Watching molecules grow into microtubes
2013-02-23
(Press-News.org) Newswise — Sometimes the best discoveries come by accident.
A team of researchers at Washington University in St. Louis, headed by Srikanth Singamaneni, PhD, assistant professor of mechanical engineering & materials science, unexpectedly found the mechanism by which tiny single molecules spontaneously grow into centimeter-long microtubes by leaving a dish for a different experiment in the refrigerator.
Once Singamaneni and his research team, including Abdennour Abbas, PhD, a former postdoctoral researcher at Washington University, Andrew Brimer, a senior undergraduate majoring in mechanical engineering, and Limei Tian, a fourth-year graduate student, saw that these molecules had become microtubes, they set out to find out how.
To do so, they spent about six months investigating the process at various length scales (nano to micro) using various microscopy and spectroscopy techniques.
The results were published in the journal Small.
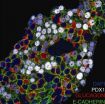
"What we showed was that we can actually watch the self-assembly of small molecules across multiple length scales, and for the first time, stitched these length scales to show the complete picture," Singamaneni says. "This hierarchical self-organization of molecular building blocks is unprecedented since it is initiated from a single molecular crystal and is driven by vesiclular dynamics in water."
Self-assembly, a process in which a disordered collection of components arrange themselves into an ordered structure, is of growing interest as a new paradigm in creating micro- and nanoscale structures and functional systems and subsystems. This novel approach of making nano- and microstructures and devices is expected to have numerous applications in electronics, optics and biomedical applications.
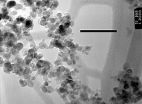
The team used small molecules p-aminothiophenol (p-ATP) or p-aminophenyl disulfide added to water with a small amount of ethanol. The molecules first assembled into nanovesicles then into microvesicles and eventually into centimeter-long microtubules. The vesicles stick onto the surface of the tube, walk along the surface and attach themselves, causing the tube to grow longer and wider. The entire process takes mere seconds, with the growth rate of 20 microns per second.
"While it was exciting to watch the self-assembly of these molecules, we are even more excited about the implications of the self-assembly of such small molecules," Singamaneni says. "This mechanism can be used to load the vesicles with the desired macromolecules, such as proteins, antibodies or antibiotics, for example, and build microtubes with a biological function."
Singamaneni says his research team collaborated with researchers in Singapore who are experts in molecular crystals, as well as with colleagues in the Department of Chemistry.
"We hope that once we can co-assemble some functional nanostructures along with these small molecules, then these molecular assemblies can have applications in biological sensors and chemical sensors," Singamaneni says.
###
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=vo_S_9XfFfE
Abbas A, Brimer A, Tian L, d'Avignon D, Hameed A, Vittal J, Singamaneni S. "Vesicle-Mediated Growth of Tubular Branches and Centimeter-Long Microtubes from a Single Molecule." Small. Early online publication Dec. 16, 2012.
Funding for this research was provided by the U.S. Army Research Office and Army Research Laboratory.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
PNNL rolls out its clean energy tech at ARPA-E
2013-02-23
NATIONAL HARBOR, Md. -- Researchers from the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory will exhibit their work at the 2013 Energy Innovation Summit of high-impact energy research funded by DOE's Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy, or ARPA-E. The summit runs Feb. 25-27 at the Gaylord Convention Center in National Harbor, Md. Below is an overview of PNNL research that will be highlighted there.
Nighttime solar power with cheaper thermal energy storage
Booth 1211
Solar power is a clean source of energy, but its use is limited to when the sun shines. ...
Lessons from cockroaches could inform robotics
2013-02-23
ANN ARBOR—Running cockroaches start to recover from being shoved sideways before their dawdling nervous system kicks in to tell their legs what to do, researchers have found. These new insights on how biological systems stabilize could one day help engineers design steadier robots and improve doctors' understanding of human gait abnormalities.
In experiments, the roaches were able to maintain their footing mechanically—using their momentum and the spring-like architecture of their legs, rather than neurologically, relying on impulses sent from their central nervous system ...
