(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
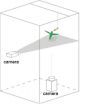
The video shows that the hummingbird produces two trails of vortices -- one under each wing per stroke -- that help generate the aerodynamic forces it requires to power and...
Click here for more information.
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — As of today, the Wikipedia entry for the hummingbird explains that the bird's flight generates in its wake a single trail of vortices that helps the bird hover. But after conducting experiments with hummingbirds in the lab, researchers at the University of California, Riverside propose that the hovering hummingbird instead produces two trails of vortices — one under each wing per stroke — that help generate the aerodynamic forces required for the bird to power and control its flight.
The results of the study could find wide application in aerospace technology and the development of unmanned vehicles for medical surveillance after natural disasters.
The researchers used high-speed image sequences — 500 frames per second — of hummingbirds hover-feeding within a white plume (emitted by the heating of dry ice) to study the vortex wake from multiple perspectives. They also used particle image velocimetry (PIV), a flow-measuring method used in fluid mechanics, to quantitatively analyze the flow around the hummingbirds. PIV allowed the researchers to record the particles surrounding the birds and extract velocity fields.
The films and velocity fields showed two distinct jets of downwards airflow — one under each wing of the hummingbird. They also revealed that vortex loops around each jet are shed during each upstroke and downstroke.
The researchers therefore propose in their paper published online last month in the journal Experiments in Fluids that the hummingbird's two wings form bilateral vortex loops during each wing stroke, which is advantageous for maneuverability.
"Previous studies have indicated that slow-flying bats and faster flying birds produced different structures in their wakes," said Douglas Altshuler, formerly an assistant professor of biology at UC Riverside, whose lab led the research. "We have been investigating the wake structure of hovering hummingbirds because this allows us to decouple the effects of different types of wings — bat versus bird — from different forward flight speeds.
Hummingbirds each weigh 2-20 grams. Because they can hover with high precision, they are able to drink nectar from flowers without any jiggling movement to their bodies. Besides using upstrokes and downstrokes, hummingbirds can rotate their wings. They can even flap their wings from front to back with a 180-degree amplitude.
"We began this study to investigate how the hummingbird used its tail while hovering," said Marko Princevac, an associate professor of mechanical engineering and a coauthor of the research paper. "After all, many insects also hover, but they have no tail. Instead, however, our research showed something interesting about the hummingbird's wings: the bilateral vortex structure. Hummingbirds hovering should cost a lot of energy but these birds are able to hover for long periods of time. Ideally, unmanned vehicles need to be operated with a very limited energy supply, which is why understanding how the hummingbird maximizes its use of energy is tremendously beneficial."
Sam Pournazeri, a former Ph.D. graduate student in Princevac's lab and a co-author on the paper, explained that in a downstroke, the air pressure difference developed as a result of wing movement creates flow from the bottom to the top of the wing. The result is a circular movement or vortex.
"Based on theories in fluid mechanics, this vortex should close either on the wing/body or create a loop around it," he said. "It's these loops that provide circulation around the wings and cause the hummingbird to overcome its weight. Hovering requires the bird to create a lift that cancels its body weight. Although the two-vortex structure we observed increases the hummingbird's energy consumption, it provides the bird a big advantage: a lot more maneuverability."
Next, the research team plans to study the hummingbird in a wind tunnel to closely observe how the bird transitions from hovering to forward motion, and vice versa.
"Current technology is not successfully mimicking how living things fly," Princevac said. "Drones don't hover, and must rely on forward motion. Research done using hummingbirds, like ours, can inform the development of the next generation of drones."
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation to Altshuler, now a faculty member at the University of British Columbia, Canada.
Paolo S. Segre, a former UCR graduate student working with Altshuler at the University of British Columbia, also participated in the study. Pournazeri and Segre contributed equally to the research.
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment has exceeded 21,000 students. The campus will open a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual statewide economic impact of more than $1 billion. A broadcast studio with fiber cable to the AT&T Hollywood hub is available for live or taped interviews. UCR also has ISDN for radio interviews. To learn more, call (951) UCR-NEWS.
2 vortex trails with 1 stroke
UC Riverside research shows hovering hummingbirds generate two trails of vortices under their wings, challenging 1-vortex consensus
2013-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Virus shows promise as prostate cancer treatment
2013-02-26
A recombinant Newcastle disease virus kills all kinds of prostate cancer cells, including hormone resistant cells, but leaves normal cells unscathed, according to a paper published online ahead of print in the Journal of Virology. A treatment for prostate cancer based on this virus would avoid the adverse side effects typically associated with hormonal treatment for prostate cancer, as well as those associated with cancer chemotherapies generally, says corresponding author Subbiah Elankumaran of Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg. The modified virus is now ready ...
Higher levels of several toxic metals found in children with autism
2013-02-26
TEMPE, Ariiz. -- In a recently published study in the journal Biological Trace Element Research, Arizona State University researchers report that children with autism had higher levels of several toxic metals in their blood and urine compared to typical children. The study involved 55 children with autism ages 5 years compared to 44 controls of similar age and gender.
