study appearing in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Has evolution given humans unique brain structures?