(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH—Recent research offers a new spin on using nanoscale semiconductor structures to build faster computers and electronics. Literally.
University of Pittsburgh and Delft University of Technology researchers reveal in the Feb. 17 online issue of Nature Nanotechnology a new method that better preserves the units necessary to power lightning-fast electronics, known as qubits (pronounced CUE-bits). Hole spins, rather than electron spins, can keep quantum bits in the same physical state up to 10 times longer than before, the report finds.
"Previously, our group and others have used electron spins, but the problem was that they interacted with spins of nuclei, and therefore it was difficult to preserve the alignment and control of electron spins," said Sergey Frolov, assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy within Pitt's Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, who did the work as a postdoctoral fellow at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands.
Whereas normal computing bits hold mathematical values of zero or one, quantum bits live in a hazy superposition of both states. It is this quality, said Frolov, which allows them to perform multiple calculations at once, offering exponential speed over classical computers. However, maintaining the qubit's state long enough to perform computation remains a long-standing challenge for physicists.
"To create a viable quantum computer, the demonstration of long-lived quantum bits, or qubits, is necessary," said Frolov. "With our work, we have gotten one step closer."
The holes within hole spins, Frolov explained, are literally empty spaces left when electrons are taken out. Using extremely thin filaments called InSb (indium antimonide) nanowires, the researchers created a transistor-like device that could transform the electrons into holes. They then precisely placed one hole in a nanoscale box called "a quantum dot" and controlled the spin of that hole using electric fields. This approach— featuring nanoscale size and a higher density of devices on an electronic chip—is far more advantageous than magnetic control, which has been typically employed until now, said Frolov.
"Our research shows that holes, or empty spaces, can make better spin qubits than electrons for future quantum computers."
"Spins are the smallest magnets in our universe. Our vision for a quantum computer is to connect thousands of spins, and now we know how to control a single spin," said Frolov. "In the future, we'd like to scale up this concept to include multiple qubits."
###
Coauthors of the paper include Leo Kouwenhoven, Stevan Nadj-Perge, Vlad Pribiag, Johan van den Berg, and Ilse van Weperen of Delft University of Technology; and Sebastien Plissard and Erik Bakkers from Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands.
The paper, "Electrical control over single hole spins in nanowire quantum dots," appeared online Feb. 17 in Nature Nanotechnology. The research was supported by the Dutch Organization for Fundamental Research on Matter, the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, and the European Research Council.
Frolov and his Netherlands colleagues were recent winners of the 2012 Newcomb Cleveland Prize, an annual honor awarded to the author/s of the best research article/report appearing in Science, which is published weekly by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). Read more about the award here.
2/26/13/mab/cjhm END
Connecting the (quantum) dots
New spin technique moves researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and Delft University of Technology closer to creating the first viable high-speed quantum computer
2013-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
American Chemical Society podcast: New super-nutritious puffed rice for breakfast cereals, snacks
2013-02-26
The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series reports a new process for blowing up grains of rice to produce a super-nutritious form of puffed rice, with three times more protein and a rich endowment of other nutrients. That makes it ideal for breakfast cereals, snack foods and nutrient bars for school lunch programs.
Based on a report by Syed S.H. Rizvi, Ph.D., and colleagues in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, the new podcast is available without charge at iTunes and from ...
Persistent negative attitude can undo effectiveness of exposure therapy for phobias
2013-02-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Because confronting fear won't always make it go away, researchers suggest that people with phobias must alter memory-driven negative attitudes about feared objects or events to achieve a more lasting recovery from what scares them the most.
Ohio State University psychology researchers determined that people who retained negative attitudes about public speaking after exposure therapy were more likely to experience a return of their fear a month later than were people whose attitudes were less negative. The fear returned among those with unchanged attitudes ...
Kauai, the Petrified Forest, Costa Rica, and more: New GSA Bulletin articles now online
2013-02-26
Boulder, Colo., USA – New GSA Bulletin articles cover wind erosion and sediment traps in the Qaidam basin; rain erosion on Kauai; new insights from the Petrified Forest, USA; a forearc sliver in Costa Rica; Quebec's St. Lawrence rift system; a new model for the development of Ries Crater Lake, Germany; bending and buckling mountain belts; a record of 22 large earthquakes in northern Fiordland, New Zealand; and the evolution of the ancient Montana landscape.