UNC-led study documents head and neck cancer molecular tumor subtypes
2013-02-23
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. - Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the seventh most common form of cancer in the United States, but other than an association with the human papillomavirus, no validated molecular profile of the disease has been established. By analyzing data from DNA microarrays, a UNC-led team has completed a study that confirms the presence of four molecular classes of the disease and extends previous results by suggesting that there may be an underlying connection between the molecular classes and observed genomic events, some of which affect known ...
Reprogramming cells to fight diabetes
2013-02-23
PHILADELPHIA – For years researchers have been searching for a way to treat diabetics by reactivating their insulin-producing beta cells, with limited success. The "reprogramming" of related alpha cells into beta cells may one day offer a novel and complementary approach for treating type 2 diabetes. Treating human and mouse cells with compounds that modify cell nuclear material called chromatin induced the expression of beta cell genes in alpha cells, according to a new study that appears online in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
"This would be a win-win situation ...
Color in fossil insects, diamonds from the ancient ocean floor and modeling the world's largest rivers
2013-02-23
Boulder, Colo., USA – Geology articles posted online ahead of print on 20 Feb. 2013 include several modeling and simulation studies as well as studies on the Exmouth Sub-basin, Australia; the West Kunlun Range, northern Tibetan Plateau; Krakenes Lake, Norway; the Azores islands; and the hot springs of Colorado. The 12 new papers cover a variety of topics:
Taking the easiest pathway to Earth's surface
A challenge to climate change and biotic factors to explain post-glacial lake acidification
Upper-crustal shortening in the Tibetan Plateau
Analysis of diamonds with ...
Geoscience Currents No. 70: Student choices for society membership in the geosciences
2013-02-23
Alexandria, VA – Geoscience Currents #70 presents the final data collected from
the GeoConnection Recruitment Packets distributed from 2009 to 2011. The
packets, which included informational brochures from several of AGI's member
societies, fliers with internship information, and a copy of EARTH Magazine's
"Workforce" edition, also offered students the opportunity to register with up
to five of AGI's professional member societies for free. This endeavor was meant
to increase student participation in the greater geoscience community.
Geoscience Currents #70 details ...
New device better traps viruses, airborne pathogens
2013-02-23
Washington University engineering researchers have created a new type of air-cleaning technology that could better protect human lungs from allergens, airborne viruses and ultrafine particles in the air.
The device, known as the SXC ESP, was created by a team led by Pratim Biswas, PhD, the Lucy & Stanley Lopata Professor and chair of the Department of Energy, Environmental & Chemical Engineering in the School of Engineering & Applied Science.
A recent study of the device, published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, found that it could help to prevent respiratory ...
Cyclone Haruna makes landfall in Madagascar
2013-02-23
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Haruna after it made landfall in southwestern Madagascar.
Haruna's center made landfall near Manombo, Madagascar around 0600 UTC (1 a.m. EST/U.S.) The METEO-7 satellite captured a visible image of Haruna at the time of landfall and showed that its eye had already become cloud-filled.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Haruna on Feb. 22 at 1105 UTC (6:05 a.m. EST) after it moved inland and its eye was completed cloud-filled. ...
Flipping the 'off' switch on cell growth
2013-02-23
A protein known for turning on genes to help cells survive low-oxygen conditions also slows down the copying of new DNA strands, thus shutting down the growth of new cells, Johns Hopkins researchers report. Their discovery has wide-ranging implications, they say, given the importance of this copying — known as DNA replication — and new cell growth to many of the body's functions and in such diseases as cancer.
"We've long known that this protein, HIF-1α, can switch hundreds of genes on or off in response to low oxygen conditions," says Gregg Semenza, M.D., Ph.D., ...
PA's adoption laws make it possible for families to grow
2013-02-23
PA's adoption laws make it possible for families to grow
Article provided by The Law Offices of Marguerite Nealon
Visit us at http://www.pafamilylaw.com
Pennsylvania, as a whole, is quite liberal in its policies regarding adoption. For instance, the state does not have any age restrictions, thereby allowing persons above the age of eighteen to be adopted. Furthermore, Pennsylvania allows adoption by both single adults and married couples. Most recently, the state made it legal for same-sex couples to adopt a child. Pennsylvania's liberal adoption regulations make ...