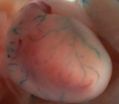
(Press-News.org) Alexandria, VA – On June 5, 2012, a massive dock made landfall on Oregon's Agate Beach, just north of Newport. The dock carried with it a host of castaways, including as many as a hundred species of mollusks, anemones, sponges, oysters, crabs, barnacles, worms, sea stars, mussels and sea urchins. A placard on the side written in Japanese revealed that the dock had been unmoored from the Japanese coastal city of Misawa during the catastrophic tsunami on March 11, 2011, bringing with it an essentially intact subtidal community of Asian species to the Pacific Northwest. Although natural rafts have likely been ferrying organisms around the planet since the very beginning of life on Earth, the geologically recent advent of human settlement, culture and infrastructure is fundamentally changing the rafting game, as EARTH explores in our March issue.
Anything that floats can be used as a raft: algae mats, detached wads of kelp, dead whales, ice floes, volcanic pumice, uprooted trees, docks or plastics. What was once a rare phenomenon is now happening much more frequently. "Rafting opportunities for organisms are much higher now than they have been at any time in the past," says Martin Thiel, an evolutionary biologist at the Catholic University of the North in Coquimbo, Chile. What are the implications for the spread of invasive species and the health of native ecosystems around the world? Read the story at EARTH online at http://bit.ly/YSThEo.
###
Read this story and more in the March issue of EARTH Magazine. Uncover surface scars from an earthquake that killed a king; discover the farthest galaxy and the youngest solar system; and learn how sea butterflies could foreshadow widespread ocean acidification all in this month's issue of EARTH.
Keep up to date with the latest happenings in Earth, energy and environment news with EARTH magazine online at http://www.earthmagazine.org/. Published by the American Geosciences Institute, EARTH is your source for the science behind the headlines.
The American Geosciences Institute is a nonprofit federation of geoscientific and professional associations that represents more than 250,000 geologists, geophysicists and other earth scientists. Founded in 1948, AGI provides information services to geoscientists, serves as a voice of shared interests in the profession, plays a major role in strengthening geoscience education, and strives to increase public awareness of the vital role the geosciences play in society's use of resources, resiliency to natural hazards, and interaction with the environment. END
EARTH: Setting sail on unknown seas
The past, present and future of species rafting
2013-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pain can be a relief
2013-02-26
If you accidently kick your toe against a doorframe you are probably going to find it very painful. As a purely intellectual experiment, imagine purposefully kicking a doorframe hard enough to potentially break your toe. When it turns out your toe has been battered but not broken, the pain may be interpreted more as a relief.
"It is not hard to understand that pain can be interpreted as less severe when an individual is aware that it could have been much more painful. Less expected, however, is the discovery that pain may be experienced as pleasant if something worse ...
When morning sickness lasts all day
2013-02-26
Almost all women experience some nausea or vomiting when pregnant. Approximately one out of every hundred suffers from acute nausea during pregnancy (hyperemesis gravidarum) and may need hospital treatment to restore hydration, electrolytes and vitamins intravenously.
"At worst, women may die if they go untreated. Many women find that the condition has an adverse effect on their work and family lives," states Åse Vikanes, senior researcher at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health and specialist in gynaecology and obstetrics.
Making up for insufficient research activity ...
Blood vessels 'sniff' gut microbes to regulate blood pressure
2013-02-26
Researchers at The Johns Hopkins University and Yale University have discovered that a specialized receptor, normally found in the nose, is also in blood vessels throughout the body, sensing small molecules created by microbes that line mammalian intestines, and responding to these molecules by increasing blood pressure. The finding suggests that gut bacteria are an integral part of the body's complex system for maintaining a stable blood pressure.
A description of the research, conducted in mice and test tubes, appeared online Feb. 11 in the journal Proceedings of the ...
Cell discovery could hold key to causes of inherited diseases
2013-02-26
Fresh insights into the protective seal that surrounds the DNA of our cells could help develop treatments for inherited muscle, brain, bone and skin disorders.
Researchers have discovered that the proteins within this coating – known as the nuclear envelope – vary greatly between cells in different organs of the body.
This variation means that certain disease causing proteins will interact with the proteins in the protective seal to cause illness in some organs, but not others.
Until now scientists had thought that all proteins within the nuclear envelope were the ...
Afterschool programs evaluated for community support, resources
2013-02-26
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Afterschool programs seem to be most effective when their organization and implementation is supported by both organizational and community resources, according to Penn State human development researchers.
Using a tool to help bridge the gap between research and real life, the researchers evaluated an afterschool program called the Good Behavior Game.
"The Interactive System Framework for Dissemination and Implementation is the tool that helps us to bridge research and practice by synthesizing the available research and figuring out what it ...
In probing mysteries of glass, researchers find a key to toughness
2013-02-26
New Haven, Conn. — In a paper published online Feb. 26 in the journal Nature Communications, a Yale University team and collaborators propose a way of predicting whether a given glass will be brittle or ductile — a desirable property typically associated with metals like steel or aluminum — and assert that any glass could have either quality.
Ductility refers to a material's plasticity, or its ability to change shape without breaking.
"Most of us think of glasses as brittle, but our finding shows that any glass can be made ductile or brittle," said Jan Schroers, a professor ...
Connecting the (quantum) dots
2013-02-26
PITTSBURGH—Recent research offers a new spin on using nanoscale semiconductor structures to build faster computers and electronics. Literally.
University of Pittsburgh and Delft University of Technology researchers reveal in the Feb. 17 online issue of Nature Nanotechnology a new method that better preserves the units necessary to power lightning-fast electronics, known as qubits (pronounced CUE-bits). Hole spins, rather than electron spins, can keep quantum bits in the same physical state up to 10 times longer than before, the report finds.
"Previously, our group ...
American Chemical Society podcast: New super-nutritious puffed rice for breakfast cereals, snacks
2013-02-26
The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series reports a new process for blowing up grains of rice to produce a super-nutritious form of puffed rice, with three times more protein and a rich endowment of other nutrients. That makes it ideal for breakfast cereals, snack foods and nutrient bars for school lunch programs.
Based on a report by Syed S.H. Rizvi, Ph.D., and colleagues in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, the new podcast is available without charge at iTunes and from ...
Persistent negative attitude can undo effectiveness of exposure therapy for phobias
2013-02-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Because confronting fear won't always make it go away, researchers suggest that people with phobias must alter memory-driven negative attitudes about feared objects or events to achieve a more lasting recovery from what scares them the most.
Ohio State University psychology researchers determined that people who retained negative attitudes about public speaking after exposure therapy were more likely to experience a return of their fear a month later than were people whose attitudes were less negative. The fear returned among those with unchanged attitudes ...
Kauai, the Petrified Forest, Costa Rica, and more: New GSA Bulletin articles now online
2013-02-26
Boulder, Colo., USA – New GSA Bulletin articles cover wind erosion and sediment traps in the Qaidam basin; rain erosion on Kauai; new insights from the Petrified Forest, USA; a forearc sliver in Costa Rica; Quebec's St. Lawrence rift system; a new model for the development of Ries Crater Lake, Germany; bending and buckling mountain belts; a record of 22 large earthquakes in northern Fiordland, New Zealand; and the evolution of the ancient Montana landscape.
GSA BULLETIN articles published ahead of print are online at http://gsabulletin.gsapubs.org/content/early/recent; ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] EARTH: Setting sail on unknown seasThe past, present and future of species rafting