GSA BULLETIN articles published ahead of print are online at http://gsabulletin.gsapubs.org/content/early/recent; ...
Novel combination therapy shuts down escape route, killing glioblastoma tumor cells
2013-02-26
February 26, 2013, New York, N.Y. and San Diego, Calif. – Glioblastoma, the most common and lethal form of brain tumor in adults, is challenging to treat because the tumors rapidly become resistant to therapy. As cancer researchers are learning more about the causes of tumor cell growth and drug resistance, they are discovering molecular pathways that might lead to new targeted therapies to potentially treat this deadly cancer.
Scientists at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research in San Diego worked collaboratively across the laboratories of Drs. Paul Mischel, Web Cavenee ...
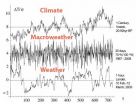
Macroweather is what you expect
2013-02-26
While short-term weather is notoriously volatile, climate is thought to represent a kind of average weather pattern over a long period of time. This dichotomy provides the analytical framework for scientific thinking about atmospheric variability, including climate change.
But the weather-climate dichotomy paints an incomplete picture – one that may be complicating efforts to untangle natural variations in climate from man-made effects, according to McGill University physics professor Shaun Lovejoy. In a paper published recently in the journal Eos, Transactions, American ...
Gender gap disappears in school math competitions, study shows
2013-02-26
The idea that boys are better at math and in competitions has persisted for a long time, and now we know why: Nobody bothered to schedule the rematch.
Most school math contests are one-shot events where girls underperform relative to their male classmates. But a new study by a Brigham Young University economist presents a different picture.
Twenty-four local elementary schools changed the format to go across five different rounds. Once the first round was over, girls performed as well or better than boys for the rest of the contest.
"It's really encouraging that seemingly ...
OHSU scientists first to grow liver stem cells in culture, demonstrate therapeutic benefit
2013-02-26
PORTLAND, Ore. — For decades scientists around the world have attempted to regenerate primary liver cells known as hepatocytes because of their numerous biomedical applications, including hepatitis research, drug metabolism and toxicity studies, as well as transplantation for cirrhosis and other chronic liver conditions. But no lab in the world has been successful in identifying and growing liver stem cells in culture -- using any available technique – until now.
In the journal Nature, physician-scientists in the Papé Family Pediatric Research Institute at Oregon Health ...
Tweaking gene expression to repair lungs
2013-02-26
PHILADELPHIA — Lung diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are on the rise, according to the American Lung Association and the National Institutes of Health.
These ailments are chronic, affect the small airways of the lung, and are thought to involve an injury-repair cycle that leads to the breakdown of normal airway structure and function. For now, drugs for COPD treat only the symptoms.
"A healthy lung has some capacity to regenerate itself like the liver," notes Ed Morrisey, Ph.D., professor of Medicine and Cell and Developmental ...
Prenatal DHA reduces early preterm birth, low birth weight
2013-02-26
LAWRENCE — University of Kansas researchers have found that the infants of mothers who were given 600 milligrams of the omega-3 fatty acid DHA during pregnancy weighed more at birth and were less likely to be very low birth weight and born before 34 weeks gestation than infants of mothers who were given a placebo. This result greatly strengthens the case for using the dietary supplement during pregnancy.
Susan CarlsonThe results are from the first five years of a 10-year, double-blind randomized controlled trial to be published in the April issue of the American Journal ...
Some family physicians' offices discriminate against people with low socio-economic status
2013-02-26
TORONTO, Feb. 25, 2013—Some family physicians' offices discriminate against people of low socio-economic status, even when there is no economic incentive to do so under Canada's system of publicly funded universal health insurance, new research has shown.
At the same time, offices appear to give preference to people with chronic health conditions, according to the research led by Dr. Stephen Hwang of St. Michael's Hospital.
In his study, published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, researchers telephoned the offices of family physicians and general practitioners ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Connecting the (quantum) dotsNew spin technique moves researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and Delft University of Technology closer to creating the first viable high-speed quantum computer