The autism group had significantly higher levels of lead in their red blood cells (+41 percent) and significantly higher urinary levels of lead (+74 percent), thallium (+77 percent), tin (+115 percent), ...
Study reveals stem cells in a human parasite
2013-02-26
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — From the point of view of its ultimate (human) host, the parasitic flatworm Schistosoma mansoni has a gruesome way of life. It hatches in feces-tainted water, grows into a larva in the body of a snail and then burrows through human skin to take up residence in the veins. Once there, it grows into an adult, mates and, if it's female, starts laying eggs. It can remain in the body for decades.
A new study offers insight into the cellular operations that give this flatworm its extraordinary staying power. The researchers, from the University of Illinois, ...
Global surveys show environmental concerns rank low among public concerns
2013-02-26
2/25/2013, Chicago, IL--A newly released international study reveals that the issue of climate change is not a priority for people in the United States and around the world.
The surveys showed that when asked to rank priority worries, people were five times more likely to point to the economy over the environment. Additionally, when asked about climate change, people identified the issue as more of a national problem than a personal concern.
Coordinated surveys, conducted by the International Social Survey Programme (ISSP) in 33 countries from 1993 through 2010, "are ...
Researchers explore PKC role in lung disease
2013-02-26
New research examines the role of PKC in airway smooth muscle contraction and raises the possibility that this enzyme could be a therapeutic target for treating asthma, COPD, and other lung diseases.
In the lungs, pathological increases in the contraction of the smooth muscle cells (SMCs) lining airway walls—a process that decreases airflow—contribute to the chain of events leading to asthma and COPD, two common lung diseases. Jose Perez-Zoghbi and colleagues from Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center designed a series of experiments to investigate the role of ...
NASA sees Cyclone Rusty threatening Western Australia
2013-02-26
Tropical Cyclone Rusty formed on Feb. 24 and has already caused warnings up for the residents of northwestern West Australia, including Port Hedland. NASA's Terra satellite saw that outer bands of this quick-forming tropical cyclone were already affecting land.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABOM) has posted cyclone warnings and a yellow and blue alert for Western Australia as Rusty approaches for a landfall. A Cyclone Warning is in effect from Broome to Mardie, and adjacent inland areas of the Pilbara, including Marble Bar, Nullagine and Millstream. A Cyclone ...
Infrared NASA data shows Cyclone Haruna being blown away
2013-02-26
Ex-cyclone Haruna is expected to dissipate in the Southern Indian Ocean under increasing wind shear in the next day or two. Infrared imagery from a NASA satellite shows that Haruna is being blown apart several hundred miles away from La Reunion Island.
Wind shear has been a problem for Haruna for days. A night-time image from the VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite taken on Feb. 21 at 22:23 UTC showed the eye of Cyclone Haruna had elongated from northwest to southeast as a result of wind shear. For more information about the Suomi NPP satellite, visit: ...
NASA spots active Southern Indian Ocean's Tropical Storm 18S
2013-02-26
The eighteenth tropical cyclone of the Southern Indian Ocean season formed over the weekend of Feb. 23-24 along with Cyclone Rusty as Cyclone Haruna crossed southern Madagascar. NASA's Aqua satellite measured Tropical Storm 18S' cloud top temperatures and saw powerful thunderstorms around the storm's core.
Cyclone Rusty is nearing a landfall in northwestern West Australia, while Tropical Storm 18S is headed in a similar direction.
Tropical Storm 18S (TS18S) was born on Feb. 24 and achieved tropical storm strengthe with maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph). ...
PTSD symptoms common among ICU survivors
2013-02-26
One in three people who survived stays in an intensive care unit (ICU) and required use of a mechanical ventilator showed substantial post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms that lasted for up to two years, according to a new Johns Hopkins study of patients with acute lung injury.
Because acute lung injury (ALI) — a syndrome marked by excessive fluid in the lungs and frequent multi-organ failure — is considered an archetype for critical illness, the researchers suspect PTSD is common among other ICU survivors as well.
"We usually think of PTSD as something you ...
Potentially dangerous Mirena IUDs sparking U.S. lawsuits
2013-02-26
Potentially dangerous Mirena IUDs sparking U.S. lawsuits
Article provided by Bohrer Law Firm, L.L.C.
Visit us at http://www.bohrernationallawfirm.com
Millions of women in the United States and around the world are living with implanted Mirena intrauterine devices, commonly called Mirena IUDs, and some of these women have had nightmarish experiences from dangerous side effects of the devices. Approved by the U.S. government for birth control and to lessen abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding, reports of severe injuries and ectopic pregnancies (outside the uterus) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] 2 vortex trails with 1 strokeUC Riverside research shows hovering hummingbirds generate two trails of vortices under their wings, challenging 1-vortex consensus